Abstract
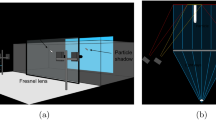
A set of stereoscopic imaging techniques is proposed for the measurement of rapidly flowing dispersions of opaque particles observed near a transparent wall. The methods exploit projective geometry and the Voronoï diagram. They rely on purely geometrical principles to reconstruct 3D particle positions, concentrations, and velocities. The methods are able to handle position and motion ambiguities, as well as particle-occlusion effects, difficulties that are common in the case of dense dispersions of many identical particles. Fluidization cell experiments allow validation of the concentration estimates. A mature debris-flow experimental run is then chosen to test the particle-tracking algorithm. The Voronoï stereo methods are found to perform well in both cases, and to present significant advantages over monocular imaging measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (1991) Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 23:261–304
Ahuja N (1982) Dot pattern processing using Voronoï neighborhoods. IEEE PAMI 4:336–343
Armanini A, Fraccarollo L, Guarino L, Martino R, Bin Y (2000) Experimental analysis of the general features of uniform debris flow over a loose bed. In: Wieczorek GF, Naeser ND (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Debris-flow hazard mitigation, Taipei, August 2000. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 327–334
Azanza E, Chevoir F, Moucheront P (1999) Experimental study of collisional granular flows down an inclined plane. J Fluid Mech 400:199–227
Bernardeau F, van de Weygaert R (1996) A new method for accurate estimation of velocity field statistics. Mon Not R Astron Soc 279:693–711
Campbell CS (1990) Rapid granular flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 22:57–92
Capart H (2000) Dam-break induced geomorphic flows and the transition from solid-to fluid-like behaviour across evolving interfaces. PhD thesis, Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium
Capart H, Liu HH, Van Crombrugghe X, Young DL (1997) Digital imaging characterization of the kinematics of water-sediment interaction. Water Air Soil Pollut 99:173–177
Capart H, Young DL, Zech Y (2002) Voronoï imaging methods for the measurement of granular flows. Exp Fluids 32:121–135
Cui MM, Adrian RJ (1997) Refractive index matching and marking methods for highly concentrated solid-liquid flows. Exp Fluids 22: 261–264
De Backer A (2001) Développement et application de techniques d’imagerie digitale pour l’analyse tridimensionnelle d’un écoulement complexe. BEng thesis, Haute école Leonardo da Vinci (ECAM), Belgium (in French)
Douxchamps D, Devriendt D, Capart H, Craeye C, Macq B, Zech Y (2000) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the oscillatory free-surface of a flow over antidunes: stereoscopic and velocimetric techniques. In: Proceedings of the Oceans 2000 Conference, Rhode Island, USA, September 2000. IEEE, Piscataway, N.J.
Drake TG (1991) Granular flow: physical experiments and their implications for microstructural theories. J Fluid Mech 225:121–152
Fairhurst PG, Barigou M, Fryer PJ, Pain JP, Parker DJ (2001) Using positron emission particle tracking (PEPT) to study nearly neutrally buoyant particles in high solid fraction pipe flow. Int J Multiphase Flow 27:1881–1901
Faugeras O (1999) Three-dimensional computer vision: a geometric viewpoint. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Fortes AF, Joseph DD, Lundgren TS (1987) Nonlinear mechanics of fluidization of beds of spherical particles. J Fluid Mech 177:467–483
Guler M, Edil TB, Bosscher PJ (1999) Measurement of particle movement in granular soils using image analysis. J Comp Civ Eng 13:116–122
Hsiau SS, Jang HW (1998) Measurements of velocity fluctuations of granular materials in a shear cell. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 17:202–209
Hryciw RD, Raschke SA, Ghalib AM, Horner DA, Peters JF (1997) Video tracking for experimental validation of discrete elements simulations of large discontinuous deformations. Comput Geotech 21:235–253
Jähne B (1995) Digital image processing. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg Berlin New York
Jain R, Kasturi R, Schunck BG (1995) Machine vision. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kang SY, Sangani AS, Tsao HK, Koch DL (1997) Rheology of dense bubble suspensions. Phys Fluids 9:1540–1561
Kim W, Kak A (1991) 3D object recognition using bipartite matching embedded in discrete relaxation. IEEE PAMI 13:224–251
Lorz U (1990) Cell-area distributions of planar sections of spatial Voronoï mosaics. Mater Characteriz 25:297–309
Malik NA, Dracos T, Papantoniou D (1993) Particle tracking velocimetry in three dimensional flows — II: Particle tracking. Exp Fluids 15:279–294
Menon N, Durian DJ (1997) Diffusing-wave spectroscopy of dynamics in a three-dimensional granular flow. Science 275:1920–1922
Murai Y, Matsumoto Y, Yamamoto F (2001) Three-dimensional measurement of void fraction in a bubble plume using statistic stereoscopic image processing. Exp. Fluids 30:11–21
Nakagawa M, Altobelli SA, Caprihan A, Fukushima E, Jeong EK (1993) Noninvasive measurements of granular flows by magnetic-resonance-imaging. Exp Fluids 16:54–60
Natarajan VVR, Hunt ML, Taylor ED (1995) Local measurements of velocity fluctuations and diffusion coefficients for a granular material flow. J Fluid Mech 304:1–25
Okabe A, Boots B, Sugihara K (1992) Spatial tessellations: concepts and applications of Voronoï diagrams. Wiley, Chichester
Phillips RJ, Armstrong RC, Brown RA (1992) A constitutive equation for concentrated suspensions that accounts for shear-induced particle migration. Phys Fluids A 4:30–40
Preparata FP, Shamos MI (1985) Computational geometry: an introduction. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg Berlin New York
Richardson JF, Zaki WN (1954) Sedimentation and fluidization: part I. Trans Instn Chem Engrs 32:35–53
Ross SM (1990) A course in simulation. Macmillan, Basingstoke
Rouyer F, Lhuillier D, Martin J, Salin D (2000) Structure, density, and velocity fluctuations in quasi-two-dimensional non-Brownian suspensions of spheres. Phys Fluids 12:958–963
Savage SB, Dai R (1993) Studies of granular shear flows, wall slip velocities, “layering” and self-diffusion. Mech Mater 16:225–238
Seymour JD, Caprihan A, Altobelli SA, Fukushima E (2000) Pulsed gradient spin echo nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of diffusion in granular flow. Phys Rev Lett 84:266–269
Song XQ, Yamamoto F, Iguchi M, Murai Y (1999) A new tracking algorithm of PIV and removal of spurious vectors using Delaunay tessellation. Exp Fluids 26:371–380
Spinewine B, Capart H, Zech Y (2000) Stereoscopic imaging measurement of solid concentrations in dense granular flows. In: Proceeding of the 10th International Conference on Transport and sedimentation of solid particles, Wroclaw, September 2000. Akademia Rolnicza we Wroclawiu, Wroclaw, Poland, pp 497–509
Trucco E, Verri A (1998) Introductory techniques for 3-D computer vision. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, N.J.
Tsai RY (1987) A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3D machine vision metrology using off-the-shelf TV cameras and lenses. IEEE J Robotics Auto 3:323–344
Ushijima S, Tanaka N (1996) Three-dimensional particle tracking velocimetry with laser-light sheet scannings. J Fluid Eng 118:352–357
Veber P, Dahl J, Hermansson R (1997) Study of the phenomena affecting the accuracy of a video-based particle tracking velocimetry technique. Exp Fluids 22:482–488
Virant M, Dracos T (1997) 3D PTV and its application on Lagrangian motion. Meas Sci Technol 8:1539–1552
Wildman RD, Huntley JM, Parker DJ (2001) Granular temperature profiles in three-dimensional vibrofluidized granular beds. Phys Rev E 63:1311–1320
Wildman RD, Huntley JM, Hansen JP (1999) Self-diffusion of grains in a two-dimensional vibrofluidized bed. Phys Rev E 60:7066–7075
Zhang DZ, Prosperetti A (1994) Averaged equations for inviscid disperse two-phase flow. J Fluid Mech 267:185–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online: 19 December 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinewine, B., Capart, H., Larcher, M. et al. Three-dimensional Voronoï imaging methods for the measurement of near-wall particulate flows. Experiments in Fluids 34, 227–241 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-002-0550-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-002-0550-4