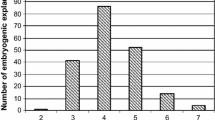
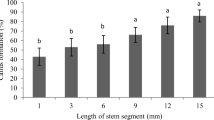
Abstract
We established a simple and effective system to induce somatic embryos in Arabidopsis via ovule culture. Agar-solidified B5 basic medium supplemented with 10 μ M 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid was used for callus induction. Ovules at all developmental stages were tested, and among these, ovules older than 48 h after anthesis could be successfully induced to form embryogenic calli at high frequencies (42–82%). Structural and molecular probe analyses confirmed that the embryogenic calli were derived from embryos in the ovules. These calli were then easily induced to generate somatic embryos at frequencies of 63–95%. Subculture of the somatic embryos onto 1/2 strength MS medium resulted in their direct conversion into plants. The regenerants appeared morphologically normal and were fertile. This method provides a useful alternative tool to create sufficient numbers of somatic embryos for the study of biochemical and molecular mechanisms of embryogenesis, especially to recover early defective embryos in some mutations for cell-biological analyses.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CIM:
-
Callus-induction medium
- EC:
-
Embryogenic calli
- HAA:
-
Hours after anthesis
- SE:
-
Somatic embryo
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Berleth T (1998) Experimental approaches to Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:69–82
Berleth T, Chatfield C (2002) Embryogenesis: pattern formation from a single cell. In: Somerville CR, Meyerowitz EM (eds) The Arabidopsis Book. American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, MD
Chen JG, Ullah H, Young JC, Sussman MR, Jones AM (2001) ABP1 is required for organized cell elongation and division in Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Genes Dev 15:902–911
Gaj MD (2001) Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Org 64:39–46
Gambog OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirement of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Hadfi K, Speth V, Neuhaus G (1998) Auxin—induced developmental patterns in Brassica juncea embryos. Development 125:879–887
Higashi K, Shiota H, Kamada H (1998) Patterns of expression of the genes for glutamine synthetase isoforms during somatic and zygotic emryogenesis in carrot. Plant Cell Physiol 39:418–424
Hoagland DR, Arnon DJ (1938) The Water culture method for growing plants without soil. Univ Calif Agr Expt Sta Cire, 347p
Ikeda-Iwai M, Satoh S, Kamada H (2002) Establishment of a reproducible tissue culture system for induction Arabidopsis somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 53:1575–1580
Jürgens G, Mayer U (1994) Embryos: color atlas of development. In: Bard JBL (ed) Arabidopsis. Wolfe Publishers, London, pp 7–21
Jürgens G, Mayer U, Ruiz RAT, Berleth T (1991) Genetic analysis of pattern formation in the Arabidopsis embryo. Development Suppl 1:27–38
Laux T, Jürgens G (1997) Embryogenesis: a new start in life. Plant Cell 9:989–1000
Liu CM, Xu ZH, Chua NH (1993) Auxin polar transport is essential for the establishment of bilateral symmetry during early plant embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5:621–630
Luo Y, Koop HU (1997) Somatic embryogenesis in cultured immature zygotic embryos and leaf protoplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana ecotypes. Planta 202:387–396
Malamy JE, Benfey PN (1997). Organization and cell differentiation in lateral roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 124:33–44
Mansfield SG, Briarty LG (1991) Early embbryogensis in arabidopsis thaliana: II The developing embryo. Can J Bot 69:461–476
Meinke DW (1991) Perspectives on genetic analysis of plant Embryogenesis. Plant Cell 3:857–866
Meinke DW (1995) Molecular genetics of plant embryogenesis. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:369–394
Mordhorst AP, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) Plant embryogenesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:535–576
Mordhorst AP, Voerman KJ, Hartog MV, Meijer EA, VanWent J, Koornneef M, de Vries SC (1998) Somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana is facilitated by mutation in genes repressing meristematic cell divisions. Genetics 149:549–563
Müller AJ (1961) Zur chrakterisierung der bluten und infloreszenzen von Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Kulturpflanze 9:364–393
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:437–497
O’Neill CM, Matthias RJ (1993) Regeneration of plants from protoplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana L. cv. Columbia (C24) via direct embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 44:1579–1585
Pillon E, Teriz M, Baldan B, Mariani P, Schiavo FL (1996) A protocol for obtaining embryogenic cell lines from Arabidopsis. Plant J 9:573–577
Raghavan V (2002) Induction of vivipary in Arabidopsis by silique culture: Implications for seed dormancy and germination. Am J Bot 89:766–776
Sangwan RS, Bourgeois Y, Duboid F, Sangwan NBS (1992) In vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana of cultured zygotic embryos and analysis of regenerants. J Plant Physiol 140:588–595
Sauer M, Friml J (2004) In vitro culture of Arabidopsis embryos within their ovules. Plant J 40:835–843
Schneider T, Dinkins R, Robinson K, Shellhammer J, Meinke DW (1989) An embryo-lethal mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana is a biotin auxotroph. Dev Biol 131:161–167
Shellhammer J, Meinke DW (1990) Arrested embryos from the bio1 auxotroph of Arabidopsis thaliana contain reduced levels of biotin. Plant Physiol 93:1162–1167
Shiota H, Satoh R, Watabe K, Harada H, Kamade H (1998) C-ABI3, the carrot homologue of the Arabidopsis ABI3, is expressed during both zygotic and somatic embryogenesis and functions in the regulation of embryo-specific ABA-inducible genes. Plant Cell Physiol 39:1184–1193
Shiota H, Tachikawa K, Watabe K, Kamada H (1999) Successful long-term preservation of abscisic acid-treated and desiccated carrot somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 18:749–753
Wu Y, Haberland G, Zhou C, Koop HU (1992) Somatic embryogenesis, formation of morphogenetic callus and normal development in zygotic embryos of Arabidopsis thaliana in vitro. Protoplasma 169:89–96
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plant. Plant Cell 5:1411–1423
Acknowledgement
We thank Professor Tom J. Guilfoyle for his kindness in providing us DR5::GUS (Columbia ecotype). This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30370743, 90408002), National Outstanding Youth Science Fund (30225006), and “PCSIRT.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Lakshmanan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Li, XR. & Sun, MX. Establishment of a simple and efficient system for somatic embryo induction via ovule culture in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Cell Rep 25, 1275–1280 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0166-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0166-x