Abstract
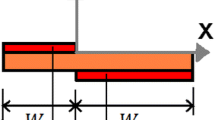
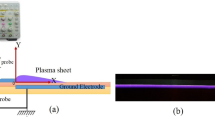
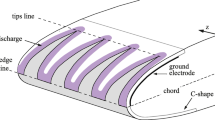
Several studies have shown that a surface dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) may be used as an electrohydrodynamic (EHD) actuator in order to control airflows. In this paper, a parametric study has been performed in order to increase the velocity of the ionic wind induced by such actuators. The results show that an optimization of geometrical and electrical parameters allows us to obtain a time-averaged ionic wind velocity up to 8 m/s at 0.5 mm from the wall. Moreover, non-stationary measurements of the induced wind have been performed with synchronized records of current and voltage signals. These experiments show that the DBD actuator seems to generate a pulsed velocity at the same frequency than the applied high voltage.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artana G, D’Adamo J, Léger L, Moreau E, Touchard G (2002) Flow control with electrohydrodynamic actuators. AIAA J 40(9):1773–1779
Boeuf JP, Pitchford LC (2005) Electrohydrodynamic force and aerodynamic flow acceleration in surface dielectric barrier discharge. J Appl Phys 97:103307
Boeuf JP, Lagmich Y, Unfer T, Callegari T, Pitchford LC (2007) Electrohydrodynamic force in dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:652–662
Corke TC, Post ML (2005) Overview of plasma flow control: concepts, optimization and applications. In: AIAA Paper 2005–563. 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Enloe CL, McLaughlin TE, VanDyken RD, Kachner KD, Jumper EJ, Corke TC (2004a) Mechanisms and responses of a single dielectric barrier plasma actuator: plasma morphology. AIAA J 42(3):589–594
Enloe CL, McLaughlin TE, VanDyken RD, Kachner KD, Jumper EJ, Corke TC (2004b) Mechanisms and responses of a single dielectric barrier plasma actuator: geometric effects. AIAA J 42(3):595–605
Forte M, Léger L, Pons J, Moreau E, Touchard G (2005) Plasma actuators for airflow control: measurement of the non-stationary induced flow velocity. J Electrostat 63(6–10):929–936
Gaitonde DV, Visbal MR, Roy S (2006) A coupled approach for plasma-based flow control simulations of wing sections. In: AIAA Paper 2006–1205. 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Grundmann S, Klumpp S, Tropea C (2006) Stabilizing a laminar boundary-layer using plasma-actuators. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Congress of the Aeronautical Sciences, Hamburg, September 2006
Léger L, Moreau E, Touchard G (2002) Electrohydrodynamic airflow control along a flat plate by a DC surface corona discharge—velocity profile and wall pressure measurements. In: AIAA Paper 2002–2833. 1st AIAA Flow Control Conference, St Louis, MO
Likhanskii AV, Shneider MN, Macheret SO, Miles RB (2006) Modeling of interaction between weakly ionized near-surface plasmas and gas flow. In: AIAA Paper 2006–1204. 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
List L, Byerley AR, McLaughlin TE, Van Dyken RD (2003) Using a plasma actuator to control laminar separation on a linear cascade turbine blade. In: AIAA-Paper 2003–1026. 41st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Moreau E (2007) Airflow control by non-thermal plasma actuators. J Phys D: Appl Phys 40:605–636
Moreau E, Léger L, Touchard G (2006) Effect of a DC surface non-thermal plasma on a flat plate boundary layer for airflow velocity up to 25 ms−1. J Electrostat 64:215–225
Pons J, Moreau E, Touchard G (2005) Asymmetric surface dielectric barrier discharge in air at atmospheric pressure: electrical properties and induced airflow characteristics. J Phys D Appl Phys 38:3635–3642
Post ML, Corke TC (2004) Separation control on high angle of attack airfoil using plasma actuators. AIAA J 42(11):2177–2184
Rivir R, White LtA, Carter C, Ganguly B, Forelines A, Crafton J (2003) Turbine flow control, plasma flows. In: AIAA-Paper 2003–6055. 41st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Roth JR, Dai X (2006) Optimization of the aerodynamic plasma actuator as an ElectroHydroDynamic (EHD) electrical device. In: AIAA Paper 2006–1203. 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Roth JR, Sherman DM, Wilkinson SP (1998) Boundary layer flow control with a one atmosphere uniform glow discharge surface plasma. In: AIAA Paper 98–0328. 36th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Roth JR, Sherman DM, Wilkinson SP (2000) Electrohydrodynamic flow control with a glow-discharge surface plasma. AIAA J 38(7):1166–1172
Roth JR, Madhan RCM , Yadav M, Rahel J and Wilkinson SP (2004) Flow field measurements of paraelectric, peristaltic, and combined plasma actuators based on the one atmosphere uniform glow discharge plasma OAUGDPTM). In: AIAA Paper 2004–0845. 42nd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical and financial support of SNECMA (SAFRAN Group) (Contract N°920 430961). This work has been performed in the frame of a working group including researchers from two CNRS laboratory, LAPLACE (LAboratoire PLAsma et Conversion d’Energie) and LEA (Laboratoire d’Etudes Aérodynamiques) and also from ONERA (Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales). The authors would like to thank members of this group for sharing their results and for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forte, M., Jolibois, J., Pons, J. et al. Optimization of a dielectric barrier discharge actuator by stationary and non-stationary measurements of the induced flow velocity: application to airflow control. Exp Fluids 43, 917–928 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-007-0362-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-007-0362-7