Abstract
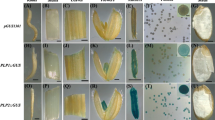
SBgLR (Solanum tuberosum genomic lysine-rich) is a pollen-specific gene cloned from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). The region from −269 to −9 (The A of translation start site “ATG” as +1) of the SBgLR promoter was identified as critical for gene specific expression in pollen grains. Sequence analysis indicates a palindromic sequence “TTTCTATTATAATAGAAA” in the −227 to −209 region, in which two pollen-specific motifs TTTCT and AGAAA surround a unique putative TATA box. Moreover, nine putative pollen-specific motifs are located in the region between the TATA box and ATG. We placed the −227 to −9 region (reserving the palindrome) and the −222 to −9 region (breaking the palindrome) downstream of the CaMV35S enhancer, respectively, to construct two fusion promoters. Histochemical assays in transgenic plants demonstrated that the region from −222 to −9 is necessary and sufficient for pollen-specific expression of the uidA gene. However, the region of −227 to −9 is incapable of driving GUS expression in pollen grains and parts of vegetative tissues. A series of 5′ deletions from −269 to −9 of SBgLR promoter were constructed. A transient expression assay indicated that the region from the −227 to −9 suppressed gfp gene expression in pollen, and a positive regulatory element was present in the region of −253 to −227. The function of the palindromic sequence as a repressor inhibiting gene expression in pollen was further confirmed by the mutated promoter, breaking the palindrome by substituting its 3′-flanking five base pairs, which resumes the reporter gene expression in mature pollen.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bate N, Twell D (1998) Functional architecture of a late pollen promoter: pollen-specific transcription is developmentally regulated by multiple stage-specific and co-dependent activator elements. Plant Mol Biol 37:859–869
Benfey PN, Chua N-H (1990) The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter: combinatorial regulation of transcription in plants. Science 250:959–966
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Dimova DK, Dyson NJ (2005) The E2F transcriptional network: old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 24:2810–2826
Eyal Y, Curie C, McCormick S (1995) Pollen specificity elements reside in 30 bp of the proximal promoters of two pollen-expressed genes. Plant Cell 7:373–384
Filichkin SA, Leonard JM, Monteros A, Liu PP, Nonogaki H (2004) A novel endo-β-mannanase gene in tomato LeMAN5 is associated with anther and pollen development. Plant Physiol 134:1080–1087
Hamilton DA, Schwarz YH, Mascarenhas JP (1998) A monocot pollen-specific promoter contains separable pollen-specific and quantitative elements. Plant Mol Biol 38:663–669
Honys D, Twell D (2003) Comparative analysis of the Arabidopsis pollen transcriptome. Plant Physiol 132:640–652
Honys D, Twell D (2004) Transcriptome analysis of haploid male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 5:R85
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jeon JS, Chung YY, Lee S, Yi GH, Oh BG, An G (1999) Isolation and characterization of an anther-specific gene, RA8 from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 39:35–44
Kong LJ, Chang JT, Bild AH, Nevins JR (2007) Compensation and specificity of function within the E2F family. Oncogene 26:321–327
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y, Nakajima K, Arai Y (1990) An improved assay for β-glucuronidase in transformed cell: methanol almost completely suppresses a putative endogenous β-glucuronidase activity. Plant Sci 710:133–140
Lang ZH, Zhou P, Yu JJ, Ao GM, Zhao Q (2008) Functional characterization of the pollen-specific SBgLR promoter from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Planta 227(2):387–396
Lemon B, Tjian R (2000) Orchestrated response: a symphony of transcription factors for gene control. Genes Dev 14:2551–2569
Liu JQ, Seul U, Thompson R (1997) Cloning and characterization of a pollen-specific cDNA encoding a glutamic-acid-rich protein (GARP) from potato Solanum berthaultii. Plant Mol Biol 33:291–300
Ma H (2005) Molecular genetic analyses of microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis in flowering plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:393–434
Mariani C, Beuckeleer MD, Truettner J (1993) Induction of male sterility in plants by a chimaeric ribonuclease gene. Nature 363:715–717
Mascarenhas JP (1989) The male gametophyte of flowering plants. Plant Cell 1:657–664
Mascarenhas JP, Hamilton DA (1992) Artifacts in the localization of GUS activity in anthers of petunia transformed with a CaMV 35S-GUS construct. Plant J 2:405–408
Morishita R, Gibbons HG, Horiuchi M, Ellison EK, Nakajima M, Zhang L, Kanedat Y, Ogiharat T, Dzau JV (1995) A gene therapy strategy using a transcription factor decoy of the E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5855–5859
Paglino J, Burnett E, Tattersall P (2007) Exploring the contribution of distal P4 promoter elements to the oncoselectivity of Minute Virus of Mice. Virology 361(1):174–184
Rabinovich A, Jin XV, Rabinovich R, Xu X, Farnham JP (2008) E2F in vivo binding specificity: comparison of consensus versus nonconsensus binding sites. Genome Res 18:1763–1777
Rogers HJ, Bate N, Combe J, Sullivan J, Sweetman J, Swan C, Lonsdale DM, Twell D (2001) Functional analysis of cis-regulatory elements within the promoter of the tobacco late pollen gene g10. Plant Mol Biol 45:577–585
Scholz-Starke J, Buttner M, Sauer N (2003) AtSTP6, a new pollen-specific H+-monosaccharide symporter from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131:70–77
Slansky JE, Farnham PJ (1996) Introduction to the E2F family: protein structure and gene regulation. In: Farnham PJ (ed) Transcriptional control of cellgrowth: the E2F gene family. Springer, New York, pp 1–30
Smith B, Fang H, Pan Y, Walker PR, Famili AF, Sikorska M (2007) Evolution of motif variants and positional bias of the cyclic-AMP response element. BMC Evol Biol 7(Suppl 1):S15
Sorensen AM, Krober S, Unte US, Huijser P, Dekker K, Saedler H (2003) The Arabidopsis ABORTED MICROSPORES (AMS) gene encodes a MYC class transcription factor. Plant J 33:413–423
Swoboda I, Bhalla PL, Xu H, Zhang Y, Mittermann I, Valenta R, Singh MB (2001) Identification of pronp1, a tobacco profilin gene activated in tip-growing cells. Plant Mol Biol 46:531–538
Tao Y, Kassatly FR, Cress WD, Horowitz MJ (1997) Subunit Composition Determines E2F DNA-Binding Site Specificity. Mol Cell Biol 17:6994–7007
Twell D, Wing R, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S (1989) Isolation and expression of an anther-specific gene from tomato. Mol Gen Genomics 217:240–245
Twell D, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S (1990) Pollen-specific expression in transgenic plants: coordinate regulation of two different promoters during microsporogenesis. Development 109:705–713
Twell D, Yamaguchi J, Wing RA, Ushiba J, McCormick S (1991) Promoter analysis of genes that are coordinately expressed during pollen development reveals pollen-specific enhancer sequences and shared regulatory elements. Genes Dev 5:496–507
Twell D, Oh SA, Honys D (2006) Pollen development, a genetic and transcriptomic view. In: Malho R (ed) The pollen tube: cellular and molecular perspective. Plant Cell Monographs, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, pp 15–45
Wang X, Zhu L, Liu B, Wang C, Jin LF, Zhao Q, Yuan M (2007) Arabidopsis MICROTUBULE-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN18 functions in directional cell growth by destabilizing cortical microtubules. Plant Cell 19:877–889
Weinmann SA, Bartley MS, Zhang T, Zhang QM, Farnham JP (2001) Use of chromatin immunoprecipitation to clone novel E2F target promoters. Mol Cell Biol 21:6820–6832
Weterings K, Schrauwen J, Wullems G, Twell D (1995) Functional dissection of the promoter of the pollen-specific gene NTP303 reveals a novel pollen-specific, and conserved cis-regulatory element. Plant J 8:55–63
Xu X, Bieda M, Jin VX, Rabinovich A, Oberley MJ, Green R, Farnham PJ (2007) A comprehensive ChIP-chip analysis of E2F1, E2F4 and E2F6 in normal and tumor cells reveals interchangeable roles of E2F family members. Genome Res 17:1550–1561
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. J0730639 and 30971638).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Puigdomenech.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, P., Yang, F., Yu, J. et al. Several cis-elements including a palindrome involved in pollen-specific activity of SBgLR promoter. Plant Cell Rep 29, 503–511 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0839-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0839-3