Abstract
Purpose
Few data exist regarding the functional outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder. The aim of this study was to evaluate the urodynamic and functional outcomes in patients undergoing RARC and totally intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder for bladder cancer.
Methods
In this monocentric, observational study carried out between 2016 and 2020, consecutive patients undergoing RARC and intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder in the Department of Urology, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, were included. Reconstruction was totally intracorporeal Y-shaped neobladder. Main outcomes were urodynamic findings 6 months post-surgery, continence and quality of life (QoL). Continence was defined by no pad or one safety pad. International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ), International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire (IIEF-5) and Bladder Cancer Index (BCI) scores were recorded.
Results
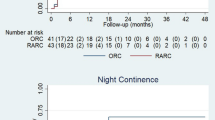
Fourteen male patients were included (median age: 64 years [IQR 54–67]. Median maximal neobladder cystometric capacity was 495 ml [IQR 410–606] and median compliance was 35.5 ml/cm H2O [IQR 28–62]. All patients had post-void residual volume < 30 ml, except for three (22%) who required clean intermittent-self catheterisation. Daytime continence was achieved in 10 patients (71%) and night-time continence in two (14.3%). Median ICIQ score was 7 [IQR 5–11]. Postoperative erectile function was present in 7% of patients (mean IIEF-5 = 5 [IQR 2–7]). Thirteen patients (93%) were satisfied with their choice of neobladder.
Conclusion
RARC with totally intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder for bladder cancer provides satisfactory urodynamic results and good QoL. These findings should be confirmed long-term.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R et al (2021) European Association of Urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur Urol 79:82–104
Bochner BH, Dalbagni G, Marzouk KH et al (2018) Randomized trial comparing open radical cystectomy and robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy: oncologic outcomes. Eur Urol 74:465–471
Parekh DJ, Reis IM, Castle EP et al (2018) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 391:2525–2536
Dutta SC, Chang SC, Coffey CS, Smith JA, Jack G, Cookson MS (2002) Health related quality of life assessment after radical cystectomy: comparison of ileal conduit with continent orthotopic neobladder. J Urol 168:164–167
Lenfant L, Verhoest G, Campi R et al (2018) Perioperative outcomes and complications of intracorporeal vs extracorporeal urinary diversion after robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a real-life, multi-institutional French study. World J Urol 36:1711–1718
Benamran D, Phé V, Drouin SJ et al (2020) Functional outcomes obtained with intracorporeal neobladder after robotic radical cystectomy for cancer: a narrative review. J Robot Surg 14:813–820
Studer UE, Burkhard FC, Schumacher M et al (2006) Twenty years experience with an ileal orthotopic low pressure bladder substitute–lessons to be learned. J Urol 176:161–166
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Koie T, Ohyama C, Yoneyama T et al (2018) Robotic cross-folded U-configuration intracorporeal ileal neobladder for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Initial experience and functional outcomes. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 14:e1955
Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P (2004) ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 23:322–330
Yao M, Simoes A (2021) Urodynamic testing and interpretation. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Janssen GWB, Ramkumar RR, Lee BH, van der Heijden AG (2021) Orthotopic urinary diversions after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: lessons learned last decade. Curr Opin Urol 31:580–585
Khan A, Vuppalapati JK, Sarath LR, Mujeeburahiman M, D’Souza N (2021) Functional outcome of robotic-assisted intracorporeal versus extracorporeal neobladder following radical cystectomy: Initial experience. Urol Ann 13:9–13
Nam JK, Kim TN, Park SW, Lee SD, Chung MK (2013) The Studer orthotopic neobladder: long-term (more than 10 years) functional outcomes, urodynamic features, and complications. Yonsei Med J 54:690–695
Obrecht F, Youssef NA, Burkhardt O et al (2020) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy and intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder: 1-year functional outcomes. Asian J Androl 22:145–148
Satkunasivam R, Santomauro M, Chopra S et al (2016) Robotic intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder: urodynamic outcomes, urinary function, and health-related quality of life. Eur Urol 69:247–253
Minervini A, Di Maida F, Tasso G et al (2021) Robot assisted radical cystectomy with Florence robotic intracorporeal neobladder (FloRIN): analysis of survival and functional outcomes after first 100 consecutive patients upon accomplishment of phase 3 IDEAL framework. Eur J Surg Oncol 47:2651–2657
Nayak AL, Cagiannos I, Lavallée LT et al (2018) Urinary function following radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder urinary reconstruction. Can Urol Assoc J 12:181–186
Palleschi G, Pastore AL, Ripoli A, Silvestri L, Petrozza V, Carbone A (2015) Videourodynamic evaluation of intracorporeally reconstructed orthotopic U-shaped ileal neobladders. Urology 85:883–889
Zhou X, Zheng J, He P et al (2020) Refinement surgical technique, and perioperative and functional outcomes in patients with robotic intracorporeal Hautmann orthotopic neobladder. Urology 138:45–51
Canda AE, Atmaca AF, Altinova S, Akbulut Z, Balbay MD (2012) Robot-assisted nerve-sparing radical cystectomy with bilateral extended pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) and intracorporeal urinary diversion for bladder cancer: initial experience in 27 cases. BJU Int 110:434–444
Tyritzis SI, Hosseini A, Collins J et al (2013) Oncologic, functional, and complications outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy with totally intracorporeal neobladder diversion. Eur Urol 64:734–741
Gu Q, Xia J, Xu A, Zhang T, Wang Z (2020) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy with totally intracorporeal neobladder diversion: perioperative, oncologic, and functional outcomes. Transl Androl Urol 9:2606–2615
Asimakopoulos Anastasios D, Campagna A, Gakis G et al (2016) Nerve sparing, robot-assisted radical cystectomy with intracorporeal bladder substitution in the male. J Urol 196:1549–1557
Strączyńska A, Weber-Rajek M, Strojek K et al (2019) The impact of pelvic floor muscle training on urinary incontinence in men after radical prostatectomy (RP) - a systematic review. Clin Interv Aging 14:1997–2005
Tyson MD, Barocas DA (2018) Quality of life after radical cystectomy. Urol Clin North Am 45:249–256
Imbimbo C, Mirone V, Siracusano S et al (2015) Quality of life assessment with orthotopic ileal neobladder reconstruction after radical cystectomy: results from a prospective Italian multicenter observational study. Urology 86:974–980
Cacciamani GE, De Marco V, Sebben M et al (2019) Robot-assisted vescica ileale padovana: a new technique for intracorporeal bladder replacement reproducing open surgical principles. Eur Urol 76:381–390
Simone G, Papalia R, Misuraca L et al (2018) Robotic intracorporeal padua ileal bladder: surgical technique, perioperative, oncologic and functional outcomes. Eur Urol 73:934–940
Mistretta FA, Musi G, Collà Ruvolo C et al (2021) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy for nonmetastatic urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder: a comparison between intracorporeal versus extracorporeal orthotopic ileal neobladder. J Endourol 35:151–158
Funding
There are no funding sources to report for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EG-J: conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, statistical analysis. DB: conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, statistical analysis. UP: acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, statistical analysis. JB: acquisition of data, statistical analysis. JP: acquisition of data, critical revision. CV: acquisition of data, critical revision. TS: acquisition of data, critical revision. MR: conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision, supervision. VP: conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to report.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière (APHP) and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
All patients gave their written informed consent before taking part.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Grobet-Jeandin, E., Benamran, D., Pinar, U. et al. Urodynamic assessment and quality of life outcomes of robot-assisted totally intracorporeal radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder for bladder cancer: a preliminary study. World J Urol 40, 2535–2541 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04126-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04126-9