Abstract
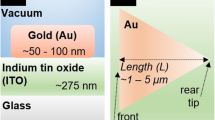
Metal-coated dielectric tetrahedral tips (T-tip) have long been considered to be interesting structures for the confinement of light to nanoscopic dimensions, and in particular as probes for scanning near-field optical microscopy. Numerical investigations using the Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) method are used to explore the operation of a T-tip in extraction mode. A dipole source in close proximity to the apex excites the tip, revealing the field evolution in the tip, the resulting edge and face modes on the metal-coated surfaces, and the coupling from these modes into highly directional radiation into the dielectric interior of the tip. These results are the starting point for illumination-mode numerical investigations by a Volume Integral equation method, which compute the field distribution that develops in a T-tip when a Gaussian beam is incident into the tip, and which show that a highly confined electric field is produced at the apex of the tip. The process of light confinement can be considered as a superfocussing effect, because the intensity of the tightly confined light spot is significantly higher than that of the focussed yet much wider incident beam. The mechanism of superfocussing can be considered as a dimensional reduction of surface plasmon modes, where an edge plasmon is the most important link between the waveguide-modes inside the tip and the confined near field at the apex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yatsui, M. Kourogi, M. Ohtsu, Plasmon waveguide for optical far/near-field conversion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 4583–4586 (2001)
U.C. Fischer, The tetrahedral tip as a probe for scanning near-field optical microscopy, in Near-Field Optics, ed. by D.W. Pohl, D. Courjon. NATO ASI Series E, vol. 242 (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1993), pp. 255–262
U.C. Fischer, J. Koglin, H. Fuchs, The tetrahedral tip as a probe for scanning near-field optical microscopy at 30 nm resolution. J. Microsc. 176, 231–237 (1994)
U.C. Fischer, A. Dereux, J.-C. Weeber, Controlling light confinement by excitation of localized surface plasmons. Top. Appl. Phys. 81, 49–69 (2001)
H.-J. Maas, A. Naber, H. Fuchs, U.C. Fischer, J.C. Weeber, A. Dereux, Imaging of photonic nanopatterns by scanning near-field optical microscopy. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19, 1295–1300 (2002)
H.-J. Maas, J. Heimel, H. Fuchs, U.C. Fischer, J.C. Weeber, A. Dereux, Photonic nanopatterns of gold nanostructures indicate the excitation of surface plasmon modes of a wavelength of 50–100 nm by scanning near-field optical microscopy. J. Microsc. 209, 241–248 (2003)
J. Heimel, U.C. Fischer, H. Fuchs, SNOM/STM using a tetrahedral tip and a sensitive current-to-voltage converter. J. Microsc. 202, 53–59 (2001)
U.C. Fischer, J. Heimel, H.-J. Maas, H. Fuchs, J.C. Weeber, A. Dereux, Super-resolution scanning near-field optical microscopy, in Optical Nanotechnologies—the Manipulation of Surface and Local Plasmons, ed. by J. Tominaga, D.P. Tsai. Topics in Applied Physics, vol. 88 (Springer, Berlin, 2003), pp. 141–151
E.G. Bortchagovsky, J. Heimel, H. Fuchs, U.C. Fischer, Dual wavelength snom imaging of monolayers of j-aggregated dye molecules. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 47, S48–S55 (2005)
S. Klein, J. Reichert, H. Fuchs, U.C. Fischer, Near-field Raman spectroscopy using a tetrahedral snom tip, in Proc. of SPIE, vol. 6195 61951F (1–7), 2006
E.G. Bortchagovsky, S. Klein, H. Fuchs, U.C. Fischer, Surface plasmon mediated tip enhanced Raman scattering. Oral contribution to the XXI International Conference on Raman Spectroscopy ICORS, 17–22 August 2008. Uxbridge, West London, UK
G. Veronis, S. Fan, Guided subwavelength plasmonic mode supported by a slot in a thin metal film. Opt. Lett. 30, 3359–3361 (2005)
I.V. Novikov, A.A. Maradudin, Channel polaritons. Phys. Rev. B 66, 035403 (2002)
D.K. Gramotnev, D.F.P. Pile, Single mode subwavelength waveguide with channel plasmon-polaritons in triangular grooves on a metal surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 6323–6325 (2006)
S. Bozhevolnyi, V.S. Volkov, E. Devaux, J.-Y. Laluet, T.W. Ebbesen, Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440, 508–510 (2006)
D.F.P. Pile, T. Oawa, D.K. Gamotnev, T. Okamoto, M. Haraguchi, M. Fukui, S. Matsuo, Theoretical and experimental investigation of strongly localized plasmons on triangular metal wedges for subwavelength waveguiding. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 061106 (2005)
E. Moreno, S.G. Rodrigo, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, L. Martin Moreno, F.J. Garcia-Vidal, Guiding and focusing of electromagnetic fields with wedge plasmon polaritons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 023901 (2008)
K. Tanaka, M. Tanaka, Simulations of nanometric optical circuits based on surface plasmon polariton gap waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82(8) (2003)
A. Bouhelier, J. Renger, M.R. Beversluis, L. Novotny, Plasmon—coupled tip enhanced near-field microscopy. J. Microsc. 210, 220–224 (2002)
F. Keilmann, Surface polariton propagation for scanning near-field microscopy. J. Microsc. 194, 567 (1999)
K. Li, M.I. Stockman, D.J. Bergman, Self similar chain of metal nanospheres as an efficient nanolens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 2274021 (2003)
A.J. Babadjanyan, N.L. Margaryan, Kh.V. Nerkararyan, Superfocusing of surface polaritons in the conical structure. J. Appl. Phys. 87(8), 3785–3788 (2000)
M.I. Stockman, Nanofocussing of optical energy in tapered plasmonic waveguides. Phys. Rev Lett. 93, 137404 (2004)
Kh.V. Nerkarayan, Superfocussing of a surface polariton in a wedge-like structure. Phys. Lett. A 237, 103–105 (1997)
D.F.P. Pile, D.K. Gramotnev, Adiabatic and non adiabatic nanofocusing of plasmons by tapered gap plasmon waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 041111 (2006)
D.K. Gramotnev, Adiabatic nanofocussing of plasmons by sharp metallic grooves: Geometrical optics approach. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 104302 (2005)
A. Taflove, S.C. Hagness, Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method, 3rd edn. (Artech House, Boston, 2005)
D.A. Christensen, Analysis of near-field tip patterns including object interaction using finite-difference time-domain calculations. Ultramicroscopy 57(2–3), 189–195 (1995)
J.L. Kann, T.D. Milster, F.F. Froehlich, R.W. Ziolkowski, J.B. Judkins, Linear behavior of a near-field optical-scanning system. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 12(8), 1677–1682 (1995)
A. Gara, M.A. Blumrich, D. Chen, G.L.T. Chiu, P. Coteus, M.E. Giampapa, R.A. Haring, P. Heidelberger, D. Hoenicke, G.V. Kopcsay, T.A. Liebsch, M. Ohmacht, B.D. Steinmacher-Burow, T. Takken, P. Vranas, Overview of the Blue Gene/L system architecture. IBM J. Res. Dev. 49(2–3), 195–212 (2005)
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6(12), 4370–4379 (1972)
J.A. Roden, S.D. Gedney, Convolution PML (CPML): an efficient fdtd implementation of the CFS-PML for arbitrary media. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 27(5), 334–339 (2000)
P. Zwamborn, P.M. van den Berg, The three-dimensional weak form of the conjugate gradient FFT method for solving scattering problems. IEEE Trans. MTT 40, 1757–1766 (1992)
K. Tanaka, M. Tanaka, T. Sugiyama, Simulation of practical nanometric optical circuits based on surface plasmon polariton gap waveguide. Opt. Express 13(1), 256–266 (2005)
G.S. Smith, An Introduction to Classical Electromagnetic Radiation (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997)
D.E. Chang, A.S. Soerensen, P.R. Hemmer, M.D. Lukin, Quantum optics with surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 053002 (2006)
D.E. Chang, A.S. Soerensen, P.R. Hemmer, M.D. Lukin, Strong coupling of single emitters to surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 76, 035402 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Burr, G.W., Grosjean, T. et al. Superfocussing in a metal-coated tetrahedral tip by dimensional reduction of surface-to edge-plasmon modes. Appl. Phys. B 93, 257–266 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-008-3147-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-008-3147-7