Abstract
Key message
Heterologous expression of VaMYB44 gene in Arabidopsis and V. vinifera cv. ‘Thompson Seedless’ increases cold sensitivity, which is mediated by the interaction of VaMYC2 and VaTIFY5A with VaMYB44
MYB transcription factors play critical roles in plant stress response. However, the function of MYB44 under low temperature stress is largely unknown in grapes. Here, we isolated a VaMYB44 gene from Chinese wild Vitis amurensis acc. ‘Shuangyou’ (cold-resistant). The VaMYB44 is expressed in various organs and has lower expression levels in stems and young leaves. Exposure of the cold-sensitive V. vinifera cv. ‘Thompson Seedless’ and cold-resistant ‘Shuangyou’ grapevines to cold stress (−1 °C) resulted in differential expression of MYB44 in leaves with the former reaching 14 folds of the latter after 3 h of cold stress. Moreover, the expression of VaMYB44 was induced by exogenous ethylene, abscisic acid, and methyl jasmonate in the leaves of ‘Shuangyou’. Notably, the subcellular localization assay identified VaMYB44 in the nucleus. Interestingly, heterologous expression of VaMYB44 in Arabidopsis and ‘Thompson Seedless’ grape increased freezing-induced damage compared to their wild-type counterparts. Accordingly, the transgenic lines had higher malondialdehyde content and electrolyte permeability, and lower activities of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase. Moreover, the expression levels of some cold resistance-related genes decreased in transgenic lines. Protein interaction assays identified VaMYC2 and VaTIFY5A as VaMYB44 interacting proteins, and VaMYC2 could bind to the VaMYB44 promoter and promote its transcription. In conclusion, the study reveals VaMYB44 as the negative regulator of cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis and transgenic grapes, and VaMYC2 and VaTIFY5A are involved in the cold sensitivity of plants by interacting with VaMYB44.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin B, Atif MJ, Meng H, Ghani MI, Ali M, Wang X, Cheng Z (2022) Biochemical and physiological responses of Cucumis sativus cultivars to different combinations of low-temperature and high humidity. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10556-3
An D, Ma Q, Wang H, Yang J, Zhou W, Zhang P (2017) Cassava C-repeat binding factor 1 gene responds to low temperature and enhances cold tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis and cassava. Plant Mol Biol 94:109–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-017-0596-6
An JP, Li R, Qu FJ, You X, Wang XF, Hao YJ (2018) R2R3-MYB transcription factor MdMYB23 is involved in the cold tolerance and proanthocyanidin accumulation in apple. Plant J 96:562577. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14050
Araz O, Ekinci M, Yuce M, Shams M, Agar G, Yildirim E (2022) Low-temperature modified DNA methylation level, genome template stability, enzyme activity, and proline content in pepper (Capsicum annuum L) genotypes. Sci Hortic 294:110761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110761
Bagni N, Tassoni A (2001) Biosynthesis, oxidation and conjugation of aliphatic polyamines in higher plants. Amino Acids 20:301–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170046
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00018060
Burnette WN (1981) “Western blotting”: electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein. Anal Biochem 112:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5
Campos PS, Quartin V, Ramalho CJ, Nunes MA (2003) Electrolyte leakage and lipid degradation account for cold sensitivity in leaves of Coffea sp. plants. J Plant Physio 160:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00833
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol 2:764–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(55)02300-8
Chen JR, Lü JJ, Liu R, Xiong XY, Wang TX, Chen SY, Guo LB, Wang HF (2010) DREB1C from Medicago truncatula enhances freezing tolerance in transgenic M. truncatula and China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.). Plant Growth Regul 60:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9434-4
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK (2007) Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.07.002
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Dai ZN, Dong SY, Miao H, Liu XP, Han JN, Li CX, Gu XF, Zhang SP (2022) Genome-wide identification of TIFY genes and their response to various pathogen infections in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Sci Hortic 295:110814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110814
Das K, Roychoudhury A (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2:53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053
Ding YL, Li H, Zhang XY, Xie Q, Gong ZZ, Yang SH (2015) OST1 kinase modulates freezing tolerance by enhancing ICE1 stability in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 32:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.12.023
Ding YL, Shi YT, Yang SH (2019) Advances and challenges in uncovering cold tolerance regulatory mechanisms in plants. New Phytol 222:1690–1704. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15696
Ding F, Wang C, Xu N, Wang ML, Zhang SX (2021) Jasmonic acid-regulated putrescine biosynthesis attenuates cold-induced oxidative stress in tomato plants. Sci Hortic 288:110373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110373
Du H, Zhang L, Liu L, Tang XF, Yang WJ, Wu YM, Huang YB, Tang YX (2009) Biochemical and molecular characterization of plant MYB transcription factor family. Biochemistry Biokhimiia 74:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006297909010015
Eremina M, Rozhon W, Poppenberger B (2016) Hormonal control of cold stress responses in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:797–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2089-6
Fan YX, Peng JY, Wu JC, Zhou P, He RJ, Allan AC, Zeng LH (2021) NtbHLH1, a JAF13-like bHLH, interacts with NtMYB6 to enhance proanthocyanidin accumulation in Chinese Narcissus. BMC Plant Boil 21:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03050-1
Feller A, Machemer K, Braun EL, Grotewold E (2011) Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J 66:94–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04459.x
Fu JJ, Sun PY, Luo YL, Zhou HY, Gao JZ, Zhao D, Pubu ZM, Liu JL, Hu TM (2019) Brassinosteroids enhance cold tolerance in Elymus nutans via mediating redox homeostasis and proline biosynthesis. Environ Exp Bot 167:103831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.103831
Gao F, Yao HP, Zhao HX, Zhou J, Luo XP, Huang YJ, Li CL, Chen H (2016) Tartary buckwheat FtMYB10 encodes an R2R3-MYB transcription factor that acts as a novel negative regulator of salt and drought response in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 109:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.10.022
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase I. occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.59.2.309
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Goossens J, Mertens J, Goossens A (2017) Role and functioning of bHLH transcription factors in jasmonate signalling. J Exp Bot 68:1333–1347. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw440
Gu B, Zhang B, Ding L, Li PY, Shen L, Zhang JX (2020) Physiological change and transcriptome analysis of Chinese wild Vitis amurensis and Vitis vinifera in response to cold stress. Plant Mol Biol Rep 38:478–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01210-5
Guo XY, Liu DF, Chong K (2018) Cold signaling in plants: insights into mechanisms and regulation. J Integr Plant Biol 60:745–756. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12706
Hao Y, Wang J, Hu C, Zhou Q, Mubeen HM, Hou X (2022) Regulation of BcMYB44 on Anthocyanin Synthesis and Drought Tolerance in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino). Horticulturae. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050351
He Y, Li M, Wang Y, Shen S (2022) The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB44 modulates carotenoid biosynthesis in Ulva prolifera. Algal Res 62:102578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102578
Heidari P, Faraji S, Ahmadizadeh M, Ahmar S, Mora-Poblete F (2021) New insights into structure and function of TIFY genes in Zea mays and Solanum lycopersicum: a genome-wide comprehensive analysis. Front Genet 12:534. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.657970
Heidarvand L, Amiri RM (2010) What happens in plant molecular responses to cold stress? Acta Physiol Plant 32:419–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0451-8
Huang YJ, Zhao HX, Gao F, Yao PF, Deng RY, Li CL, Chen H, Wu Q (2018) A R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene, FtMYB13, from Tartary buckwheat improves salt/drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 727:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.09.012
Huang X, Chen MH, Yang LT, Li YR, Wu JM (2015) Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on cell membrane and endogenous hormone contents in leaves of sugarcane seedlings under cold stress. Sugar Tech 17:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-014-0343-0
Huang XB, Shi HY, Hu ZR, Liu A, Amombo E, Chen L, Fu JM (2017) ABA is involved in regulation of cold stress response in bermudagrass. Front Plant Sci 8:1613. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01613
Jaglo-Ottosen KR, Gilmour SJ, Zarka DG, Schabenberger O, Thomashow MF (1998) Arabidopsis CBF1 overexpression induces COR genes and enhances freezing tolerance. Science 280:104–106. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5360.104
Jia DJ, Wu P, Shen F, Li W, Zheng XD, Wang YZ, Yuan YB, Zhang XZ, Han ZH (2021) Genetic variation in the promoter of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor determines fruit malate content in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol 186:549–568. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab098
Jung C, Seo JS, Han SW, Koo YJ, Kim CH, Song SI, Nahm BH, Choi YD, Cheong JJ (2008) Overexpression of AtMYB44 enhances stomatal closure to confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:623–635. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.110981
Kagale S, Rozwadowski K (2011) EAR motif-mediated transcriptional repression in plants: an underlying mechanism for epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Epigenetics 6:141–146. https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.2.13627
Karuppanapandian T, Moon JC, Kim C, Manoharan K, Kim W (2011) Reactive oxygen species in plants: their generation, signal transduction, and scavenging mechanisms. Aust J Crop Sci 5:709–725
Kou S, Chen L, Tu W, Scossa F, Wang YM, Liu J, Fernie AR, Song BT, Xie CH (2018) The arginine decarboxylase gene ADC1, associated to the putrescine pathway, plays an important role in potato cold-acclimated freezing tolerance as revealed by transcriptome and metabolome analyses. Plant J 96:1283–1298. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14126
Kranz HD, Denekamp M, Greco R, Jin H, Leyva A, Meissner RC, Petroni K, Urzainqui A, Bevan M, Martin C (1998) Towards functional characterisation of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00278.x
Kumar V, Yadav SK (2009) Proline and betaine provide protection to antioxidant and methylglyoxal detoxification systems during cold stress in Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze Acta Physiol Plant 31:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-008-0227-6
Leng P, Zhang GL, Li XX, Wang LH, Zheng ZM (2009) Cloning of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED) gene encoding a key enzyme during abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis and ABA-regulated ethylene production in detached young persimmon calyx. Sci Bull 54:2830–2838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0685-2
Li JB, Zhao S, Yu X, Du W, Li H, Sun Y, Sun H, Ruan CJ (2021a) Role of Xanthoceras sorbifolium MYB44 in tolerance to combined drought and heat stress via modulation of stomatal closure and ROS homeostasis. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.03.007
Li H, Guo Y, Lan Z, Xu K, Chang J, Ahammed GJ, Ma JX, Wei CH, Zhang X (2021b) Methyl jasmonate mediates melatonin-induced cold tolerance of grafted watermelon plants. Hort Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-021-00496-0
Li LX, Wei ZZ, Zhou ZL, Zhao DL, Tang J, Yang F, Li YH, Chen XY, Han Z, Yao GF, Hu KD, Zhang H (2021c) A single amino acid mutant in the EAR motif of IbMYB44.2 reduced the inhibition of anthocyanin accumulation in the purple-fleshed sweetpotato. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.08.012
Li M, Wang CH, Shi JL, Zhang YJ, Liu T, Qi HY (2021d) Abscisic acid and putrescine synergistically regulate the cold tolerance of melon seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 166:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.011
Li PY, Yu DD, Gu B, Zhang HJ, Liu QY, Zhang JX (2022) Overexpression of the VaERD15 gene increases cold tolerance in transgenic grapevine. Sci Hortic 293:110728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110728
Li XR, Tang Y, Li HL, Luo W, Zhou CJ, Zhang LX, Lv JY (2020) A wheat R2R3 MYB gene TaMpc1-D4 negatively regulates drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis and wheat. Plant Sci 299:110613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110613
Lin Q, Xie Y, Guan W, Duan Y, Wang Z, Sun C (2019) Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of cold stress induced sugar accumulation and heat shock proteins expression during postharvest potato tuber storage. Food Chem 297:124991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124991
Liu H, Zhou Y, Li H, Wang T, Zhang J, Ouyang B, Ye Z (2018a) Molecular and functional characterization of ShNAC1, an NAC transcription factor from Solanum habrochaites. Plant Sci 271:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.03.005
Liu JY, Shi YT, Yang SH (2018b) Insights into the regulation of C-repeat binding factors in plant cold signalling. J Integr Plant Biol 60:780–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12657
Liu R, Chen L, Jia Z, Lü B, Shi H, Shao W, Dong H (2011) Transcription factor AtMYB44 regulates induced expression of the ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE2 gene in Arabidopsis responding to a harpin protein. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1094/mpmi-07-10-0170
Lv Y, Yang M, Hu D, Yang ZY, Ma SQ, Li XH, Xiong LZ (2017) The OsMYB30 transcription factor suppresses cold tolerance by interacting with a JAZ protein and suppressing β-amylase expression. Plant Physiol 173:1475–1491. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01725
Matsui A, Ishida J, Morosawa T, Mochizuki Y, Kaminuma E, Endo TA, Okamoto M, Nambara E, Nakajima M, Kawashima M (2008) Arabidopsis transcriptome analysis under drought, cold, high-salinity and ABA treatment conditions using a tiling array. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1135–1149. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcn101
Mehrotra S, Verma S, Kumar S, Kumari S, Mishra BN (2020) Transcriptional regulation and signalling of cold stress response in plants: an overview of current understanding. Environ Exp Bot 180:104243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104243
Ming RH, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Khan MDH, Dahro B, Liu JH (2021) The JA-responsive MYC2-BADH-like transcriptional regulatory module in Poncirus trifoliata contributes to cold tolerance by modulation of glycine betaine biosynthesis. The New Phytol 229:2730–2750. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17063
Misener SR, Chen CP, Walker VK (2001) Cold tolerance and proline metabolic gene expression in drosophila melanogaster. J Insect Physiol 47:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1910(00)00141-4
Moeder W, Ung H, Mosher S, Yoshioka K (2010) SA-ABA antagonism in defense responses. Plant Signal Behav 5:1231–1233. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.10.12836
Nguyen XC, Hoang MH, Kim HS, Lee K, Liu XM, Kim SH, Bahk S, Park HC, Chung WS (2012) Phosphorylation of the transcriptional regulator MYB44 by mitogen activated protein kinase regulates Arabidopsis seed germination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423:703–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.019
Persak H, Pitzschke A (2014) Dominant repression by Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 causes oxidative damage and hypersensitivity to abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 15:2517–2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15022517
Qiu ZK, Yan SS, Xia B, Jiang J, Yu BW, Lei JJ, Chen CM, Chen L, Yang Y, Wang YQ (2019) The eggplant transcription factor MYB44 enhances resistance to bacterial wilt by activating the expression of spermidine synthase. J Exp Bot 70:5343–5354. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz259
Rao XY, Huang XL, Zhou ZC, Lin X (2013) An improvement of the 2ˆ(–delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat Bioinforma Biomath 3:71–85
Shamloo-Dashtpagerdi R, Razi H, Ebrahimie E, Niazi A (2018) Molecular characterization of Brassica napus stress related transcription factors, BnMYB44 and BnVIP1, selected based on comparative analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana and Eutrema salsugineum transcriptomes. Mol Biol Rep 45:1111–1124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4262-0
Shi YT, Ding YL, Yang SH (2015) Cold signal transduction and its interplay with phytohormones during cold acclimation. Plant Cell Physiol 56:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu115
Shi YT, Ding YL, Yang SH (2018) Molecular regulation of CBF signaling in cold acclimation. Trends Plant Sci 23:623–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.002
Shim JS, Choi YD (2013) Direct regulation of WRKY70 by AtMYB44 in plant defense responses. Plant Signal Behav 8:e20783. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.24509
Shin LJ, Lo JC, Yeh KC (2012) Copper chaperone antioxidant protein1 is essential for copper homeostasis. Plant Physiol 159:1099–1110. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.195974
Shu X, Ding L, Gu B, Zhang HJ, Guan PY, Zhang JX (2021) A stress associated protein from Chinese wild Vitis amurensis, VaSAP15, enhances the cold tolerance of transgenic grapes. Sci Hortic 285:110147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110147
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00199-0
Sun X, Wang Y, Sui N (2018) Transcriptional regulation of bHLH during plant response to stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:397–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.123
Tamás L, Huttová J, Žigová Z (1997) Accumulation of stress-proteins in intercellular spaces of barley leaves induced by biotic and abiotic factors. Biol Plant 39:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1001028226434
Thomashow MF (2010) Molecular basis of plant cold acclimation: insights gained from studying the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Physiol 154:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.161794
Vanholme B, Grunewald W, Bateman A, Kohchi TKY, Gheysen G (2007) The tify family previously known as ZIM. Trends Plant Sci 12:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.004
Verma D, Jalmi SK, Bhagat PK, Verma N, Sinha AK (2020) A bHLH transcription factor, MYC2, imparts salt intolerance by regulating proline biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. FEBS J 287:2560–2576. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15157
Vogel JT, Zarka DG, Van Buskirk HA, Fowler SG, Thomashow MF (2005) Roles of the CBF2 and ZAT12 transcription factors in configuring the low temperature transcriptome of Arabidopsis. Plant J 41:195–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02288.x
Wan YZ, Schwaninger HR, Li D, Simon CJ, Wang YJ, He PC (2008) The eco-geographic distribution of wild grape germplasm in China. Vitis 47:77
Wang W, Vignani R, Scali M, Cresti M (2006) A universal and rapid protocol for protein extraction from recalcitrant plant tissues for proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis 27:2782–2786. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500722
Wang J, Sun PP, Chen CL, Wang Y, Fu XZ, Liu JH (2011) An arginine decarboxylase gene PtADC from Poncirus trifoliata confers abiotic stress tolerance and promotes primary root growth in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 62:2899–2914. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq463
Wang D, Jiang C, Liu W, Wang Y (2020) The WRKY53 transcription factor enhances stilbene synthesis and disease resistance by interacting with MYB14 and MYB15 in Chinese wild grape. J Exp Bot 71:3211–3226. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa097
Wang SS, Shi MY, Zhang Y, Xie XB, Sun PP, Fang CB, Zhao J (2021a) FvMYB24, a strawberry R2R3-MYB transcription factor, improved salt stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 569:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.06.085
Wang Y, Jiang H, Mao Z, Liu W, Jiang S, Xu H, Chen X (2021b) Ethylene increases the cold tolerance of apple via the MdERF1B-MdCIbHLH1 regulatory module. Plant J 106:379–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15170
Wani SH, Kumar V, Shriram V, Sah SK (2016) Phytohormones and their metabolic engineering for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Crop J 4:162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2016.01.010
Wei LZ, Mao WW, Jia MR, Xing SN, Ali U, Zhao Y, Chen YT, Cao ML, Dai ZR, Zhang K, Dou ZC, Jia WS, Li B (2018) FaMYB44.2, a transcriptional repressor, negatively regulates sucrose accumulation in strawberry receptacles through interplay with FaMYB10. J Exp Bot 69:4805–4820. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery249
Wei ZZ, Hu KD, Zhao DL, TangJ HZQ, Jin P, Li YH, Han Z, Hu LY, Yao GF, Zhang H (2020) MYB44 competitively inhibits the formation of the MYB340-bHLH2-NAC56 complex to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple-fleshed sweet potato. BMC Plant Biol 20:258. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02451-y
Wu RG, Wang Y, Wu T, Xu XF, Han ZH (2018) Functional characterisation of MdMYB44 as a negative regulator in the response to cold and salt stress in apple calli. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 93:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2017.1373038
Yang Y, Ahammed GJ, Wan C, Liu H, Chen R, Zhou Y (2019) Comprehensive analysis of TIFY transcription factors and their expression profiles under jasmonic acid and abiotic stresses in watermelon. Int J Genomics 2019:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6813086
Yang ZZ, Li YQ, Gao FZ, Jin W, Li SY, Kimani S, Yang S, Bao T, Gao X, Wang L (2020) MYB21 interacts with MYC2 to control the expression of terpene synthase genes in flowers of Freesia hybrida and Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 71:4140–4158. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa184
Yang GH, Chen YX, Yu H, Zhang H, Han DG, Guo XY, Yan EQ, Quan H, Li T (2021) Raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) NCED1 gene enhances high salinity and cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. In Vitro Cell Dev-Pl 57:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-021-10230-z
Yao PF, Sun ZX, Li CL, Zhao XR, Li MF, Deng RY, Huang YJ, Zhao HX, Chen H, Wu Q (2018) Overexpression of Fagopyrum tataricum FtbHLH2 enhances tolerance to cold stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 125:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.01.028
Yin Y, Ma QP, Zhu ZX, Cui QY, Chen CS, Chen X, Fang WP, Li XH (2016) Functional analysis of CsCBF3 transcription factor in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) under cold stress. Plant Growth Regul 80:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-016-0172-0
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2:1565–1572. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.199
Yu DD, Zhang LH, Zhao K, Niu RX, Zhai H, Zhang JX (2017) VaERD15, a transcription factor gene associated with cold-tolerance in Chinese wild Vitis amurensis. Front Plant Sci 8:297. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00297
Zhai H, Bai X, Zhu Y, Li Y, Cai H, Ji W, Ji Z, Liu X, Liu X, Li J (2010) A single-repeat R3-MYB transcription factor MYBC1 negatively regulates freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:1018–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.114
Zhang JZ, Creelman RA, Zhu JK (2004) From laboratory to field. Using information from Arabidopsis to engineer salt, cold, and drought tolerance in crops. Plant Physiol 135:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.040295
Zhang XY, Liang C, Wang GP, Luo Y, Wang W (2010) The protection of wheat plasma membrane under cold stress by glycine betaine overproduction. Biol Plant 54:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-010-0012-4
Zhang J, Wu X, Niu R, Liu Y, Liu N, Xu W, Wang Y (2012) Cold-resistance evaluation in 25 wild grape species. Vitis 51:153–160
Zhang CY, Liu HC, Zhang XS, Guo QX, Bian SM, Wang JY, Zhai LL (2020a) VcMYB4a, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor from Vaccinium corymbosum, negatively regulates salt, drought, and temperature stress. Gene 757:144935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144935
Zhang P, Wang RL, Yang XP, Ju Q, Li WQ, Lü S, Tran LSP, Xu J (2020b) The R2R3−MYB transcription factor AtMYB49 modulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis by modulating the cuticle formation and antioxidant defence. Plant Cell Environ 43:1925–1943. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13784
Zhang XY, Ma MJ, Ye B, Liu L, Ji SJ (2021) Calcium ion improves cold resistance of green peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) by regulating the activity of protective enzymes and membrane lipid composition. Sci Hortic 277:109789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109789
Zhao YH, Yang YP, Jiang JW, Zhang XM, Ma ZW, Meng LD, Cui GW, Yin XJ (2022) The caucasian clover gene TaMYC2 responds to abiotic stress and improves tolerance by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Genes 13:329. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020329
Zhou L, Yarra R, Yang Y, Liu Y, Yang M, Cao H (2022) The oil palm R2R3-MYB subfamily genes EgMYB111 and EgMYB157 improve multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Rep 41:377–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02814-1
Funding
This study was supported by the National Science-Technology Support Plan Projects of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China [grant number 2013BAD02B04-06] and the Shaanxi Province Key Project-Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China [Grant number 2017ZDXM-NY-026].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZJX designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. ZHJ performed experiments and wrote the manuscript. HYF participated in the determination of physiological-biochemical indicators. GB cloned the VaMYB44 gene. CXY participated in the revision of the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the contents of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Kinya Toriyama.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2022_2883_MOESM1_ESM.docx
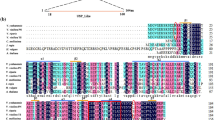
Fig. S1 Identification of transgenic Arabidopsis. a qRT-PCR analysis of VaMYB44 expression in transgenic Arabidopsis lines, with wild-type (WT) used as a negative control. Error bars refer to ± SE (n = 3). Significance was analyzed by the method of Least Significant Difference (LSD) (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) with SPSS software. b Western blot analysis of VaMYB44-GFP protein expression in transgenic lines OE1#, OE2#, and OE5#; WT was used as the control. Fig. S2 Generation and identification of transgenic ‘Thompson Seedless’ grapes. a Generation of transgenic ‘Thompson Seedless’ grapes. Unorganized callus (I); Transgenic dark-brown callus (II); Resistance screening (III); Induction of differentiation (IV); Rooting into seedlings (V); Refinement of seedlings for transplanting (VI − VII). b qRT-PCR assay for VaMYB44 overexpression in cold-resistant ‘Thompson Seedless’ grape seedlings. Error bars refer to ± SE (n = 3). Significance was analyzed by the method of Least Significant Difference (LSD) (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) with SPSS software. c Western blot detection of VaMYB44 overexpression in ‘Thompson Seedless’ grape seedlings. Fig. S3 Conserved domain of VaMYC2. Fig. S4 Sequence alignment of MdMYB44 and VaMYB44. Supplementary file1 (DOCX 1459 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Hu, Y., Gu, B. et al. VaMYB44 transcription factor from Chinese wild Vitis amurensis negatively regulates cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and V. vinifera. Plant Cell Rep 41, 1673–1691 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02883-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02883-w