Abstract
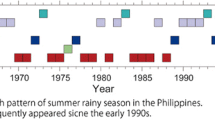
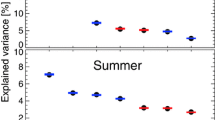
The dominant patterns of summer rainfall anomalies in East China were studied using Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) analysis. The results indicate that after the late 1970s, the first and second dominant patterns switched. During the period before the late 1970s, the spatial pattern of the first (second) dominant mode was the “Yangtze River pattern” (the “South China pattern”), but this changed to the “South China pattern” (the “Yangtze River pattern”) after the late 1970s. This decadal change in the dominant patterns resulted from a significant decadal change in summer rainfall over South China after the late 1970s, i.e., a negative phase during 1978–1992 and a positive phase during 1993–2006. When the decadal variation of rainfall in East China is omitted from the analysis, the first and second dominant patterns represent the “Yangtze River pattern” and the “South China pattern”, respectively. These results suggest that when decadal variation is included, the rainfall in China may be dominated by one mode during certain periods and by another in other periods. For the interannual variability when decadal variation is excluded, however, the first and second modes can be easily distinguished, and their order has been stable since at least 1951.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, C.-P., Y. S. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000: Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part II: Meridional structure of the monsoon. J. Climate, 13, 4326–4340.
Chen, W., L. Kang, and D. Wang, 2006: The coupling relationship between summer rainfall in China and global sea surface temperature. Climatic and Environmental Research, 11, 259–269. (in Chinese)
Deng, A., S. Tao, and L. Chen, 1989: EOF analysis of flood season in China. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 13, 289–295. (in Chinese)
Ding, Y., Z. Wang, and Y. Sun, 2008: Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. International Journal of Climatology, 28, 1139–1162.
Ding, Y. H., and J. C. L. Chan, 2005: The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 89, 117–142.
Gong, D.-Y., and C.-H. Ho, 2002: Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, doi: 10.1029/2001GL014523.
Han, J., and R. Zhang, 2009: The dipole mode of the summer rainfall over East China during 1958–2001. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 727–735, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9014-6.
He, M., and X. Li, 1992: The relationship between summer rainfall in China and tropical circulation anomaly. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 3, 181–189. (in Chinese)
Ho, C.-H., J. Lee, M. Ahn, and H. Lee, 2003: A sudden change in summer rainfall characteristics in Korea during the late 1970s. International Journal of Climatology, 23, 117–128.
Ho, C.-H., J.-H. Kim, K.-M. Lau, K.-M. Kim, D. Gong and Y.-B. Lee, 2005: Interdecadal changes in heavy rainfall in China during the northern summer. The Journal of Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 16, 1163–1176.
Huang, R., L. T. Zhou, and W. Chen, 2003: The progresses of recent studies on the variabilities of the East Asian monsoon and their causes. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 55–69.
Huang, R., J. Chen, G. Huang, and Q. Zhang, 2006: The quasi-biennial oscillation of summer monsoon rainfall in China and its cause. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 545–560. (in Chinese)
Huang, R., J. Chen, and G. Huang, 2007: Characteristics and variations of the East Asian monsoon system and its impacts on climate disasters in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 993–1023.
Huang, R., J. Chen, and Y. Liu, 2011: Interdecadal variation of the leading modes of summertime precipitation anomalies over Eastern China and its association with water vapor transport over East Asia. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 35, 589–606. (in Chinese)
Kwon, M., J.-G. Jhun, and K.-J. Ha, 2007: Decadal change in East Asian summer monsoon circulation in the mid-1990s. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L21706, doi: 10.1029/2007GL031977.
Lu, R.-Y., 2004: Associations among the components of the East Asian summer monsoon system in the meridional direction. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 155–165.
North, G. R., T. Bell, R. Cahalan, and F. Moeng, 1982: Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 699–706.
Ren, B., R. Lu, and Z. Xiao, 2004: A possible linkage in the interdecadal variability of rainfall over North China and the Sahel. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21, 699–707.
Shen, S., and K. M. Lau, 1995: Biennial oscillation associated with the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical sea surface temperatures. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 73, 105–124.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and K. M. Lau, 2001: Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacificeast Asian monsoons. J. Climate, 14, 4073–4090.
Wang, H.-J., 2001: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 376–386.
Wang, S. W., D. Y. Gong, and J. H. Zhu, 2001: Twentieth-century climatic warming in China in the context of the Holocene. The Holocene, 11, 313–321.
Wang, X., and G. Wu, 1996: Regional characteristics of summer precipitation anomalies over China identified in a spatial uniform network. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 54, 324–332. (in Chinese)
Webster, P., and S. Yang, 1992: Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 118, 877–926.
Weng, H., K. M. Lau, and Y. Xue, 1999: Multi-scale summer rainfall variability over China and its long-term link to global sea surface temperature variability. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 77, 845–857.
Wu, R., P. Wen, S. Yang, and Y. Li, 2010: An interdecadal change in southern China summer rainfall around 1992/93. J. Climate, 23, 2389–2403.
You, Y., Y. Zhou, X. Yang, and L. Fang, 2003: Using EOF method to analysis the spatial distribution and temporal variation of summer rainfall in China. Journal of Sichuan Meteorology, 23, 22–23. (in Chinese)
Zhou, T.-J., and R.-C. Yu, 2005: Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J. Geophys. Res., 110, 1–10.
Zhu, Q., and X. Chen, 1992: Objective division of natural rainfall regions in China. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 15, 467–475. (in Chinese)
Zou, L., and Y. Ni, 1997: Impact of ENSO on the variability of the summer monsoon over Asia and the summer rainfall in China. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 13, 306–314. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, H., Lu, R. Dominant patterns of summer rainfall anomalies in East China during 1951–2006. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 29, 695–704 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1153-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1153-5