Abstract
Purpose
To compare the urological and sexual outcomes of using either tamsulosin/finateride or tadalafil/finasteride as combination therapies in patients with large prostate.
Patients and methods
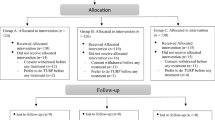
Selection criteria included prostate volume > 40 ml and IPSS > 7. Patients with severe erectile dysfunction (IIEF-erectile functions ≤ 10) were excluded. Patients were randomized into group I (tamsulosin/finasteride) and group II (tadalafil/finasteride). The primary endpoint was to define urinary and sexual function changes (IPSS, IPSS-quality of life, urinary flow rates and IIEF domains) within each group. The secondary endpoint was to compare the treatment induced changes between both groups.
Results
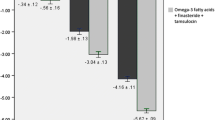
At 4th and 12th weeks, 131 and 127 patients were available in both groups, respectively. Both groups showed significant LUTS improvement (IPSS changes: − 4.9 ± 2.7 and − 4.3 ± 2.9 at 4th week and − 6.1 ± 3 and − 5.4 ± 2.8 points by the 12th week in both groups, respectively). Group I had better average flow rates at both follow-up visits. Meanwhile, maximum flow rates were comparable in both groups at 12th week (13.5 ± 3.9vs. 12.6 ± 3.7, p > 0.05). In group I, all IIEF domains were significantly lowered at both visits (p < 0.05). Group II showed significant increase in IIEF-erectile function scores (1.3 ± 1.1 and 1.8 ± 1.2 at the 4th and 12th weeks) with a transient significant reduction of IIEF-orgasm and sexual desire noted only by the 4th week (− 0.8 ± 0.4 and − 0.6 ± 0.4, respectively).
Conclusion
Within three months, both combinations are comparably effective in improving BPH related LUTS. Tamsulosin/finasteride provided significantly better Qmax only at 4th week. Tadalafil/finasteride had the advantage of improving sexual performance over the other combination.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All inclusion data are available upon contact with authors.
References
Lepor H (2007) Alpha blockers for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev Urol 9(4):181–190
Gacci M et al (2014) Impact of medical treatments for male lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia on ejaculatory function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med 11(6):1554–1566
Giuliano F (2006) Impact of medical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia on sexual function. BJU Int 97 Suppl 2:34–38 (discussion 44-5)
Song SH et al (2011) Effect of tamsulosin on ejaculatory function in BPH/LUTS. Asian J Androl 13(6):846–850
Kaplan SA, Gonzalez RR (2007) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms. Rev Urol 9(2):73–77
Pattanaik S et al (2019) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors for lower urinary tract symptoms consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 124(1):27–34
Gravas S et al (2020) EAU guidelines on management of non-neurogenic male LUTS. In: Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam. ISBN 978-94-92671-07-3
Giuliano F et al (2013) The mechanism of action of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 63(3):506–516
Vignozzi L et al (2013) PDE5 inhibitors blunt inflammation in human BPH: a potential mechanism of action for PDE5 inhibitors in LUTS. Prostate 73(13):1391–1402
Pereira ML et al (2017) Effects of nitric oxide inhibitors in mice with bladder outlet obstruction. Int Braz J Urol 43(2):356–366
Nickel JC et al (2011) Comparison of dutasteride and finasteride for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Enlarged Prostate International Comparator Study (EPICS). BJU Int 108(3):388–394
Gratzke C et al (2015) EAU guidelines on the assessment of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 67(6):1099–1109
McVary KT et al (2011) Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 185(5):1793–1803
Traish AM et al (2011) Adverse side effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors therapy: persistent diminished libido and erectile dysfunction and depression in a subset of patients. J Sex Med 8(3):872–884
Kiguradze T et al (2017) Persistent erectile dysfunction in men exposed to the 5alpha-reductase inhibitors, finasteride, or dutasteride. PeerJ 5:e3020
Gur S, Kadowitz PJ, Hellstrom WJ (2013) Effects of 5-α reductase inhibitors on erectile function, sexual desire and ejaculation. Expert Opin Drug Saf 12(1):81–90
Carbone DJ, Hodges S (2003) Medical therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia: sexual dysfunction and impact on quality of life. Int J Impot Res 15(4):299–306
Favilla V et al (2016) Impact of combination therapy 5-α reductase inhibitors (5-ARI) plus alpha-blockers (AB) on erectile dysfunction and decrease of libido in patients with LUTS/BPH: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Aging Male 19(3):175–181
Welliver C et al (2014) Impact of alpha blockers, 5-α reductase inhibitors and combination therapy on sexual function. Curr Urol Rep 15(10):441
Casabe A et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of the coadministration of tadalafil once daily with finasteride for 6 months in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and prostatic enlargement secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 191(3):727–733
Glina S et al (2015) Sexual function in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and prostatic enlargement secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of tadalafil coadministered with finasteride. J Sex Med 12(1):129–138
Gotoh D et al (2022) Efficacy and safety of dutasteride with tadalafil add-on therapy in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. BMC Res Notes 15(1):288
Hutchison A et al (2007) The efficacy of drugs for the treatment of LUTS/BPH, a study in 6 European countries. Eur Urol 51(1):207–215 (discussion 215-6)
Sebastianelli A et al (2019) Tadalafil 5 mg alone or in combination with tamsulosin 0.4 mg for the management of men with lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: results of a prospective observational trial. J Clin Med 8(8):1126
Singh DV et al (2014) A comparative randomized prospective study to evaluate efficacy and safety of combination of tamsulosin and tadalafil vs. tamsulosin or tadalafil alone in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Sex Med 11(1):187–196
Gandhi J et al (2017) The impact and management of sexual dysfunction secondary to pharmacological therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Transl Androl Urol 6(2):295–304
Rigatti P et al (2003) A comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of tamsulosin and finasteride in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 6(4):315–323
Gul A et al (2020) Effect of tadalafil on penile nitric oxide synthase and corporal smooth muscle in rats under dutasteride treatment. Aging Male 23(2):161–167
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMT contributed to protocol/project development and manuscript writing/editing. MA-E, MG, SS and AZ performed data collection or management. AE-A contributed to protocol/project development. IS performed data analysis and protocol/project development. AG performed manuscript writing/editing and protocol/project development.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest with any other person, institution or organization.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Research was carried on human, approved by institutional ethical committees at Tanta university (36264PR164/2/23) and Ibn Sina national college of medical studies (IRRB-03-19032023).
Informed consent
All participants were informed, discussed and asked to sign an informed written consent including all steps of the study including all possible side effects. Only those who signed the study were included.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tawfik, A., Abo-Elenen, M., Gaber, M. et al. Tadalafil versus tamsulosin as combination therapy with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors in benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary and sexual outcomes. World J Urol 42, 70 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04735-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04735-y