Abstract
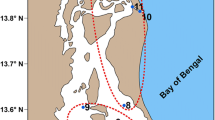
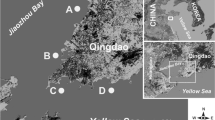
Ciliated protozoa play important roles in micro-ecosystems, especially in marine biotopes. However, few studies have been carried out on the periphytic, or aufwuch, forms in mariculture waters so far. In this study, we sampled periphytic ciliate communities in two closed mariculture ponds (ponds CP1 and CP2) and a natural seawater reservoir (pond RP) using a glass slide method to evaluate their colonizing processes and general ecological features, as well as their application as water quality indicators. We analyzed species compositions, structural parameters (species number, richness, diversity, evenness, abundance and d BP) and functional parameters (G, S eq and T 90%). Pond RP was characterized by higher levels of structural parameters (except for abundance and d BP) and more equal proportion of the major taxonomic groups. The values of S eq were significantly higher in pond RP and similar in both pond CP1 and CP2. It was also demonstrated that environmental factors, including NO2-H, NO3-H, NH3-H, soluble reactive phosphate, temperature and pH, were the first principal factors affecting the communities. Among them, temperature and chemical factors were all significantly and negatively correlated with species number (P<0.01), richness (P<0.01), diversity (P<0.01), and positive correlated with abundance (P<0.01). Opposite correlations between pH and structural parameters were observed. This study showed that there were significant differences in species composition, structural parameters and functional parameters of the periphytic ciliate communities among the ponds, which were in agreement with the water quality. Results of this study confirmed the periphytic ciliate communities to be useful bioindicators of water quality in intensive mariculture waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cairns Jr J. 1979. A strategy for use of protozoans in the evaluation of hazardous substances. In: James A, Evison L ed. Biological Indicators of Water Quality. John Wiley and Sons, Great Britain. p. 6–17.
Carey P G, Carey P. 1992. Marine Interstitial Ciliates. An Illustrated Key. Chapman and Hall, London. p. 1–368.
Decamp O, Warren A, Sánchez R. 1999. The role of ciliated protozoa in subsurface flow wetlands and their potential as bioindicators. Water Sci. Technol., 40 (3): 91–98.
Gong J, Song W, Warren A. 2005. Periphytic ciliate colonization: annual cycle and responses to environmental conditions. Aquatic Microbial. Ecology, 39: 159–170.
Li J, Xu H, Lin X, Song W. 2009. Colonization of periphytic ciliated protozoa on an artificial substrate in mariculutre waters with notes on responses to environmental factors. Prog. Nat. Sci., 19: 123 5–124 0.
Lin X, Li, J, Gong J, Warren A, Song W. 2008. Taxonomic studies on three marine pleurostomatid ciliates, Litonotus bergeri nov. spec., L. blattereri nov. spec. and L. petzi nov. spec. (Ciliophora, Pleurostomatida) from north China sea. Europ. J. Protistol., 44: 91–102.
MacArthur R H, Wilson E O. 1967. The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton. p. 1–224.
Madoni P, Braghiroli S. 2007. Changes in the ciliate assemblage along a fluvial system related to physical, chemical and geomorphological characteristics. Europ. J. Protistol., 43: 67–75.
Martín-Cereceda M, Pérez-Uz B, Serrano S, Guinea A. 2001. Dynamics of protozoan and metazoan communities in a full scale wastewater treatment plant by rotating biological contactors. Microbiol. Res., 156: 225–238.
Patrick R. 1988. Importance of diversity in the function and structure of riverine communities. Limnol. Oceanogr., 33: 130 4–130 7.
Peštová D, Macek M, Pérez M E M. 2008. Ciliates and their picophytoplankton-feeding activity in a high-altitude warm-monomictic saline lake. Europ. J. Protistol., 44: 13–25.
Pisani K A, Landers S C, Pappanastos E. 2008. Salinity tolerance in Hyalophysa chattoni (Ciliophora, Apostomatida), a sysmbiont of the estuarine grass shrimp Palaemonetes pugio. Europ. J. Protistol., 44: 141–148.
Porter K G, Feig Y S. 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr., 25: 943–948.
Ravera O. 2001. A comparison between diversity, similarity and biotic indices applied to the macroinvertebrate community of a small stream: the Ravera river (Como Province, Northern Italy). Aquat. Ecol., 33: 97–107.
Shen Y, Zhang Z, Gong X, Gu M, Shi Z, Wei Y. 1990. Modern biomonitoring techniques using freshwater microbiota. China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing. p. 1–524. (in Chinese)
Sherr B F, Sherr E B, Hopkinson C S. 1988. Trophic interactions within pelagic microbial communities: interactions of feedback regulation of carbon flow. Hydrobiologia, 159: 19–26.
Song W, Wilbert N. 1995. Benthische Ciliaten des Süsswassers. In: Röttger R ed. Praktikum der Protozoologie. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany. p. 156–168.
Song W, Xu K, Shi X, Hu X, Lei Y, Wei J, Chen Z, Shi X, Wang M. 1999. Progress in Protozoology. Oceana University of China Press, Qingdao, China. 362 p. (in Chinese)
Song W, Zhao Y, Xu K, Gong J. 2003. Pathogenic Protozoa in Mariculture. Science Press, Beijing, China. 483p. (in Chinese)
Wilbert N. 1975. Eine verbesserte Technik der Protargolimprägnation für Ciliaten. Mikrokosmos 64: 171–179.
Xu H, Min G, Choi J, Kim S, Jung J, Lin B. 2009a. Peiphytic ciliate colonization of an artificial substrate in Korean coastal waters. Protistology, 6: 55–65.
Xu H, Min G, Choi, J, Kim S, Jung J, Lim B. 2009b. Approach to analyses of periphytic ciliate communities for monitoring water quality using a modified artificial substrate in Korean coastal waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK., 89: 779–679.
Xu H, Min G, Choi, J, Kim S, Jung J, Park M. 2009c. An approach to analyses of periphytic ciliate colonization for monitoring water quality using a modified artificial substrate in Korean coastal waters. Mar. Poll. Bull., 58: 127 8–128 5.
Xu H, Song W, Warren A, Al-Rasheid K A S, Al-Farraj S A, Gong J, Hu X. 2008. Planktonic protist communities in a semi-closed mariculture pond: structural variation and correlation with environmental conditions. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK., 88: 135 3–136 2.
Xu K, Choi J K, Yang E J, Lee K C, Lei Y. 2002. Biomonitoring of coastal pollution status using protozoan communities with a modified PFU method. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 44: 877–886.
Xu M, Cao H, Xie P, Deng D, Feng W, Xu J. 2005. Use of PFU protozoan community structural and functional characteristics in assessment of water quality in a large, highly polluted freshwater lake in China. J. Environ. Monit., 7: 670–674.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U0633006, 30700069, 41076089) and from the Center of Excellence in Biodiversity Research, King Saud University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Xu, H., Lin, X. et al. Assessing mariculture water quality with the structural and functional characteristics of a ciliate community. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 29, 128–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-9063-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-9063-4