Abstract
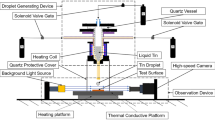
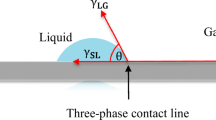
The spreading and wetting behavior of metal droplets impacting substrate surface has an important influence on the quality of jet forming, additive manufacturing, and other products. Nonetheless, due to the high speed and complexity of the impact process, there are few studies on the impact behavior of metal droplet impacting metal substrate. In this paper, the dynamic wetting behavior of Sn droplet impinging on Cu substrate is studied by simulation and experiment. Numerical simulation uses CLSVOF method to establish a single droplet of tin impact on cold copper substrate (temperature below 230 ℃) model. The effects of substrate temperature (50–200 ℃), droplet impact velocity (1–6 m/s) and substrate average roughness (0.05 μm, 0.1 μm, 0.5 μm, 1 μm, and smooth surface) on droplet spreading behavior were investigated. The spreading and wetting behavior of the single droplet liquid impinging on a cold copper substrate was studied by a high-speed camera. The results show that the substrate temperature has a great influence on the droplet spreading process and the final spreading factor but has little influence on the final contact angle. The droplet impact velocity has a great influence on the droplet spreading process, the final spreading factor, and the final contact angle. The average surface roughness of the substrate has little effect on the whole spreading process, but the final contact angle decreases first and then increases with the increase of surface roughness. The results reflect the morphology change of the droplet spreading solidification process, and explain the dynamic wetting state of the droplet spreading more directly.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Vardelle, C. Moreau, J. Akedo et al., The 2016 thermal spray roadmap. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 25(8), 1376–1440 (2016)
M.R. Dorfman, A. Sharma, Challenges and strategies for growth of thermal spray markets: the six-pillar plan. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 22(5), 559–563 (2013)
K.A. Khor, L.G. Yu, Global research trends in thermal sprayed coatings technology analyzed with bibliometrics tools. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 24(8), 1346–1354 (2015)
K. Takagi, S. Masuda, H. Suzuki et al., Preparation of monosized copper micro particles by pulsated orifice ejection method. Mater. Trans. 47(5), 1380–1385 (2006)
S. Zhong, L. Qi, J. Luo et al., Effect of process parameters on copper droplet ejecting by pneumatic drop-on-demand technology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 214(12), 3089–3097 (2014)
A. Miura, W. Dong, M. Fukue et al., Preparation of Fe-based monodisperse spherical particles with fully glassy phase. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(18), 5581–5586 (2011)
S. Masuda, K. Takagi, W. Dong et al., Solidification behavior of falling germanium droplets produced by pulsated orifice ejection method. J. Cryst. Growth 310(11), 2915–2922 (2008)
C.W. Visser, R. Pohl, C. Sun et al., Toward 3D printing of pure metals by laser-induced forward transfer. Adv. Mater. 27(27), 4087–4092 (2015)
J. Luo, R. Pohl, L. Qi et al., Printing functional 3D microdevices by laser-induced forward transfer. Small 13(9), 1602553 (2017)
R. Rioboo, M. Marengo, C. Tropea, Time evolution of liquid drop impact onto solid, dry surfaces. Exp. Fluids 33(1), 112–124 (2002)
S. Shakeri, S. Chandra, Splashing of molten tin droplets on a rough steel surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45(23), 4561–4575 (2002)
W. Li, W. Zhu, S. Quan, Visual experimental study on droplet impacted onto horizontal solid surface. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 7(2), 155–160 (2008)
L. Huang, Z. Liu, Y. Liu et al., Effect of contact angle on water droplet freezing process on a cold flat surface. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 40, 74–80 (2012)
Q. Xu, Z. Li, J. Wang et al., Characteristics of single droplet impact on cold plate surfaces. Drying Technol. 30(15), 1756–1762 (2012)
L. Gang-Tao, G. Ya-Li, S. Sheng-Qiang, Observation and analysis of drop impact on wetted spherical surfaces with low velocity. Acta Physica Sinica 62(18), 184703 (2013)
A.L. Yarin, Drop impact dynamics: splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing [J]. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38, 159–192 (2006)
Berberovic E, Investigation of free-surface flow associated with drop impact: numerical simulations and theoretical modeling. Technische Universität, (2010)
K. Okumura, F. Chevy, D. Richard et al., Water spring: a model for bouncing drops. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 62(2), 237 (2003)
M. Pasandideh-Fard, S.D. Aziz, S. Chandra et al., Cooling effectiveness of a water drop impinging on a hot surface. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 22(2), 201–210 (2001)
G. Strotos, G. Aleksis, M. Gavaises et al., Non-dimensionalisation parameters for predicting the cooling effectiveness of droplets impinging on moderate temperature solid surfaces. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(5), 698–711 (2011)
J. Blake, D. Thompson, D. Raps et al., Simulating the freezing of supercooled water droplets impacting a cooled substrate. AIAA J. 53(7), 1725–1739 (2015)
Y. Yao, C. Li, H. Zhang et al., Modelling the impact, spreading and freezing of a water droplet on horizontal and inclined superhydrophobic cooled surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 419, 52–62 (2017)
K. Zhao, Y.Z. She, Y.L. Jiang et al., Numerical study on phase change behavior of liquid nitrogen droplets impinging on solid surface. Acta Physica Sinica 68(24), 20190945 (2019)
J. Hou, J. Gong, X. Wu et al., Numerical study on impacting-freezing process of the droplet on a lateral moving cold superhydrophobic surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 183, 122044 (2022)
X. Wang, W. Yu, M. Wang et al., Spreading behavior of Sn droplets impacting Cu and stainless steel substrates. Surf. Interfaces 29, 101790 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51465032 and No.52061023).
Funding
Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing, Chongqing Science and Technology Commission, 51465032, Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 52061023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Wang, M., Wang, F. et al. Study of the dynamic wetting behavior of Sn droplet impacting Cu substrate. Appl. Phys. A 128, 646 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05795-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05795-4