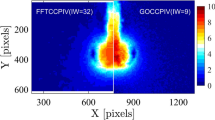
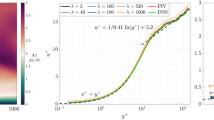
Abstract
Two particle image velocimetry (PIV) softwares applied to turbulent flows are compared. One is based on a standard cross-correlation (CC) algorithm and the other is based on an iterative multi-pyramid optical flow (OF) algorithm. First, still particle images are used to evaluate the cut-off frequency induced by each method. Then a step response analysis highlights the capabilities of each method to minimise the effect of unresolved velocity gradients. Two different benchmarks with various turbulent length-scales, down to the Taylor microscale, are then used to analyse the velocity spectra and the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation estimation. First, a synthetic PIV dataset of homogeneous isotropic turbulence is processed and compared with direct numerical simulation (DNS) results. Then a grid turbulence wind tunnel experimental dataset is used to calculate velocity spectra and second-order structure functions, which are compared to laser Doppler velocimetry spectra. All these results point to the fact that, although OF is more diffusive and up to 5% less accurate than cross-correlation, the numerical diffusion improves the calculation of sub-window unresolved gradients and allows for direct and more robust measurement of the onset of the viscous subrange in experimental turbulent flows.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelson E, Anderson C, Bergen J, Burt P, Ogden J (1983) Pyramid methods in image processing. RCA Eng 29:11
Cai S, Liang J, Gao Q, Xu C, Wei R (2020) Particle image velocimetry based on a deep learning motion estimator. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(6):3538–3554
Camassa R, Hurley MW, McLaughlin RM, Passaggia P-Y, Thomson CF (2018) Experimental investigation of nonlinear internal waves in deep water with miscible fluids. J Ocean Eng Marine Ener 4(4):243–257
Carlier J (2005) Second set of fluid mechanics image sequences. in: European project ’fluid image analysis and description, fluid, FLUID
Champagnat F, Plyer A, Le Besnerais G, Leclaire B, Davoust S, Le Saint Y (2011) Fast and accurate PIV computation using highly parallel iterative correlation maximization. Exp Fluids 50:1169–1182
Davoust S, Jacquin L, Leclaire B (2012) Dynamics of m = 0 and m = 1 modes and of streamwise vortices in a turbulent axisymmetric mixing layer. J Fluid Mech 709:408–444
Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Häusser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V, Smagt Pvd, Cremers D, Brox T (2015) Flownet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 2758–2766,
Foucaut J-M, Carlier J, Stanislas M (2004) Piv optimization for the study of turbulent flow using spectral analysis. Meas Sci Technol 15(6):1046
Foucaut J-M, Stanislas M (2002) Some considerations on the accuracy and frequency response of some derivative filters applied to particle image velocimetry vector fields. Meas Sci Tech 13(7):1058
Gautier N (2014) Flow control using optical sensors. Ph. D thesis,
Gautier N, Aider J-L (2013) Control of the separated flow downstream of a backward-facing step using visual feedback. Proc Royal Soc A: Math, Phys Eng Sci 469(2160):20130404
Gautier N, Aider J-L (2015) Frequency-lock reactive control of a separated flow enabled by visual sensors. Exp Fluids 56(1):16
Gautier N, Aider J-L (2015) Real-time planar flow velocity measurements using an optical flow algorithm implemented on gpu. J Visual 18(2):277–286
Gautier N, Aider J-L, DUriez T, Segond B, Agel M (2015) Closed-loop separation control using machine learning. J Fluid Mech 770:442–457
George WK, Stanislas M (2020) On the noise in statistics of piv measurements
Giannopoulos A, Aider J-L (2020) Data-driven order reduction and velocity field reconstruction using neural networks: the case of a turbulent boundary layer. Phys Fluids 32(9):095117
Giannopoulos A, Aider J-L (2020) Prediction of the dynamics of a backward-facing step flow using focused time-delay neural networks and particle image velocimetry data-sets. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 82:108533
Horn BK, Shunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17:08
Kähler CJ, Scharnowski S, Cierpka C (2012) On the resolution limit of digital particle image velocimetry. Exp fluids 52(6):1629–1639
Kähler CJ, Astarita PP, Tommaso andVlachos, Sakakibara J, Hain R, Discetti S, La Foy R, Cierpka C (2016) Main results of the fourth international piv challenge. Experiments in Fluids, 57
Liu T, Merat A, Makhmalbaf H, Fajardo C, Merati P (2015) Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Exp Fluids 56:166
Liu T, Merat A, Makhmalbaf MHM, Fajardo Ca (2015) Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Experiments in Fluids, 56
Liu T, Salazar DM, Fagehi H, Ghazwani H, Montefort J, Merati P (2020) Hybrid optical-flow-cross-correlation method for particle image velocimetry. J Fluids Eng 142(5):054501
Lourenco L (2000) True resolution piv: a mesh-free second order accurate algorithm. In 10th Int. Symp. on Applications of Laser Techniques in Fluid Mechanics (Lisbon), 2000,
Mazellier N, Danaila L, Renou B (2010) Multi-scale energy injection: a new tool to generate intense homogeneous and isotropic turbulence for premixed combustion. J Turb 11:N43
Mendes L, Bernardino A, Ferreira RM (2020) Piv-image-generator: an image generating software package for planar piv and optical flow benchmarking. SoftwareX 12:100537
Meunier P, Leweke T (2003) Analysis and treatment of errors due to high velocity gradients in particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 35(5):408–421
Pan C, Dong X, Yang X, Jinjun W, Runjie W (2015) Evaluating the accuracy performance of lucas-kanade algorithm in the circumstance of piv application. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron., 58
Passaggia P-Y, Chalamalla VK, Hurley MW, Scotti A, Santilli E (2020) Estimating pressure and internal-wave flux from laboratory experiments in focusing internal waves. Exp Fluids 61(11):1–29
Passaggia P-Y, Leweke T, Ehrenstein U (2012) Transverse instability and low-frequency flapping in incompressible separated boundary layer flows: an experimental study. J Fluid Mech 703:363
Quénot G, Pakleza J, Kowalewski T (1998) Particle image velocimetry with optical flow. Exp Fluids 25(3):177–189
Rabault J, Kolaas J, Jensen A (2017) Performing particle image velocimetry using artificial neural networks: a proof-of-concept. Meas Sci Technol 28(12):125301
Raffel M, Willert CE, Kompenhans J et al (1998) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, Berlin
Ruhnau P, Kohlberger T, Schnörr C, Nobach H (2005) Variational optical flow estimation for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 38:21–32
Sartor F, Losfeld G, Bur R (2012) Piv study on a shock-induced separation in a transonic flow. Exp Fluids 53:815–827
Scarano F, Riethmuller M (2012) Advances in iterative multigrid piv image processing. Exp Fluids 29:S051–S060
Schmidt B, Sutton J (2020) Improvements in the accuracy of wavelet-based optical flow velocimetry (wofv) using an efficient and physically based implementation of velocity regularisation. Exp Fluids 61:01
Schmidt BE, Sutton JA (2019) High-resolution velocimetry from tracer particle fields using a wavelet-based optical flow method. Exp Fluids 60(3):37
Sciacchitano A, Wieneke B, Scarano F (2013) Piv uncertainty quantification by image matching. Meas Sci Technol 24:045302
Seong JH, Song M, Nunez D, Manera A, Kim E (2019) Velocity refinement of piv using global optical flow. Exp Fluids 60:10
Shanmughan R, Passaggia P-Y, Mazellier N, Kourta A (2020) Optimal pressure reconstruction based on planar particle image velocimetry and sparse sensor measurements. Exp Fluids 61(11):1–19
She Z-S, Leveque E (1994) Universal scaling laws in fully developed turbulence. Phys Rev Lett 72(3):336
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, hler C.K. (2003) Main results of theFirst international PIV challenge. Meas Sci Technol 14(10):R63–R89
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, Kähler CJ, Westerweel J (2005) Main results of the second international piv challenge. Exp Fluids 39:170–191
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, Kähler CJ, Westerweel J, Scarano F (2008) Main results of the third international piv challenge. Exp Fluids 45:27–71
Stoica P, Moses R (2005) Spectral analysis of signals. Prentice Hall, USA
Thielicke W, Stamhuis EJ (2014) PIVlab – towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in MATLAB. Journal of Open Research Software, 2,
Tran CV, Bowman JC (2004) Robustness of the inverse cascade in two-dimensional turbulence. Phy Rev E 69(3):036303
Varon E, Aider J-L, Eulalie Y, Edwige S, Gilotte P (2019) Adaptive control of the dynamics of a fully turbulent bimodal wake using real-time piv. Exp Fluids 60(8):124
Varon E, Eulalie Y, Edwige S, Gilotte P, Aider J-L (2017) Chaotic dynamics of large-scale structures in a turbulent wake. Phys Rev Fluids 2:034604
Vig D, Hamby A, Wolgemuth C (2016) On the quantification of cellular velocity fields. Biophys J 110(7):1469–1475
Wang H, He G, Wang S (2020) Globally optimized cross-correlation for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 61:10
Westerweel J (1993) Digital particle image velocimetry - theory and application. Delft University Press, Netherlands
Acknowledgements
A. G. and J.-L. A. acknowledge the support by ANRT and Photon Lines. P.-Y. P. and N. M. acknowledge the support by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) through the Investissements d’Avenir program under the Labex CAPRYSSES Project (ANR-11-LABX-0006-01), the project APR IA PRESERVE, Région Centre-Val-de-Loire (2019 134933), and the project APR IA APROPORE, Région Centre-Val-de-Loire (2017 119967). Authors would also like to thank the anonymous referee who helped improving the overall quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of interest:
The doctoral thesis of the author A. Giannopoulos was funded by Photon Lines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giannopoulos, A., Passaggia, PY., Mazellier, N. et al. On the optimal window size in optical flow and cross-correlation in particle image velocimetry: application to turbulent flows. Exp Fluids 63, 57 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03410-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03410-z