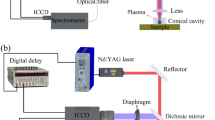
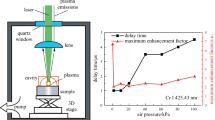
Abstract
A hemispherical cavity can be used to improve the sensitivity of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by increasing the emission spectra of the plasma. In this work, laser-induced plasma plume images were obtained with and without confinement. The results have confirmed that the reason for the signal enhancement caused by the hemispherical cavity was the reflected shockwave “compressing” effect. The dependence of spectral signal enhancement on the material property of the cavities was investigated. Four cavities in different materials, which include K-resin, aluminum alloy, photosensitive resin and nylon, were used to confine the plasma. It has shown that the material physical properties of the cavities influence the enhancement effect. We found that the main influencing factor was surface roughness of the material. Smoother cavity surfaces induced stronger enhancement effects due to the larger specular reflection component of the reflected shockwave and the more intense subsequent interaction between the plasma and shockwave. The spectral intensities of the characteristic lines approximately doubled with surface roughness values changing from 0.2 to 16.1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.I. Chernov, M.A. Kozhaev, A. Khramova, A.N. Shaposhnikov, A.R. Prokopov, V.N. Berzhansky, Control of the phase of the magnetization precession excited by circularly polarized femtosecond-laser pulses. Photonics Res. 6, 1079–1083 (2018)
L.L. Yan, Y.Y. Zhang, Z.Y. Tai, P. Zhang, X.F. Zhang, W.G. Guo, S.G. Zhang, H.F. Jiang, Multi-cavity-stabilized ultrastable laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 16, 121403 (2018)
L. Radziemski, D. Cremers, A brief history of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy From the concept of atoms to LIBS 2012. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 87, 3–10 (2013)
Galbács and Gábor, A critical review of recent progress in analytical laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 407, 7537–7562 (2015)
D. Girón, T. Delgado, J. Ruiz, L.M. Cabalin, J.J. Laserna, In-situ monitoring and characterization of airborne solid particles in the hostile environment of a steel industry using stand-off LIBS. Measurement 115, 1–10 (2018)
U.A. Taparli, L. Jacobsen, A. Griesche, K. Michalik, D. Mory, T. Kannengiesser, In situ laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy measurements of chemical compositions in stainless steels during tungsten inert gas welding. Spectroc. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 139, 50–56 (2018)
S. Moncayo, S. Manzoor, J.D. Rosales, J. Anzano, J.O. Caceres, Qualitative and quantitative analysis of milk for the detection of adulteration by Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Food Chem. 232, 322–328 (2017)
R. Wiens, S. Maurice, J. Lasue, O. Forni, R. Anderson, S. Clegg et al., Pre-flight calibration and initial data processing for the ChemCam laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy instrument on the Mars Science Laboratory rover. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 82, 1–27 (2013)
D.S. Vogt, K. Rammelkamp, S. Schröder, H.W. Hübers, Molecular emission in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy an investigation of its suitability for chlorine quantification on Mars. Icarus 302, 470–482 (2018)
C. Li, X. Gao, Q. Li, C. Song, J.Q. Lin, Spectral enhancement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in external magnetic field. Plasma Sci. Technol. 17, 919–922 (2015)
P. Liu, D. Wu, L. Sun, R. Hai, J. Liu, H. Ding, Magnetic field selective enhancement of Li I lines comparing Li II line in laser ablated lithium plasma at 10(-2) mbar air ambient gas. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 137, 77–84 (2017)
P.K. Diwakar, S.S. Harilal, J.R. Freeman, A. Hassanein, Role of laser pre-pulse wavelength and inter-pulse delay on signal enhancement in collinear double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 87, 65–73 (2013)
E. Tognoni, G. Cristoforetti, Basic mechanisms of signal enhancement in ns double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in a gas environment. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 29, 1318–1338 (2014)
Z.Y. Hou, Z. Wang, J.M. Liu, W.D. Ni, Z. Li, Combination of cylindrical confinement and spark discharge for signal improvement using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Express 22, 12909–12914 (2014)
Y.T. Fu, Z.Y. Hou, Z. Wang, Physical insights of cavity confinement enhancing effect in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Express 24, 3055–3066 (2016)
A. Li, S. Guo, N. Wazir, K. Chai, L. Liang, M. Zhang, Y. Hao, P.F. Nan, R.B. Liu, Accuracy enhancement of laser induced breakdown spectra using permittivity and size optimized plasma confinement rings. Opt. Express 25, 27559–27569 (2017)
X. Gao, L. Liu, C. Song, J.Q. Lin, The role of spatial confinement on nanosecond YAG laser-induced Cu plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48, 175205 (2015)
Z. Wang, Z.Y. Hou, S.L. Lui, D. Jiang, J.M. Liu, Z. Li, Utilization of moderate cylindrical confinement for precision improvement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal. Opt. Express 20, A1011–A1018 (2012)
Z.Y. Hou, Z. Wang, J.M. Liu, W.D. Ni, Z. Li, Signal quality improvement using cylindrical confinement for laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Express 21, 15974–15979 (2013)
X.W. Li, Z. Wang, X.L. Mao, R.E. Russo, Spatially and temporally resolved spectral emission of laser-induced plasmas confined by cylindrical cavities. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 29, 2127–2135 (2014)
X.J. Su, W.D. Zhou, H.G. Qian, Optimization of cavity size for spatial confined laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Express 22, 28437–28442 (2014)
L.B. Guo, Z.Q. Hao, M. Shen, W. Xiong, X.N. He, Z.Q. Xie, M. Gao, X.Y. Li, X.Y. Zeng, Y.F. Lu, Accuracy improvement of quantitative analysis by spatial confinement in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Opt. Express 21, 18188–18195 (2013)
X.L. Li, J.G. Wang, L.P. Zhang, X.Z. Li, Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of plasma confined by hemispherical cavity. Acta Opt. Sin. 38, 0830001-1–0830001-7 (2018)
J.Z. Zhou, J.C. Yang, M. Zhou, Y.K. Zhang, D.H. Guo, H.X. Wu, Experimental study on the effects of overlay properties on laser-induced shockwave. Chin. J. Las. 29(11), 1041–1044 (2002)
X. Hong, S.B. Wang, D.H. Guo, H.G. Wu, J. Wang, Y.S. Dai, X.P. Xia, Y.N. Xie, Confining medium and absorptive overlay: their effects on a laser-induced shockwave. Opt. Laser Eng. 29(6), 447–455 (1998)
P. Peyre, R. Fabbro, Laser shock processing: a review of the physics and applications. Opt. Quant. Electron. 27(12), 1213–1229 (1995)
N. Arnold, J. Gruber, J. Heitz, Spherical expansion of the vapor plume into ambient gas: an analytical model. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 69(S1), S87–S93 (1999)
S. Harilal, B. O’Shay, Y. Tao, M.S. Tillack, Ambient gas effects on the dynamics of laser-produced tin plume expansion. J. Appl. Phys. 99(8), 083303 (2006)
S. Harilal, G. Miloshevsky, P. Diwakar, N. LaHaye, A. Hassanein, Experimental and computational study of complex shockwave dynamics in laser ablation plumes in argon atmosphere. Phys. Plasmas 19(8), 083504 (2012)
X.D. He, K.E. Torrance, F.X. Sillion, D.P. Greenberg, A comprehensive physical model for light reflection. Conference on Computer Graphics & Interactive Techniques. ACM. 25(4), 175–186 (1991).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11504091, 61775052, 61674052, 31500300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, J., Li, H. et al. Enhancement characteristics of laser-induced plasma confined by hemispherical cavities in different materials. Appl. Phys. B 125, 236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7349-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7349-y