Abstract
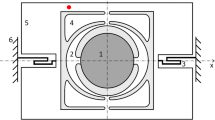
Custom modes at a wavelength of 1064 nm were generated with a deformable mirror. The required surface deformations of the adaptive mirror were calculated with the Collins integral written in a matrix formalism. The appropriate size and shape of the actuators as well as the needed stroke were determined to ensure that the surface of the controllable mirror matches the phase front of the custom modes. A semipassive bimorph adaptive mirror with five concentric ring-shaped actuators and one defocus actuator was manufactured and characterised. The surface deformation was modelled with the response functions of the adaptive mirror in terms of an expansion with Zernike polynomials. In the experiments the Nd:YAG laser crystal was quasi-CW pumped to avoid thermally induced distortions of the phase front. The adaptive mirror allows to switch between a super-Gaussian mode, a doughnut mode, a Hermite-Gaussian fundamental beam, multi-mode operation or no oscillation in real time during laser operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hudgson N, Weber H (1997) Optical Resonators. Springer, London
A.E. Siegman, New developments in laser resonators, in: Laser resonators, vol 1224 (Proc. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. 1990), pp 2–14
Bélanger P (1991) Beam propagation and the ABCD ray matrices. Opt. Lett. 16:196
Paré C, Bélanger P (1992) Beam propagation in a linear or nonlinear lens-like medium using the ABCD ray matrices: the method of moments. Opt. Quantum Electron. 24:1051
W. Bloehs F Dausinger, Shaping systems for hardening with high-power Nd:YAG-lasers, in: Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Laser Treatment of Materials (ECLAT ’96, Stuttgart 1996)
Craxton R (1981) High efficiency frequency tripling schemes for high-power Nd:glass lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-17:1771
Siegman A (1986) Lasers. University Science Books, Mill Valley, CA
Bélanger P, Paré C (1991) Optical resonators using graded-phase mirrors. Opt. Lett. 16:1057
Paré C, Bélanger P (1994) Custom laser resonators using graded-phase mirrors: Circular geometry. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 30:1141
Napartovich A, Elkin N, Troschieva V, Vysotsky D, Leger J (1999) Simplified intracavity phase plates for increasing laser-mode discrimination. Appl. Opt. 38:3025
Leger J, Chen D, Wang Z (1994) Diffractive optical element for mode shaping of a Nd:YAG laser. Opt. Lett. 19:108
Bélanger P, Lachance R, Paré C (1992) Super-gaussian output from a CO2 laser by using a graded-phase mirror resonator. Opt. Lett. 17:739
van Neste R, Paré C, Lachance R, Bélanger P (1994) Graded-phase mirror resonator with a super-gaussian output in a cw-CO2 laser. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-30:2663
Gerber M, Graf T (2004) Generation of super-gaussian modes in Nd:YAG lasers with a graded-phase mirror. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-40:1
Wattellier B, Fuchs J, Zou J-P, Chanteloup J-C, Bandulet H, Michel P, Labaune C, Depierreux S, Kudryashov A, Aleksandrov A (2003) Generation of a single hot spot by use of a deformable mirror and study of its propagation in an underdense plasma. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20:1632
A. Kudryashov T Cherezova L Kaptsov, Adaptive optical system for control of the cw technological YAG:Nd3+laserbeamparameters, in: High-power gas and solid state lasers, vol 2206 (Proc. SPIE, Europto Series 1994), pp 574–576
Cherezova T, Kaptsov L, Kudryashov A (1996) Cw industrial rod YAG:Nd3+ laser with an intracavity active bimorph mirror. Appl. Opt. 35:2554
Lubeigt W, Valentine G, Girkin J, Bente E, Burns D (2002) Active transverse mode control and optimisation of an all-solid-state laser using an intracavity adaptive-optic mirror. Opt. Express 10:550
U. Wittrock, I. Buske, H. Heuck() Adaptive aberration control in laser amplifiers and laser resonators, in: Laser Resonators and Beam Control VI, vol 4969 (Proc. SPIE 2003), pp 122–136
Gonté F, Courteville A, Dändliker R (2002) Optimization of single-mode fiber coupling efficiency with an adaptive membrane mirror. Opt. Eng. 41:1073
Liang J, Williams D, Miller D (1997) Supernormal vision and high-resolution retinal imaging through adaptive optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 14:2884
Cherezova T, Chesnokov S, Kaptsov L, Samarkin V, Kudryashov A (2001) Active laser resonator performance: formation of a specified intensity output. Appl. Opt. 40:6026
Leger J, Chen D, Mowry G (1995) Design and performance of diffractive optics for custom laser resonators. Appl. Opt. 34:2498
Makki S, Leger J (2001) Mode shaping of a graded-reflectivity mirror unstable resonator with an intracavity phase element. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-37:80
Kudryashov A, Shmalhausen V (1996) Semipassive bimorph flexible mirrors for atmospheric adaptive optics applications. Opt. Eng. 35:3064
M. Born, E. Wolf, Principles of optics (Cambridge University Press 1999)
Wang J, Silva D (1980) Wave-front interpretation with zernike polynomials. Appl. Opt. 19:1510
Noll RJ (1976) Zernike polynomials and atmospheric turbulence. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 66:207
Weber R, Graf T, Weber H (2000) Self-adjusting compensating thermal lens to balance the thermally induced lens in solid-state lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-36:757
Wyss E, Roth M, Graf T, Weber H (2002) Thermooptical compensation methods for high-power lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-38:1620
Michel D, Graf T, Glur H, Luethy W, Weber H (2004) Thermo-optically driven adaptive mirror for laser applications. Appl. Phys. B 77:721
Reinert F, Graf T, Luethy W, Weber H (2004) Optically controlled adaptive mirror. Laser Phys. Lett. 1:551
E. Wyss, T. Graf, Verfahren, Anordnung und Beeinflussungseinheit fuer die Anordnung zur Veraenderung einer Wellenfront eines optischen Strahls, EU Patent 03 405 128.4, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
42.60.Jf; 42.60.Da; 42.60.By
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerber, M., Graf, T. & Kudryashov, A. Generation of custom modes in a Nd:YAG laser with a semipassive bimorph adaptive mirror. Appl. Phys. B 83, 43–50 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-2068-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-2068-y