Abstract
This study investigates the decadal and interannual variability of the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD). It is found that the long-term IOD index displays a decadal phase variation. Prior to 1920 negative phase dominates, but after 1960 positive phase prevails. Under the warming background of the tropical ocean, a larger warming trend in the western Indian Ocean is responsible for the decadal phase variation of the IOD mode. Due to reduced latent heat loss from the local ocean, the western Indian Ocean warming may be caused by the weakened Indian Ocean westerly summer monsoon.
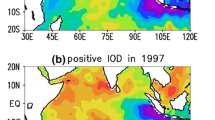
The interannual air-sea coupled IOD mode varies on the background of its decadal variability. During the earlier period (1948–1969), IOD events are characterized by opposing SST anomaly (SSTA) in the western and eastern Indian Ocean, with a single vertical circulation above the equatorial Indian Ocean. But in the later period (1980–2003), with positive IOD dominating, most IOD events have a zonal gradient perturbation on a uniform positive SSTA. However, there are three exceptionally strong positive IOD events (1982, 1994, and 1997), with opposite SSTA in the western and eastern Indian Ocean, accompanied by an El Niño event. Consequently, two anomalous reversed Walker cells are located separately over the Indian Ocean and western-eastern Pacific; the one over the Indian Ocean is much stronger than that during other positive IOD events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai, H., J. Potemra, R. Murtugudde, and J. P. McCreary, 2005: Effect of preconditioning on the extreme climate events in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Climate, 18, 3450–3469.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, and T. Yamagata, 2001: Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 4499–4502.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, and T. Yamagata, 2003: A look at the relationship between the ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 41–56.
Ashok, K., W. L. Chan, T. Motoi, and T. Yamagata, 2004: Decadal variability of the Indian Ocean dipole. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, DOI: 10.1029/2004GL021345.
Behera, S. K., and T. Yamagata, 2003: Influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on the southern oscillation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 169–177.
Bingham, C., M. D. Godfrey, and J. W. Tukey, 1967: Modern techniques of power spectrum estimation. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineeers Transaction on Audio and Electroacoustics, 15, 56–66.
Black, E., J. Slingo, and K. R. Sperber, 2003: An observational study of the relationship between excessively strong short rains in coastal East Africa and Indian Ocean SST. Mon. Wea. Rev., 131, 74–94.
Bretherton, C., M. Widmann, V. P. Dymnikov, J. M. Wallace, and I. Blade, 1999: The effective number of spatial degrees of freedom of a time-varying field. J. Climate, 12, 1990–2009.
Carton, J. A., G. Chepurin, X. Cao, and B. Giese, 2000: A simple ocean data assimilation analysis of the global upper ocean 1950–1995. Part I: Methodology. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 30, 294–309.
Chao, J. P., Q. C. Chao, and L. Liu, 2005: The ENSO events in the tropical Pacific and dipole events in the Indian Ocean. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 63, 594–602. (in Chinese)
Chervin, R. M., and S. H. Schneider, 1976: On determining the statistical significance of climate experiments with General Circulation Models. J. Atmos. Sci., 33, 405–412.
Fischer, A. S., P. Terray, E. Guilyardi, S. Gualdi, and P. Delecluse, 2005: Two independent triggers for the Indian Ocean dipole/zonal mode in a coupled GCM. J. Climate, 18, 3428–3449.
Guan, Z., K. Ashok, and T. Yamagata, 2003: The summertime response of the tropical atmosphere to the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomalies. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 533–561.
Kaplan, A., M. Cane, Y. Kushnir, A. Clement, M. Blumenthal, and B. Rajagopalan, 1998: Analyses of global sea surface temperature 1856–1991. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 567–589.
Kistler, R., and Coauthors, 2001: The NCEP-NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 82, 247–268.
Klein, S. A., B. J. Soden, and N. C. Lau, 1999: Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: Evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge. J. Climate, 12, 917–932.
Kripalani, R. H., and P. Kumar, 2004: Northeast monsoon rainfall variability over south peninsular India vis-a-vis Indian Ocean dipole mode. International Journal of Climatology, 24, 1267–1282.
Kulkarni, A., S. S. Sabade, and R. H. Kripalani, 2007: Association between extreme monsoons and the dipole mode over the Indian subcontinent. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 95, 255–268.
Lau, N. C., and M. J. Nath, 1996: The role of the atmospheric bridge in linking tropical Pacific ENSO events to extratropical SST anomalies. J. Climate, 9, 965–985.
Li, C. Y., and M. Q. Mu, 2001: The influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on atmospheric circulation and climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 831–843.
Li, C. Y., M. Q. Mu, and J. Pan, 2002: Indian Ocean temperature dipole and SSTA in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47, 236–239.
Li, T., B. Wang, C. P. Chang, and Y. Zhang, 2003: A theory for the Indian Ocean dipole-zonal mode. J. Atmos. Sci., 60, 2119–2135.
Nitta, T., and S. Yamada, 1989: Recent warming of tropical sea surface temperature and its relationship to the Northern Hemisphere circulation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 67, 375–383.
Rayner, N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan, 2003: Global analyses of SST, sea ice and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D14), 4407, DOI: 10.1029/2002JD002670.
Saji, N. H., and T. Yamagata, 2003a: Structure of SST and surface wind variability during Indian Ocean dipole mode years: COADS observations. J. Climate, 16, 2735–2751.
Saji, N. H., and T. Yamagata, 2003b: Possible impacts of Indian Ocean dipole mode events on global climate. Climate Research, 25, 151–169.
Saji, N. H., B. N. Goswami, P. N. Vinayachandran, and T. Yamagada, 1999: A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature, 401, 360–363.
Smith, T. M., and R. W. Reynolds, 2003: Extended reconstruction of global sea surface temperatures based on COADS data (1854–1997). J. Climate, 16, 1495–1510.
Tan, Y. K., R. H. Zhang, and J. H. He, 2003: Features of the interannual variation of sea surface temperature anomalies and the air-sea interaction in tropical Indian Ocean. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 27, 53–66. (in Chinese)
Tozuka, T., J. J. Luo, S. Masson, and T. Yamagata, 2007: Decadal modulations of the Indian Ocean dipole in the SIMTEX-F1 coupled GCM. J. Climate, 20, 2881–2894.
Venzke, S., M. Latif, and A. Villwock, 2000: The coupled GCM ECHO-2. Part II: Indian Ocean response to ENSO. J. Climate, 13, 1371–1383.
Wang, H. J., 2001: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 376–386.
Webster, P. J., A. M. Moore, J. P. Loschnigg, and R. R. Leben, 1999: Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature, 401, 356–360.
Xue, F., 2001: Interannual to interdecadal variation of East Asian summer monsoon and its association with the global atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 567–575.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Chan, C.L.J., Zhou, W. et al. Decadal and interannual variability of the Indian Ocean Dipole. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 25, 856–866 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-008-0856-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-008-0856-0