Abstract
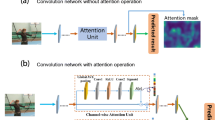
In this work, we propose 3D Residual Attention Networks (3D RANs) for action recognition, which can learn spatiotemporal representation from videos. The proposed network consists of attention mechanism and 3D ResNets architecture, and it can capture spatiotemporal information in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, we separately add the attention mechanism along channel and spatial domain to each block of 3D ResNets. For each sliced tensor of an intermediate feature map, we sequentially infer channel and spatial attention maps by channel and spatial attention mechanism submodules in each residual unit block, and the attention maps are multiplied to the input feature map to reweight the key features. We validate our network through extensive experiments in UCF-101, HMDB-51 and Kinetics datasets. Our experiments show that the proposed 3D RANs are superior to the state-of-the-art approaches for action recognition, demonstrating the effectiveness of our networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4489–4497 (2015)
Li, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, X., Wang, M., Poiana, S.I., Chaudhry, E., Zhang, J.: Efficient convolutional hierarchical autoencoder for human motion prediction. Vis. Comput. 35, 1143–1156 (2019)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4724–4733 (2017)
Wang, L., Qiao, Y., Tang, X.: Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4305–4314 (2015)
Wang, X., Farhadi, A., Gupta, A.: Actions\({}^\sim \) transformations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2658–2667 (2016)
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Lin, D., Tang, X., Van Gool, L.: Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 20–36 (2016)
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthankar, R., Fei-Fei, L.: Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1725–1732 (2014)
Zhang, B., Wang, L., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Wang, H.: Real-time action recognition with enhanced motion vector CNNs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2718–2726 (2015)
Wang, H., Schmid, C.: Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3551–3558 (2013)
Scovanner, P., Ali, S., Shah, M.: A 3-dimensional sift descriptor and its application to action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 357–360 (2007)
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Schmid, C., Liu, C. L.: Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3169–3176 (2011)
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., Rozenfeld, B.: Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. CVPR, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27, 568–576 (2014)
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., Yu, K.: 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35, 221–231 (2013)
Wang, Y., Jiang, L., Yang, M. H., Li, L. J., Long, M., Fei-Fei, L.: Eidetic 3D LSTM: A Model for Video Prediction and Beyond (2013)
Ma, Z., Sun, Z.: Time-varying LSTM networks for action recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77, 32275–32285 (2018)
Liang, D., Liang, H., Yu, Z., Zhang, Y.: Deep convolutional BiLSTM fusion network for facial expression recognition. Vis. Comput (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01636-3
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., Satoh, Y.: Learning spatio-temporal features with 3D residual networks for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the ICCV Workshop on Action, Gesture, and Emotion Recognition, pp. 4 (2017)
Nair, V., Hinton, G. E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814 (2010)
Ba, J., Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K.: Multiple object recognition with visual attention (2014)
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A.: Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv, Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27, 2204–2212 (2014)
Soomro, K., Zamir, A.R., Shah, M.: UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild (2012)
Kuehne, H., Jhuang, H., Stiefelhagen, R., Serre, T.: Hmdb51: a large video database for human motion recognition. High Perform. Comput. Sci. Eng. 12, 571–582 (2013)
Kay, W., Carreira, J., Simonyan, K., Zhang, B., Hillier, C., Vijayanarasimhan, S., Suleyman, M.: The kinetics human action video dataset (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., Zisserman, A.: Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1933–1941 (2016)
Li, W., Nie, W., Su, Y.: Human action recognition based on selected spatio-temporal features via bidirectional LSTM. In: IEEE Access, pp. 44211–44220 (2018)
Song, S., Lan, C., Xing, J., Zeng, W., Liu, J.: Spatio-temporal attention based LSTM networks for 3D action recognition and detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27, 3459–3471 (2018)
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11, 1254–1259 (1998)
Rensink, R.A.: The dynamic representation of scenes. Vis. Cognit. 7, 17–42 (2000)
Corbetta, M., Shulman, G.L.: Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 201 (2002)
Larochelle, H., Hinton, G.E.: Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order Boltzmann machine. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 23, 1243–1251 (2010)
Olshausen, B. A., Anderson, C. H., Van Essen, D. C.: A neurobiological model of visual attention and invariant pattern recognition based on dynamic routing of information. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4700–4719 (1993)
Cao, C., Liu, X., Yang, Y., Yu, Y., Wang, J., Wang, Z., Ramanan, D.: Look and think twice: capturing top-down visual attention with feedback convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2956–2964 (2015)
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Recurrent spatial transformer networks. In: Computer Science, (2015)
Wang, F., Jiang, M., Qian, C., Yang, S., Li, C., Zhang, H., Tang, X.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6450–6458 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks (2017)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J. Y., Kweon, I. S.: CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision (2018)
Sharma, S., Kiros, R., Salakhutdinov, R.: Action recognition using visual attention. In: Computer Science (2015)
Kim, D. , Cho, D. , Kweon, I. S.: Self-supervised video representation learning with space-time cubic puzzles. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.09795 (2018)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Hinton, G. E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines Vinod Nair (2010)
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2921–2929 (2016)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. pp. 448–456 (2015)
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y.: Towards good practices for very deep two-stream ConvNets. In: Computer Science (2015)
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., Satoh, Y.: Can spatiotemporal 3D CNNs retrace the history of 2D CNNs and ImageNet?. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 18–22 (2017)
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., Tu, Z., He, K.: Aggregated Residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5987–5995 (2017)
Qiu, Z., Yao, T., Mei, T.: Learning spatio-temporal representation with Pseudo-3D residual networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5534–5542 (2017)
Zhou, Y., Sun, X., Zha, Z. J., Zeng, W.: MiCT: mixed 3D/2D convolutional tube for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 449–458 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the 2016 Guangzhou Innovation and Entrepreneurship Leader Team under Grant CXLJTD-201608 and the Development Research Institute of Guangzhou Smart City.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Hu, J. 3D RANs: 3D Residual Attention Networks for action recognition. Vis Comput 36, 1261–1270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01733-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01733-3