Abstract
Objectives
To assess important features for risk stratification of gallbladder (GB) polyps >10 mm using high-resolution ultrasonography (HRUS) and texture analysis.
Methods
We included 136 patients with GB polyps (>10 mm) who underwent both HRUS and cholecystectomy (non-neoplastic, n = 58; adenomatous, n = 32; and carcinoma, n = 46). Two radiologists retrospectively assessed HRUS findings and texture analysis. Multivariate analysis was performed to identify significant predictors for neoplastic polyps and carcinomas.
Results
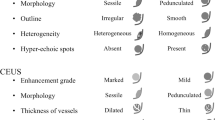
Single polyp (OR, 3.680–3.856) and larger size (OR, 1.450–1.477) were independently associated with neoplastic polyps (p < 0.05). In a single or polyp >14 mm, sensitivity for differentiating neoplastic from non-neoplastic polyps was 92.3%. To differentiate carcinoma from adenoma, sessile shape (OR, 9.485–41.257), larger size (OR, 1.267–1.303), higher skewness (OR, 6.382) and lower grey-level co-occurrence matrices (GLCM) contrast (OR, 0.963) were significant predictors (p < 0.05). In a polyp >22 mm or sessile, sensitivity for differentiating carcinomas from adenomas was 93.5–95.7%. If a polyp demonstrated at least one HRUS finding and at least one texture feature, the specificity for diagnosing carcinoma was increased to 90.6–93.8%.
Conclusion
In a GB polyp >10 mm, single and diameter >14 mm were useful for predicting neoplastic polyps. In neoplastic polyps, sessile shape, diameter >22 mm, higher skewness and lower GLCM contrast were useful for predicting carcinoma.
Key Points
• Risk of neoplastic polyp is low in <14 mm and multiple polyps
• A sessile polyp or >22 mm has increased risk for GB carcinomas
• Higher skewness and lower GLCM contrast are predictors of GB carcinoma
• HRUS is useful for risk stratification of GB polyps >1 cm




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Chen CY, Lu CL, Chang FY, Lee SD (1997) Risk factors for gallbladder polyps in the Chinese population. Am J Gastroenterol 92:2066–2068
Jorgensen T, Jensen KH (1990) Polyps in the gallbladder. A prevalence study. Scand J Gastroenterol 25:281–286
Mellnick VM, Menias CO, Sandrasegaran K et al (2015) Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: disease spectrum with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 35:387–399
Bhatt NR, Gillis A, Smoothey CO, Awan FN, Ridgway PF (2016) Evidence based management of polyps of the gall bladder: a systematic review of the risk factors of malignancy. Surgeon 14:278–286
Babu BI, Dennison AR, Garcea G (2015) Management and diagnosis of gallbladder polyps: a systematic review. Langenbecks Arch Surg 400:455–462
Jang JY, Kim SW, Lee SE et al (2009) Differential diagnostic and staging accuracies of high resolution ultrasonography, endoscopic ultrasonography, and multidetector computed tomography for gallbladder polypoid lesions and gallbladder cancer. Ann Surg 250:943–949
Kim JH, Lee JY, Baek JH et al (2015) High-resolution sonography for distinguishing neoplastic gallbladder polyps and staging gallbladder cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204:W150–159
Chijiiwa K, Tanaka M (1994) Polypoid lesion of the gallbladder: indications of carcinoma and outcome after surgery for malignant polypoid lesion. Int Surg 79:106–109
Yang HL, Sun YG, Wang Z (1992) Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: diagnosis and indications for surgery. Br J Surg 79:227–229
Mainprize KS, Gould SW, Gilbert JM (2000) Surgical management of polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Br J Surg 87:414–417
Terzi C, Sokmen S, Seckin S, Albayrak L, Ugurlu M (2000) Polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: report of 100 cases with special reference to operative indications. Surgery 127:622–627
Koga A, Watanabe K, Fukuyama T, Takiguchi S, Nakayama F (1988) Diagnosis and operative indications for polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Arch Surg 123:26–29
Park HY, Oh SH, Lee KH, Lee JK, Lee KT (2015) Is cholecystectomy a reasonable treatment option for simple gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm? World J Gastroenterol 21:4248–4254
Kim JS, Lee JK, Kim Y, Lee SM (2016) US characteristics for the prediction of neoplasm in gallbladder polyps 10 mm or larger. Eur Radiol 26:1134–1140
Cho JH, Park JY, Kim YJ et al (2009) Hypoechoic foci on EUS are simple and strong predictive factors for neoplastic gallbladder polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 69:1244–1250
Joo I, Lee JY, Kim JH et al (2013) Differentiation of adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder from early-stage, wall-thickening-type gallbladder cancer using high-resolution ultrasound. Eur Radiol 23:730–738
Ganeshan B, Miles KA (2013) Quantifying tumour heterogeneity with CT. Cancer Imaging 13:140–149
Davnall F, Yip CS, Ljungqvist G et al (2012) Assessment of tumor heterogeneity: an emerging imaging tool for clinical practice? Insights Imaging 3:573–589
Holli K, Laaperi AL, Harrison L et al (2010) Characterisation of breast cancer types by texture analysis of magnetic resonance images. Acad Radiol 17:135–141
Ryu YJ, Choi SH, Park SJ, Yun TJ, Kim JH, Sohn CH (2014) Glioma: application of whole-tumor texture analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging for the evaluation of tumor heterogeneity. PLoS One 9:e108335
Chae HD, Park CM, Park SJ, Lee SM, Kim KG, Goo JM (2014) Computerised texture analysis of persistent part-solid ground-glass nodules: differentiation of preinvasive lesions from invasive pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Radiology 273:285–293
Wibmer A, Hricak H, Gondo T et al (2015) Haralick texture analysis of prostate MRI: utility for differentiating non-cancerous prostate from prostate cancer and differentiating prostate cancers with different Gleason scores. Eur Radiol 25:2840–2850
Haralick RM (1979) Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc IEEE 67:786–804
Albores-Saavedra J, Chable-Montero F, Gonzalez-Romo MA, Ramirez Jaramillo M, Henson DE (2012) Adenomas of the gallbladder. Morphologic features, expression of gastric and intestinal mucins, and incidence of high-grade dysplasia/carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. Hum Pathol 43:1506–1513
Trivedi V, Gumaste VV, Liu S, Baum J (2008) Gallbladder cancer: adenoma-carcinoma or dysplasia-carcinoma sequence? Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 4:735–737
Roa I, de Aretxabala X, Araya JC, Roa J (2006) Preneoplastic lesions in gallbladder cancer. J Surg Oncol 93:615–623
Cha BH, Hwang JH, Lee SH et al (2011) Pre-operative factors that can predict neoplastic polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. World J Gastroenterol 17:2216–2222
Sun XJ, Shi JS, Han Y, Wang JS, Ren H (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of polypoid lesions of the gallbladder: report of 194 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 3:591–594
Shinkai H, Kimura W, Muto T (1998) Surgical indications for small polypoid lesions of the gallbladder. Am J Surg 175:114–117
Park JY, Hong SP, Kim YJ et al (2009) Long-term follow up of gallbladder polyps. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:219–222
Sugiyama M, Atomi Y, Yamato T (2000) Endoscopic ultrasonography for differential diagnosis of polypoid gall bladder lesions: analysis in surgical and follow up series. Gut 46:250–254
Azuma T, Yoshikawa T, Araida T, Takasaki K (2001) Differential diagnosis of polypoid lesions of the gallbladder by endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Surg 181:65–70
Lee JS, Kim JH, Kim YJ et al (2016) Diagnostic accuracy of transabdominal high-resolution US for staging gallbladder cancer and differential diagnosis of neoplastic polyps compared with EUS. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-016-4646-2
Yuan HX, Cao JY, Kong WT, Xia HS, Wang X, Wang WP (2015) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in diagnosis of gallbladder adenoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 14:201–207
Sugimoto M, Takagi T, Konno N et al (2016) The efficacy of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography in diagnosing gallbladder cancer. Sci Rep 6:25848
Choi JH, Seo DW, Choi JH et al (2013) Utility of contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS in the diagnosis of malignant gallbladder polyps (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 78:484–493
Acknowledgements
We also thank Bonnie Hami, M.A. (USA) for her editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Joon Koo Han, M.D.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Statistics and biometry
Tae Won Choi MD has significant statistical expertise and no complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Ethical approval
Institutional review board approval was obtained (IRB No. 1608-144-787).
Informed consent
This retrospective study was approved by our institutional review board, and patient informed consent was waived.
Methodology
• Retrospective
• Diagnostic study
• Performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, T.W., Kim, J.H., Park, S.J. et al. Risk stratification of gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm using high-resolution ultrasonography and texture analysis. Eur Radiol 28, 196–205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4954-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4954-1