Abstract
Objective
To investigate dual-energy CT of hypervascular liver lesions in patients with HCC.
Methods
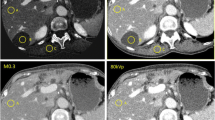
Forty patients with hepatocellular carcinomas were investigated with abdominal dual-energy CT. In each patient unenhanced and contrast-enhanced imaging with arterial und portovenous delay were performed. Hypervascular lesions were documented on arterial phase 80-kVp images, 140-kVp images, and the averaged arterial images by two radiologists. Subjective image quality (5-point scale, from 5 [excellent] to 1 [not interpretable]) was rated on all images.
Results
The mean number of hypervascular HCC lesions detected was 3.37 ± 1.28 on 80-kVp images (p < 0.05), 1.43 ± 1.13 on 140-kVp images (p < 0.05), and 2.57 ± 1.2 on averaged images. The image quality was 0.3 ± 0.5 for 80-kVp (p < 0.05), 1.6 ± 0.5 for 140-kVp (p < 0.05) and 3.2 ± 0.4 for the averaged images.
Conclusion
Low-kVp images of dual-energy datasets are more sensitive in detecting hypervascular liver lesions. However, this increase in sensitivity goes along with a decrease in the subjective image quality of low-kVp images.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flohr TG, Mccollough CH, Bruder H et al (2006) First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol 16:256–268
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M et al (2007) Material differentiation by dual energy CT: initial experience. Eur Radiol 17:1510–1517
Scheffel H, Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T et al (2007) Dual-energy contrast-enhanced computed tomography for the detection of urinary stone disease. Invest Radiol 42:823–829
Graser A, Johnson TR, Chandarana H et al (2009) Dual energy CT: preliminary observations and potential clinical applications in the abdomen. Eur Radiol 19:13–23
Baron RL, Oliver JH 3rd, Dodd GD 3rd et al (1996) Hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation with biphasic, contrast-enhanced, helical CT. Radiology 199:505–511
Oliver JH 3rd, Baron RL (1996) Helical biphasic contrast-enhanced CT of the liver: technique, indications, interpretation, and pitfalls. Radiology 201:1–14
Oliver JH 3rd, Baron RL, Federle MP et al (1996) Detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: value of unenhanced or arterial phase CT imaging or both used in conjunction with conventional portal venous phase contrast-enhanced CT imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167:71–77
Ohashi I, Hanafusa K, Yoshida T (1993) Small hepatocellular carcinomas: two-phase dynamic incremental CT in detection and evaluation. Radiology 189:851–855
Hollett MD, Jeffrey RB Jr, Nino-Murcia M et al (1995) Dual-phase helical CT of the liver: value of arterial phase scans in the detection of small (< or = 1.5 cm) malignant hepatic neoplasms. AJR Am J Roentgenol 164:879–884
Oliver JH 3rd, Baron RL, Federle MP et al (1997) Hypervascular liver metastases: do unenhanced and hepatic arterial phase CT images affect tumor detection? Radiology 205:709–715
Paulson EK, Mcdermott VG, Keogan MT et al (1998) Carcinoid metastases to the liver: role of triple-phase helical CT. Radiology 206:143–150
Huda W (2002) Dose and image quality in CT. Pediatr Radiol 32:709–713, discussion 751-704
Kalva SP, Sahani DV, Hahn PF et al (2006) Using the K-edge to improve contrast conspicuity and to lower radiation dose with a 16-MDCT: a phantom and human study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:391–397
Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Hahn PF et al (2007) 16-MDCT angiography in living kidney donors at various tube potentials: impact on image quality and radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:115–120
Schueller-Weidekamm C, Schaefer-Prokop CM, Weber M et al (2006) CT angiography of pulmonary arteries to detect pulmonary embolism: improvement of vascular enhancement with low kilovoltage settings. Radiology 241:899–907
Heyer CM, Mohr PS, Lemburg SP et al (2007) Image quality and radiation exposure at pulmonary CT angiography with 100- or 120-kVp protocol: prospective randomized study. Radiology 245:577–583
Sigal-Cinqualbre AB, Hennequin R, Abada HT et al (2004) Low-kilovoltage multi-detector row chest CT in adults: feasibility and effect on image quality and iodine dose. Radiology 231:169–174
Waaijer A, Prokop M, Velthuis BK et al (2007) Circle of Willis at CT angiography: dose reduction and image quality–reducing tube voltage and increasing tube current settings. Radiology 242:832–839
Graser A, Wintersperger BJ, Suess C et al (2006) Dose reduction and image quality in MDCT colonography using tube current modulation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:695–701
Bongartz G, Golding SJ, Jurik AG, European, Computed Gfm, Tomography et al (2004) European guidelines for multislice computed tomography. European Commission, Brussels
Chandarana H, Godoy MC, Vlahos I et al (2008) Abdominal aorta: evaluation with dual-source dual-energy multidetector CT after endovascular repair of aneurysms—initial observations. Radiology 249:692–700
Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T, Pfammatter T et al (2008) Endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: detection with dual-energy dual-source CT. Radiology 249:682–691
Nakayama Y, Awai K, Funama Y et al (2005) Abdominal CT with low tube voltage: preliminary observations about radiation dose, contrast enhancement, image quality, and noise. Radiology 237:945–951
Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E et al (2001) Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:289–296
Avrin DE, Macovski A, Zatz LE (1978) Clinical application of Compton and photo-electric reconstruction in computed tomography: preliminary results. Invest Radiol 13:217–222
Graser A, Johnson TR, Hecht EM et al (2009) Dual-energy CT in patients suspected of having renal masses: can virtual nonenhanced images replace true nonenhanced images? Radiology
Chae EJ, Song JW, Seo JB et al (2008) Clinical utility of dual-energy CT in the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules: initial experience. Radiology 249:671–681
Kalra MK, Maher MM, Blake MA et al (2004) Detection and characterization of lesions on low-radiation-dose abdominal CT images postprocessed with noise reduction filters. Radiology 232:791–797
Kalra MK, Maher MM, Sahani DV et al (2003) Low-dose CT of the abdomen: evaluation of image improvement with use of noise reduction filters pilot study. Radiology 228:251–256
Kalra MK, Wittram C, Maher MM et al (2003) Can noise reduction filters improve low-radiation-dose chest CT images? Pilot study. Radiology 228:257–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altenbernd, J., Heusner, T.A., Ringelstein, A. et al. Dual-energy-CT of hypervascular liver lesions in patients with HCC: investigation of image quality and sensitivity. Eur Radiol 21, 738–743 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1964-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1964-7