Abstract
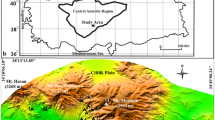
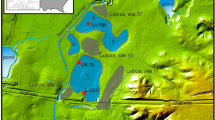
Prehistoric agriculture and vegetation in Lithuania have so far been reconstructed largely using palynological data. This paper reports the archaeobotanical investigation of macroremains from the Late Bronze-early Iron Age (LBA–EIA) lakeside settlement Luokesa 1 (L1) in eastern Lithuania, with the aim of elucidating the settlement’s history and crop diversity. The single phase settlement was fortified with an onshore palisade and is dated between 625 and 535 cal. bc. Samples were taken along a land to lake transect, and in the centre of L1. The stratigraphy consisted of three distinct layers: lake marl, cultural deposit and sandy limnic sediment on top. The plant spectrum shows that L1 was constructed on an exposed morainic shoal. It was surrounded by woodland, meadows, fields/gardens, ruderal habitats and riverine vegetation. Accumulated cultural deposits consisted mainly of manure (litter, fodder and dung of sheep/goat), with rubbish, sweepings from the houses or remains of the on-site vegetation. The crops were Panicum miliaceum, Triticum spelta, T. dicoccon, Hordeum vulgare s.l., Pisum sativum and Camelina sativa, the latter being the first prehistoric evidence in Lithuania. The trophic state of the lake increased during the occupation period. After the abandonment of the settlement the ruins decayed until the lake flooded the site. The results are discussed in a broader context of the LBA/EIA cultures in northern Central Europe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antanaitis-Jacobs I, Kisielienė D, Stančikaitė M (2002) Macrobotanical and palynological research at two archaeological sites in Lithuania. In: Viklund K (ed) Nordic archaeobotany - NAG 2000 in Umea, vol 15., Archaeology and environmentVMC KBC Umea Universitet, Umea, pp 5–21
Antanaitis-Jacobs I, Kisielienė D, Stančikaitė M (2004) Archeobotanika Lietuvoje: Makrobotaniniai ir palinoliginiai Tyrinėjimai. Lietuvos Archeologija 26:77–98
Antanaitis-Jacobs I, Stančikaitė M (2004) The impact of the economic acitivities of Stone and Bronze Age populations on their environment according to the archaeobotanical evidence. Lietuvos Archeologija 25:251–266
Baubonis Z, Kraniauskas R, Kvedaravičius M (2001) Luokesų ežero gyvenvietės povandeniniai archeologiniai tyrinėjimai. Archeologiniai tyrinėjimai Lietuvoje 2000 metais:228–231
Baubonis Z, Motuzaitė G, Pranckėnaitė E (2002) Luokesų ežero (Molėtų r.) senovės gyvenviečių 2 ir 3 povandeniniai archeologinia-ižvalgymai. Archeologiniai tyrinėjimai Lietuvoje 2001 metais:268–270
Baubonis Z, Kvedaravičius M, Motuzaitė G, Pranckėnaitė E (2006) Luokesų ežero polinės gyvenvietės I ir II. Archeologiniai tyrinėjimai Lietuvoje 2004 metais:315–316
Birks HH (2007) Plant macrofossil introduction. In: Elias S (ed) Encyclopedia of Quaternary science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2,266–2,288
Bleicher N (2009) Altes Holz in neuem Licht. Archäologische und dendrochronologische Untersuchungen an spätneolithischen Feuchtbodensiedlungen in Oberschwaben. (Berichte zu den Ufer- und Moorsiedlungen Südwestdeutschlands V, Materialhefte Archäol Bad-Württ 83) Theiss, Stuttgart
Bleicher, N (2014) Dendrochronological analyses of wood samples from a Late Bronze to early Iron Age site at Lake Luokesa, Lithuania. Veget Hist Archaeobot 23 (this volume)
Bogucki P (2013) People, lakes and forest in the Baltic region: a prehistoric perspective. In: O’Sullivan A, Menotti F (eds) The Oxford handbook of wetland archaeology. Oxfords handbooks in archaeology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 811–826
Brazaitis D (2005) Ankstyvasis metalų laikotarpis. In: Girininkas A (ed) Lietuvos istorija. Akmens amžius, Baltos lankos, Vilnius, pp 251–317
Brombacher C, Jacomet S (1997) Ackerbau, Sammelwirtschaft und Umwelt: Ergebnisse archäobotanischer Untersuchungen. In: Schibler J, Hüster-Plogmann H, Jacomet S, Brombacher C, Gross-Klee E, Rast-Eicher A (eds) Ökonomie und Ökologie neolithischer und bronzezeitlicher Ufersiedlungen am Zürichsee. Ergebnisse der Ausgrabungen Mozartstrasse, Kanalisationssanierungen Seefeld, AKAD/Pressehaus und Mythenschloss in Zürich. (Monographien der Kantonsarchäologie Zürich 20) Egg, Zürich, pp 220–279
Bullock P, Fedoroff N, Jongerius A, Stoops G, Tursina T, Babel U (1985) Handbook for soil thin section description. Waine Research Publication, Wolverhampton
Buurman J, Pals JP (1974) Some remarks on prehistoric flax in the Netherlands. (I.P.P. publications 196) ROB, Amersfoort
Cappers R, Bekker RM, Jans JEA (2006) Digitale Zadenatlas van Nederland (Digital seed atlas of the Netherlands). (Groningen Archaeological Studies 4) Barkhuis Publishing and Groningen University Library, Groningen
Damušytė A (2011) Post-glacial geological history of the Lithuanian coastal area (summary of doctoral thesis). Vilnus University, Vilnius
Daugnora L, Girininkas A, Guobytė R, Kisielienė D, Simniškytė A, Stančikaitė M (2004) Juodonys ir jaros apyežeris: gamta ir gyventojai. Lietuvos archeologija 26:111–134
Dixon N (2004) The crannogs of Scotland: an underwater archaeology. Tempus, Stroud
Ebersbach R (2010a) Soziale Einheiten zwischen “Haus” und “Dorf” - neue Erkenntnisse aus den Seeufersiedlungen. In: Claßen E, Doppler T, Ramminger B (eds) Familie – Verwandtschaft – Sozialstrukturen: Sozialarchäologische Forschungen zu neolithischen Befunden. Fokus Jungsteinzeit: Berichte der AG Neolithikum 1. Welt und Erde, Kerpen-Loogh, pp 141–156
Ebersbach R (2010b) Vom Entstehen und Vergehen - Überlegungen zur Dynamik von Feuchtbodenhäusern und -siedlungen. In: Matuschik I, Strahm C, Eberschweiler B et al (eds) Vernetzungen - Aspekte siedlungsarchäologischer Forschung. Lavori, Freiburg, pp 41–50
Ebersbach R (2013) Houses, households and settlements: architecture and living spaces. In: Menotti F, O’Sullivan A (eds) The Oxford handbook of wetland archaeology. Oxford University Press, London, pp 283–301
Ellenberg H (1991) Zeigerwerte von Pflanzen in Mitteleuropa, 3rd edn. (Scripta Geobotanica 18) Goltze, Göttingen
Gadamavičius A, Stančikaitė M, Kisielienė D, Mažeika J, Gryguc G (2011) Post-glacial vegetation and environment of the Labanoras Region, East Lithuania: implications for regional history. Geol Quarterly 55:269–284
Gaigalas A (2004) Environmental study of the Bronze-Iron Age transition period of eastern Europe. In: Scott EM, Alekseev AY, Zaitseva G (eds) Impact of the environment on human migration in Eurasia: Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Research Workshop, St. Petersburg, 15-18 November 2003. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 243–254
Girininkas A (2008) The influence of the environment on the human population around lake Kretuonas during the Stone Age and the Bronze Age. Archaeologia Baltica 9:15–32
Gollnisch-Moos H (1999) Ürschhausen-Horn. Haus- und Siedlungsstrukturen der spätestbronzezeitlichen Siedlung. (Archäologie im Thurgau 7) Departement für Erziehung und Kultur des Kantons Thurgau, Frauenfeld
Grabowski R (2011) Changes in cereal cultivation during the Iron Age in southern Sweden: a compilation and interpretation of the archaeobotanical material. Veget Hist Archaeobot 20:479–494
Guobytė M, Satkūnas J (2011) Pleistocene glaciations in Lithuania. Developments in Quarternary Science 15:231–246
Haas JN, Karg S, Starnberger R (2007) Vegetationswandel, Klima und prähistorische Landwirtschaftssysteme im Umfeld der Pfahlbausiedlung Pfyn Breitenloo. In: Leuzinger U (ed) Pfyn-Breitenloo - Die jungsteinzeitliche Pfahlbausiedlung. (Archäologie im Thurgau 14) Departement für Erziehung und Kultur des Kantons Thurgau, Frauenfeld, pp 111–136
Haas JN, Wahlmüller N (2010) Floren-, Vegetations- und Milieuveränderungen im Zuge der bronzezeitlichen Besiedlung von Bruszczewo (Polen) und der landwirtschaftlichen Nutzung der umliegenden Gebiete. In: Müller J, Czebreszuk J, Kneisel J (eds) Bruszczewo II - Ausgrabungen und Forschungen in einer prähistorischen Siedlungskammer Großpolens. Studien zur Archäologie in Ostmitteleuropa 6:50–81
Hall A, Kenward H (1998) Disentangling dung: pathways to stable manure. Environ Archaeol 1:123–126
Harding A, Ostoja-Zagórski J, Palmer C, Rackham J (2004) Sobiejuchy: A fortified site of the early Iron Age in Poland. Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, Polish Academy of Science, Warsaw
Heitz-Weniger, A (2014) Palynological investigations at the Late Bronze-Early Iron Age lakeshore settlement of Luokesa 1 (Moletai District, Lithuania): a contribution to the Middle-Late Holocene vegetation history of the south-eastern Baltic regions. Veget Hist Archaeobot 23 (this volume). doi10.1007/s00334-014-0456-0
Henderson JC (1998) Islets through time: the definition, dating and distribution of Scottish crannogs. J Archaeol 17:227–244
Henriksen PS (2009) Archaeobotanical evidence of flax in the prehistoric Denmark. In: Karg S (ed) The International Flax Network. Communicating Culture Aps, Copenhagen, pp 22–23
Hosch S, Zibulski P (2003) The influence of inconsistent wet-sieving procedures on the macroremains concentration in waterlogged sediments. J Archaeol Sci 30:849–857
Ismail-Meyer, K (2014) The potential of micromorphology for interpreting sedimentation processes in wetland sites: a case study of a Late Bronze-early Iron Age lakeshore settlement at Lake Luokesa (Lithuania). Veget Hist Archaeobot 23 (this volume). doi10.1007/s00334-014-0459-x
Ismail-Meyer K, Rentzel P (2004) Mikromorphologische Untersuchung der Schichtabfolge. In: Jacomet S, Leuzinger U, Schibler J (eds) Die jungsteinzeitliche Seeufersiedlung Arbon Bleiche 3. Umwelt und Wirtschaft. Archäologie im Thurgau 12. Departement für Erziehung und Kultur des Kantons Thurgau, Frauenfeld, pp 66-80
Jacomet S (1985) Botanische Makroreste aus den Sedimenten des neolithischen Siedlungsplatzes AKAD-Seehofstrasse am untersten Zürichsee. Die Reste der Uferpflanzen und ihre Aussagemöglichkeiten zu Vegetationsgeschichte, Schichtentstehung und Seespiegelschwankungen. (Zürcher Studien zur Archäologie 3) Juris, Zürich
Jacomet S (2007) Neolithic plant economies in the northern Alpine foreland from 5500 to 3500 bc cal. In: Colledge S, Conolly J (eds) The origins and spread of domestic plants in Southwest Asia and Europe. Left Coast Press, Walnut Creek, pp 221–258
Jacomet S (2008) Subsistenz und Landnutzung während des 3. Jahrtausends v. Chr. aufgrund von archäobotanischen Daten aus dem südwestlichen Mitteleuropa. In: Dörfler W, Müller J (eds) Umwelt-Wirtschaft-Siedlungen im dritten vorchristlichen Jahrtausend Mitteleuropas und Südskandinaviens. (Offa-Bücher 84) Wachholz, Neumünster, pp 355-377
Jacomet S (2013) Archaeobotany. Analyses of plant remains from waterlogged archaeological sites. In: O’Sullivan A, Menotti F (eds) The Oxford handbook of wetland archaeology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 497–514
Jacomet S, Brombacher C (2005) Reconstructing intra-site patterns in Neolithic lakeshore settlements: the state of archaeobotanical research and future prospects. In: Della Casa P, Trachsel M (eds) WES’04—Wetland economies and societies. (Collectio Archaeologica 3) Chronos, Zürich, pp 69–94
Jacomet S, Brombacher C, Dick M (1989) Archäobotanik am Zürichsee. Ackerbau, Sammelwirtschaft und Umwelt von neolitischen und bronzezeitlichen Seeufersiedlungen im Raum Zürich. Ergebnisse von Untersuchungen pflanzlicher Makroreste der Jahre 1979–1988. (Ber Zürcher Denkmalpfl Monogr 3) Orel Füssli, Zürich
Jacomet S, Rachoud-Schneider AM, Zoller H, Burga CA (1998) Vegetationsentwicklung, Vegetationsveränderung durch menschlichen Einfluss, Ackerbau und Sammelwirtschaft. In: Hochuli S, Niffeler U, Rychner V (eds) (Die Schweiz vom Paläolithikum bis zum frühen Mittelalter (SPM) 3: Bronzezeit) Basel, pp 141–170
Jacomet S, Jacquat C, Winter M, Wick L (1999) Umwelt, Ackerbau und Sammelwirtschaft. In: Müller F, Kaenel G, Lüscher G (eds) (Die Schweiz vom Paläolithikum bis zum frühen Mittelalter (SPM) 4: Eisenzeit) Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Ur- und Frühgeschichte, Basel, pp 98–115
Jacomet S, Leuzinger U, Schibler J (2004) Die jungsteinzeitliche Seeufersiedlung Arbon Bleiche 3. Umwelt und Wirtschaft. (Archäologie im Thurgau 12) Departement für Erziehung und Kultur des Kantons Thurgau, Frauenfeld
Jacquat C (1988) Hauterive-Champréveyre 1 Les plantes de l’âge du Bronze. Catalogue des fruits et des graines. (Archéologie neuchâteloise 7) Du Ruau, Saint-Blaise
Jacquat C (1989) Hauterive-Champréveyre 2 Les plantes de l’âge du Bronze. Contribution à l’histoire de l’environnement et de l’alimentation. (Archéologie Neuchâteloise 8) Du Ruau, Saint-Blaise
Jones M (1991) Sampling in palaeoethnobotany. In: Van Zeist WA, Wasylikowa K, Behre K-E (eds) Progress in Old World palaeoethnobotany. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 53–62
Kabailienė M (2006) Gamtinės aplikos raida Lietuvoje per 14 000 metų. Vilniaus universiteto leidykla, Vilnius
Karg S (2012) Oil-rich seeds from prehistoric contexts in southern Scanidinavia - reflections on the archaeobotanical records of flax, hemp, gold of pleasure, and corn spurrey. Acta Palaeobot 52:17–24
Kenward HK, Hall AR, Jones AKC (1980) A tested set of techniques for the extraction of plant and animal macrofossils from waterlogged archaeological deposits. Sci Archaeol 22:3–15
Kimmig W (1992) Die Wasserburg Buchau, eine spätbronzezeitliche Siedlung: Forschungsgeschichte und Kleinfunde. (Materialh Vor- Frühgesch Bad-Württ 16) Theiss, Stuttgart
Kisielienė D, Masiulienė I, Daugnora L, Stančikaitė M, Mažeika J, Vaikutienė G, R P (2012) History of the environment and population of the old town of Klaipėda, Western Lithuania: Multidisciplinary approach to the Last Millennium. Radiocarbon 54:1,003–1,015
Kohler-Schneider M (2007) Early agriculture and subsistence in Austria: a review of Neolithic plant records. In: Colledge S, Conolly J (eds) The origins and spread of domestic plants in southwest Asia and Europe. Left Coast Press, Walnut Creek, pp 209–220
Kondratienė O (1998) Palynological evidence for the development of agriculture in Lithuania. Pact 54:61–67
Körber-Grohne U (1994) Nutzpflanzen in Deutschland. Kulturgeschichte und Biologie, Theiss, Stuttgart
Kreuz A (2004) Landwirtschaft im Umbruch? Archäobotanische Untersuchungen zu den Jahrhunderten um Christi Geburt in Hessen und Mainfranken. Ber RGK 85:97–292
Kreuz A (2007) Archaeobotanical perspectives on the beginning of agriculture north of the Alps. In: Colledge S, Conolly J (eds) The origins and spread of domestic plants in southwest Asia and Europe. Left Coast Press, Walnut Creek, pp 259–294
Kreuz A, Schäfer E (2008) Archaeobotanical consideration of the development of Pre-Roman Iron Age crop growing in the region of Hesse, Germany, and the question of agricultural production and consumption at hillfort sites and open settlements. Veget Hist Archaeobot 17:159–181
Kriiska A, Roio M (2011) Prehistoric archaeology of wetlands in Estonia. In: Pranckėnaitė E (ed) Wetland settlements in the Baltic region. Vilnius, pp 55-73
Kriiska A, Lavento M, Peets J (2005) New AMS Dates of the Neolithic and Bronze Age ceramics in Estonia: preliminary results and interpretations. Estonian J Archaeol 9:3–31
Kroll H (2010) Die Archäobotanik von Bruszczewo – Darstellung und Interpretation wichtiger Ergebnisse. In: Müller J, Czebreszuk J, Kneisel J (eds) Bruszczewo II. Studien zur Archäologie in Ostmitteleuropa 6:250–287
Kühn M, Wick L (2010) Pflanzenreste in Koprolithen von Schafen und Ziegen: Was frassen die kleinen Wiederkäuer von Pfäffikon-Burg? In: Eberli U (ed) Die horgenzeitliche Siedlung von Pfäffikon-Burg. (Monographien der Kantonsarchäologie Zürich 40) Baudirektion Kanton Zürich, Zürich und Elgg, pp 256–261
Kühn M, Maier U, Herbig C, Isamil-Meyer K, Le Bailly M, Wick L (2013) Methods for the examination of cattle, sheep and goat dung in prehistoric wetland settlements with examples of the sites Alleshausen-Täschenwiesen and Alleshausen-Grundwiesen (around cal 2900 bc) Lake Federsee, south-west Germany. J Environ Archaeol 18:43–57
Kunskas R (ed) (2005) Development of lake and bog ecosystems - The little palaeogeographical and palaeosynecological atlas. Ciklonas, Vilnius
Lang V (2007) The Bronze and Early Iron Ages in Estonia. (Estonian Archaeology 3) Tartu University Press, Tartu
Latałowa M, Pińska K (2010) Zawartość botaniczna dwóch naczyń z pozostałości osady ludności łużyckich pól popielnicowych w Polanowie na Pojezierzu Gnieźnieńskim. In: Pydyn A (ed) Archeologia Jeziora Powidzkiego. Toruń, pp 197–226
Larsson M (2013) Cultivation and processing of Linum usitatissimum and Camelina sativa in southern Scandinavia during the Roman Iron Age. Veget Hist Archaeobot 22:509–520
Lauber K, Wagner G, Gygax A (2012) Flora Helvetica, 5th edn. Haupt, Bern
Lauer W, Frankenberg P (1988) Klimaklassifikation der Erde. (Geographische Rundschau 40) Westermann, Braunschweig
Lewis H (2007) Pile dwellings, changing lake conditions and sediment deposition: Preliminary soil micromorphology study of cultural deposits from underwater sites at Lake Luokesas, Molėtai Region, Lithuania. J Wetland Archaeol 7:33–50
Loze I (2011) Wetlands and Stone Age wetland settlements in Latvia. In: Pranckėnaitė E (ed) Wetland settlements in the Baltic region. Vilnius, pp 75–91
Maier U (2001) Archäobotanische Untersuchungen in der neolithischen Ufersiedlung Hornstaad-Hörnle IA am Bodensee. In: Maier U, Vogt R (eds) Siedlungsarchäologie im Alpenvorland VI. Botanische und pedologische Untersuchungen zur Ufersiedlung Hornstaad-Hörnle IA. (Siedlungsarchäologie im Alpenvorland 6) Forsch Ber Vor- Frühgesch Bad-Württ 74. Theiss, Stuttgart, pp 9–384
Maier U (2004) Archäobotanische Untersuchungen in jung- und endneolithischen Moorsiedlungen am Federsee. In: Köninger J, Schlichtherle H (eds) Ökonomischer und ökologischer Wandel am vorgeschichtlichen Federsee. Archäologische und naturwissenschaftliche Untersuchungen. (Hemmenhofener Skripte 5) Landesdenkmalamt Baden-Württemberg, Gaienhofen-Hemmenhofen, pp 71–159
Maier U, Harwath A (2011) Detecting intra-site patterns with systematic sampling strategies. Archaeobotanical grid sampling of the lakeshore settlement Bad Buchau-Torwiesen II, southwest Germany. Veget Hist Archaeobot 20:349–365
Masiulienė I (2009) 16th-17th cen. Klaipėda town resident‘s lifestyle (by archaeological, paleobotanical and zooarchaeological data of Kurpių street plots). Archaeologia Baltica 12:95–111
Menotti F (ed) (2004) Living on the lake in prehistoric Europe - 150 years of lake-dwelling research. Routledge, London
Menotti F (2012) Wetland archaeology and beyond: Theory and practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Menotti F, O’Sullivan A (eds) (2013) The Oxford handbook of wetland archaeology. Oxford handbooks in archaeology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Menotti F, Baubonis Z, Brazaitis D, Higham T, Kvedaravičius M, Lewis H, Motuzaite G, Pranckėnaitė E (2005) The first lake-dwellers of Lithuania: Late Bronze Age pile settlements on Lake Luokesas. Oxford J Archaeol 24:381–403
Merkevičius A, Nemickienė R (2011) Senieji laukai Šiaurės Vakarų Lietuvoje. Vilnius
Moora H (1957) Varasemaid andmeid ketramisest je kudumisest. Eesti rahvaroivad XIX sajandist ja XX sajandi algult, Tallin, pp 2(003–2):009
Motuzaite Matuzevičiūtė G (2007) Living on the lake and farming the land. Archaeobotanical investigation on Luokesai I lake dwelling site. Lietuvos Archeologija 31:123–138
Motuzaite Matuzevičiūtė G (2008) Living above the water or on dry land? The application of soil analysis methods to investigate a submerged Bronze Age to Early Iron Age lake dwelling site in eastern Lithuania. In: Girininkas A (ed) (Archaeologia Baltica 9) Klaipėda University Press, Klaipėda, pp 33–46
Polcyn M (1995) Pszenica orkisz (Triticum spelta) i jęczmień zwyczajny (Hordeum vulgare) z osady nawodnej ludności kultury kurhanów zachodniobałtyjskich w Mołtajnach woj. olsztyńskie (Stan. 1) [Spelt (Triticum spelta) and barley (Hordeum vulgare) from the lake settlement of the West Baltian Barrow Culture in Mołtajny, Olsztyn Voivodeship (Site 1), in Polish]. Acta Universitatis Nicolai Copernici Archeologia 24:53–71
Pollmann B (accepted) Geschichte einer Feuchbodensiedlung um 600 v. Chr. am See Luokesa (Litauen): Rekonstruktion von Schichtgenese, Umwelt und Ernährung anhand archäobotanischer Analysen und taphonomischer Untersuchungen biologischer Makroreste. Doctoral thesis, University of Basel, Basel
Poska A, Saarse L, Veski S, Kihno K (1999) Farming from the Neolithic to the Pre-Roman Iron Age in Estonia, as reflected in pollen diagrams. Pact 57:305–317
Pranckėnaitė E (ed) (2011) Wetland settlements of the Baltic - A prehistoric perspective. Standartų Spaustuvė, Vilnius
Pranckėnaitė E (2012) Ežerų gyvenvietės pietryčių Baltijos regione ansktyvuoju metalų laikotarpiu (Lake dwellings in the South-Eastern Baltic Sea Region during The Early Metal Period). Doctoral thesis, Klaipėda University, Klaipėda
Pranckėnaitė E (2014) Living in wetlands in the southeastern Baltic region during the Late Bronze to early Iron Age: the archaeological context of the Luokesa lake settlements. Veget Hist Archaeobot 23 (this volume)
Pydyn A, Gackowski J (2011) Wetland archaeology of the Late Bronze Age and the Early Iron Age settlements from Poland. In: Pranckėnaitė E (ed) Wetland settlements in the Baltic region. Vilnius, pp 113–149
Rasiņš A, Taurina M (1983) Übersicht über den Artenbestand der Kulturpflanzen und Unkräuter aus archäologischen Ausgrabungen in der Lettischen SSR. In: Medieval castles and towns in Latvian territory. (Archaeology and Ethnography 14) Zinātne, Riga, pp 152–176 (in Latvian with German summary).
Rasmussen P (1993) Analysis of goat/sheep faeces from Egolzwil 3, Switzerland: Evidence for branch and twig foddering of livestock in the Neolithic. J Archaeol Sci 20:479–502
Rimantienė R (2005) Die Steinzeitfischer an der Ostseelagune in Litauen. Litauisches Nationalmuseum, Vilnius
Rösch M (1985) Die Pflanzenreste der neolithischen Ufersiedlung von Hornstaad-Hörnle I am westlichen Bodensee. (Berichte zu Ufer- und Moorsiedlungen Südwestdeutschlands 2, Materialhefte Vor- Frühgesch Bad-Württ 7) Theiss, Stuttgart, pp 167–199
Runge M, Henriksen PS (2007) Danmarks ældstehørindustrie. Fynske Minder 2007:145–165
Schmidl A, Jacomet S, Oeggl K (2007) Distribution patterns of cultivated plants in the Eastern Alps (Central Europe) during Iron Age. J Archaeol Sci 34:243–254
Sillasoo Ü, Poska A, Seppä H, Blaauw M, Frank M, Chambers FM (2009) Linking past cultural developments to palaeoenvironmental changes in Estonia. Veget Hist Archaeobot 18:315–327
Smith W (2001) When method meets theory: the use and misuse of cereal producer/consumer models in archaeobotany. In: Albarella U (ed) Environmental Archaeology: Meaning and Purpose. (Environmental Science and Technology Library 17. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 283–298
Soil Atlas of Europe (2005) European Communities, Luxembourg
Stančikaitė M, Kisielienė D, Strimaitienė A (2004) Vegetation response to the climatic and human impact changes during the Late Glacial and Holocene: case study of the marginal area of Baltija Upland, NE Lithuania. Baltica 17:17–33
Stančikaitė M, Kisielienė D, Mažeika J, Blaževičius P (2008) Environmental conditions and human interference during the 6th and 13th-15th centuries AD at Vilnius Lower Castle, east Lithuania. Veget Hist Archaeobot 17:239–250
Stančikaitė M, Daugnora L, Hjelle K, Hufthammer AK (2009) The environment of the Neolithic archaeological sites in Šventoji, Western Lithuania. Quat Int 207:117–129
Stančikaitė M, Kisielienė D, Šeirienė V (2012) Paleobotanical investigations in Lithuania: Old traditions and new approach. In: Zabiela G, Baubonis Z, Marcinkevičiūtė E (eds) Archaeological investigations in independent Lithuania (1990-2010). Society of the Lithuanian Archaeology, Vilnius, pp 416–419
Stika HP, Heiss AG (2012) Bronzezeitliche Landwirtschaft in Europa – Der Versuch einer Gesamtdarstellung des Forschungsstandes. In: Willroth KH (ed) Siedlungen der älteren Bronzezeit. (Studien zur nordeuropäischen Bronzezeit 1) Wachholtz, Neumünster, pp 183–216
Tolar T, Jacomet S, Velušček A, Čufar K (2010) Recovery techniques for waterlogged archaeological sediments: a comparison of different treatment methods for samples from Neolithic lake shore settlements. Veget Hist Archaeobot 19:53–67
Tomczyńska Z, Wasylikowa K (1988) Plant material from a Hallstatt settlement at Kamieniec near Toruń, North Poland (A reinvestigation). In: Küster H (ed) Der prähistorische Mensch und seine Umwelt. (Forsch Ber Vor- Frühgesch Bad-Württ 31) Theiss, Stuttgart, pp 281–287
Tupčiauskaitė J (2012) Botanikos Mokomoji lauko praktika. Stuomeninių augalų mokomųjų ekskursijų konspektai, užduotys ir kontroliniai klausimai, Mokomoji knyga, Vilnius
Van der Veen M, Jones GEM (2006) A re-analysis of agricultural production and consumption: implications for understanding the British Iron Age. Veget Hist Archaeobot 15:217–228
Vandorpe P, Jacomet S (2007) Comparing different pre-treatment methods for strongly compacted organic sediments prior to wet-sieving: a case study on Roman waterlogged deposits. Environ Archaeol 12:207–214
Vilkonis KK (2008) Lietuvos žaliasis rūbas Atlasas. Lututė, Kaunas
Wacnik A (2009) From foraging to farming in the Great Mazurian Lake District: palynological studies on Lake Miłkowskie sediments, northeast Poland. Veget Hist Archaeobot 18:187–203
Wasylikowa K, Cârciumaru M, Hajnalová E, Hartyányi BP, Pashkevich GA, Yanushevich ZV (1991) East-Central Europe. Van Zeist W, Wasylikowa K, Behre K-E (1991) Progress in Old World palaeoethnobotany. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 207–239
Wegmüller S (1976) Pollenanalytische Untersuchungen über die Siedlungsverhältnisse der frühneolithischen Station Egolzwil 5. In: Wyss R (ed) Das jungsteinzeitliche Jäger-Bauerndorf Egolzwil 5 im Wauwiler Moos. Archäologische Forschungen, Zürich, pp 141–162
Zohary D, Hopf M, Weiss E (2012) Domestication of plants in the Old World, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Acknowledgements
My thanks go to Elena Pranckėnaitė, head of the excavation on Lake Luokesa who supported me also with the translation of Lithuanian articles, and my colleagues at Integrative Prehistory and Archaeological Science (IPAS), who helped me with the identification of macroremains and were open for many fruitful discussions, especially Örni Akeret, Patricia Vandorpe and Petra Zibulski. For help during writing I thank my colleague Angela Schlumbaum (IPAS) and two anonymous reviewers who largely improved the manuscript. Many thanks go also to Stefanie Jacomet, who supervised my doctorate work which was financed by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Project-No. K-13K1-117893/1) and by the Fritz Sarasin Stiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Latałowa.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollmann, B. Environment and agriculture of the transitional period from the Late Bronze to early Iron Age in the eastern Baltic: an archaeobotanical case study of the lakeshore settlement Luokesa 1, Lithuania. Veget Hist Archaeobot 23, 403–418 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-014-0464-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-014-0464-0