Abstract
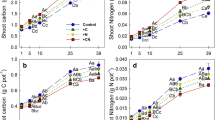
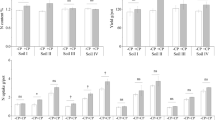
An experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of earthworm (Metaphire guillelmi) activities on rice photosynthates distribution in plant–soil system through 14C pulse-labelling method. Rice was planted in pots, and maize straw was mulched on the surface with or without earthworms. Rice plants at tillering stage or heading stage were labelled with 14CO2. Plant and soil were sampled 15 days after labelling at the tillering or heading stage and at harvest. Rice growth was inhibited by earthworms (M. guillelmi) at early stage, but the inhibition disappeared at later stage. Earthworms significantly (P < 0.01) increased the 14C percentage in root at day 15 after tillering stage labelling, but the effect disappeared at harvest. Earthworms (M. guillelmi) significantly (P < 0.01) increased the 14C percentage in root at day 15 after heading stage labelling and increased 14C percentage in soil at harvest. Earthworms decreased the percentages of total organic 14C (TO14C) present as microbial biomass 14C (MB14C) and increased the percentages of total organic 14C present as dissolved organic 14C (DO14C) at all sampling times. It is suggested that earthworms might alter the transfer of plant photosynthates from the aboveground to the belowground, and thus, soil active C pool. However, these data should be also confirmed in the field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Monroy F, Domínguez J, Mato S (2002) How earthworm density affects microbial biomass and activity in pig manure. Eur J Soil Biol 38:7–10
Amato M (1983) Determination of carbon 12C and 14C in plant and soil. Soil Biol Biochem 15:611–612
Blair JM, Parmelee RW, Allen MF, McCartney DA, Stinner BR (1997) Changes in soil N pools in response to earthworm population manipulations in agroecosystems with different N sources. Soil Biol Biochem 29:361–367
Bohlen PJ, Edwards CA (1995) Earthworm effects on N dynamics and soil respiration in microcosms receiving organic and inorganic nutrients. Soil Biol Biochem 27:341–348
Bossuyt H, Six J, Hendrix P (2005) Protection of soil carbon by microaggregates within earthworm casts. Soil Biol Biochem 37:251–258
Brown GG, Edwards CA, Brussaard L (2004) How earthworms affect plant growth: burrowing into the mechanisms. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm ecology, 2nd edn. CRC, Boca Raton, USA, pp 13–49
Burtelow AE, Bohlen PJ, Groffman PM (1998) Influence of exotic earthworm invasion on soil organic matter microbial and denitrification potential in forest soils of the northeastern United States. Appl Soil Ecol 9:197–202
Cortez J, Bouche MB (1992) Do earthworms eat living root? Soil Biol Biochem 24:913–915
Curry JP, Byrne D (1997) Role of earthworms in straw decomposition in a winter cereal field. Soil Biol Biochem 29:555–558
Garvín MH, Martínez F, Jesús JB, Gutiérrez M, Ruiz P, Cosín DJD (2001) Effect of Hormogaster elisae (Oligochaeta; Hormogastridae) on the stability of soil aggregates. Eur J Soil Biol 37:273–276
Gilot C (1997) Effects of a tropical geophageous earthworm, M. anomala (Megascolecidae), on soil characteristics and production of a yam crop in Ivory Coast. Soil Biol Biochem 29:353–359
Gilot-Villenave C, Lavelle P, Ganry F (1996) Effects of tropical geophagous earthworm, Millsonia anomala, on some soil characteristics, on maize-residue decomposition and on maize production in Ivory Coast. Appl Soil Ecol 4:201–211
Guggenberger G, Thomas RJ, Zech W (1996) Soil organic matter within earthworm casts of an anecic-endogeic tropical pasture community, Colombia. Appl Soil Ecol 3:263–274
Haimi J, Einbork M (1992) Effects of endogeic earthworms on soil processes and plant growth in coniferous forest soil. Biol Fertil Soils 13:6–10
Haynes RJ, Fraser PM (1998) A comparison of aggregate stability and biological activity in earthworm casts and uningested soil as affected by amendment with wheat or lucerne straw. Eur J Soil Sci 49:629–636
Jégou D, Cluzeau D, Balesdent J, Trehen P (1998) Effects of four ecological categories of earthworms on carbon transfer in soil. Appl Soil Ecol 9:249–255
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386
Lavelle P (1988) Earthworm activities and the soil system. Biol Fertil Soils 6:237–251
Lavelle P, Charpentier F, Villenave C, Rossi JP, Derouard L, Pashanasi B, Andre J, Ponge JF, Bernier N (2004) Effects of earthworms on soil organic matter and nutrient dynamics at a landscape scale over decades. In: Edward CA (ed) Earthworm ecology, 2nd edn. CRC, Boca Raton, USA, pp 145–157
Potthoff M, Joergensen RG, Wolters V (2001) Short-term effects of earthworm activity and straw amendment on the microbial C and N turnover in a remoistened arable soil after summer drought. Soil Biol Biochem 33:583–591
Pulleman MM, Six J, Uyl A, Marinissen JCY, Jongmans AG (2005) Earthworms and management affect organic matter incorporation and microaggregate formation in agricultural soils. Appl Soil Ecol 29:1–15
Scheu S (2003) Effects of earthworms on plant growth: patterns and perspectives. Pedobiologia 47:846–856
Schindler-Wessells ML, Bohlen PJ, Mccartney DA, Subler S, Edwards CA (1997) Earthworm effects on soil respiration in corn agroecosystems receiving different nutrient inputs. Soil Biol Biochem 29:409–412
Scullion J, Malik A (2000) Earthworm activity affecting organic matter, aggregation and microbial activity in soils restored after opencast mining for coal. Soil Biol Biochem 32:119–126
Tomati U, Grappelli A, Galli E (1988) The hormone-like effect of earthworm casts on plant growth. Biol Fertil Soils 5:288–294
Tubeileh A, Groleau-Renaud V, Plantureux S, Guckert A (2003) Effect of soil compaction on photosynthesis and carbon partitioning within a maize–soil system. Soil Till Res 71:151–161
Uyl A, Didden W, Marinissen J (2002) Earthworm activity and decomposition of 14C-labelled grass root systems. Biol Fertil Soils 36:447–455
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Wolters V, Joergensen RG (1992) Microbial carbon turnover in beech forest soils worked by Aporrectodea caliginosa (Savigny) (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). Soil Biol Biochem 24:171–177
Zhang BG, Li GT, Shen TS, Wang JK, Sun Z (2000) Changes in microbial biomass C, N, and P and enzyme activities in soil incubated with the earthworms Metaphire guillelmi or Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 32:2055–2062
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30370286). We thank professor Zhenggui Wei for manuscript revision and Dr. Ziming Wang and associate professor Yuping Che for their kind suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Hu, F., Li, H. et al. Earthworm (Metaphire guillelmi) effects on rice photosynthates distribution in the plant–soil system. Biol Fertil Soils 44, 641–647 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0250-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-007-0250-6