Abstract
Objectives
To investigate high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and pulmonary function indices (PFTs) for determining prognosis in patients with chronic fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (CHP).
Methods
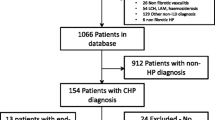
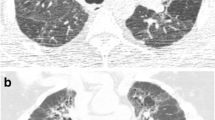
Case records, PFTs (FEV1, FVC and DLco) and HRCTs of ninety-two patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis were evaluated. HRCT studies were scored by two observers for total disease extent, ground-glass opacification, fine and coarse reticulation, microcystic and macrocystic honeycombing, centrilobular emphysema and consolidation. Traction bronchiectasis within each pattern was graded. Using Cox proportional hazards regression models the prognostic strength of individual HRCT patterns and pulmonary function test variables were determined.
Results
There were forty two deaths during the study period. Increasing severity of traction bronchiectasis was the strongest predictor of mortality (HR 1.10, P < 0.001, 95%CI 1.04-1.16). Increasing global interstitial disease extent (HR 1.02, P = 0.02, 95%CI 1.00-1.03), microcystic honeycombing (HR 1.09, P = 0.019, 95%CI 1.01-1.17) and macrocystic honeycombing (HR 1.06, P < 0.01, 95%CI 1.01-1.10) were also independent predictors of mortality. In contrast, no individual PFT variable was predictive of mortality once HRCT patterns were accounted for.
Conclusion
HRCT patterns, in particular, severity of traction bronchiectasis and extent of honeycombing are superior to pulmonary function tests for predicting mortality in patients with CHP.
Key Points
• HRCT is increasingly used to assess chronic fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
• HRCT patterns are superior to pulmonary function tests for predicting mortality.
• Extensive traction bronchiectasis strongly predicts poor survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourke SJ, Dalphin JC, Boyd G, McSharry C, Baldwin CI, and Calvert JE (2001) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts. Eur Respir J Suppl 81 s–92 s
Coleman A, Colby TV (1988) Histologic diagnosis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Am J Surg Pathol 7:514–518
Reyes CN, Wenzel FJ, Lawton BR, Emanuel DA (1982) The pulmonary pathology of farmer’s lung disease. Chest 2:142–146
Barrios RJ (2008) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: histopathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2:199–203
Selman M (1998) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In: KTJ Schwartz MI (eds) Interstitial lung disease, Decker Inc. p 394–442
Ando M, Suga M, Kohrogi H (1999) A new look at hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 5:299–304
Churg A, Sin DD, Everett D, Brown K, Cool C (2009) Pathologic patterns and survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Surg Pathol 12:1765–1770
Trahan S, Hanak V, Ryu JH, Myers JL (2008) Role of surgical lung biopsy in separating chronic hypersensitivity pneumonia from usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: analysis of 31 biopsies from 15 patients. Chest 1:126–132
Ohtani Y, Saiki S, Kitaichi M et al (2005) Chronic bird fancier’s lung: histopathological and clinical correlation. An application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Thorax 8:665–671
Lynch DA, Godwin JD, Safrin S et al (2005) High-resolution computed tomography in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and prognosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 4:488–493
Mogulkoc N, Brutsche MH, Bishop PW, Greaves SM, Horrocks AW, Egan JJ (2001) Pulmonary function in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and referral for lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1:103–108
Sumikawa H, Johkoh T, Colby TV et al (2008) Computed tomography findings in pathological usual interstitial pneumonia: relationship to survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 4:433–439
Edey AJ, Devaraj AA, Barker RP, Nicholson AG, Wells AU, Hansell DM (2011) Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: HRCT findings that predict mortality. Eur Radiol 21:1586–1593
Hanak V, Golbin JM, Hartman TE, Ryu JH (2008) High-resolution CT findings of parenchymal fibrosis correlate with prognosis in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 1:133–138
Sahin H, Brown KK, Curran-Everett D et al (2007) Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: CT features comparison with pathologic evidence of fibrosis and survival. Radiology 2:591–598
Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U et al (2003) Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 8:952–958
Lynch DA, Newell JD, Logan PM, King TE Jr, Muller NL (1995) Can CT distinguish hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? AJR Am J Roentgenol 4:807–811
Adler BD, Padley SP, Muller NL, Remy-Jardin M, Remy J (1992) Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: high-resolution CT and radiographic features in 16 patients. Radiology 1:91–95
(1990) Bronchoalveolar lavage constituents in healthy individuals, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and selected comparison groups. The BAL Cooperative Group Steering Committee. Am Rev Respir Dis 5 Pt 2:S169–202
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 3:697–722
Brennan P, Silman A (1992) Statistical methods for assessing observer variability in clinical measures. BMJ 6840:1491–1494
Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Cherniack RM et al (2004) The effect of pulmonary fibrosis on survival in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Med 10:662–668
Flaherty KR, Mumford JA, Murray S et al (2003) Prognostic implications of physiologic and radiographic changes in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 5:543–548
Collard HR, King TE Jr, Bartelson BB, Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Brown KK (2003) Changes in clinical and physiologic variables predict survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 5:538–542
Latsi PI, du Bois RM, Nicholson AG et al (2003) Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: the prognostic value of longitudinal functional trends. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 5:531–537
Silva CI, Churg A, Muller NL (2007) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: spectrum of high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2:334–344
Silva CI, Muller NL, Lynch DA et al (2008) Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: differentiation from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia by using thin-section CT. Radiology 1:288–297
Nadrous HF, Pellikka PA, Krowka MJ et al (2005) Pulmonary hypertension in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 4:2393–2399
Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M et al (2009) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 20:2493–2537
Hamada K, Nagai S, Tanaka S et al (2007) Significance of pulmonary arterial pressure and diffusion capacity of the lung as prognosticator in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 3:650–656
Nadrous HF, Pellikka PA, Krowka MJ et al (2005) The impact of pulmonary hypertension on survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 6 Suppl:616S–617S
Lettieri CJ, Nathan SD, Barnett SD, Ahmad S, Shorr AF (2006) Prevalence and outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 3:746–752
Costabel U, Matthys H, Ruehle KH (1982) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA). Am Rev Respir Dis 1:184
Lupi-Herrera E, Sandoval J, Bialostozky D et al (1981) Extrinsic allergic alveolitis caused by pigeon breeding at a high altitude (2,240 meters). Hemodynamic behavior of pulmonary circulation. Am Rev Respir Dis 5:602–607
Koschel DS, Kolditz M, Hoeffken G, Halank M (2010) Combined vasomodulatory therapy for severe pulmonary hypertension in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Med Sci Monit 5:CS55–CS57
Edey AJ, Devaraj AA, Barker RP, Nicholson AG, Wells AU, Hansell DM (2011) Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: HRCT findings that predict mortality. Eur Radiol 8:1586–1593
(2002) American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2:277–304
Flaherty KR, King TE Jr, Raghu G et al (2004) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: what is the effect of a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 8:904–910
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walsh, S.L.F., Sverzellati, N., Devaraj, A. et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: high resolution computed tomography patterns and pulmonary function indices as prognostic determinants. Eur Radiol 22, 1672–1679 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2427-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2427-0