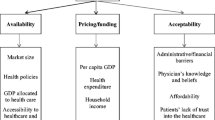
Abstract
The latest regulatory change in the distribution system of biologic disease-modifying, antirheumatic drugs limited their sale only through the designated pharmacies of the National Organization for Healthcare Services Provision (EOPYY) or the National Health System (NHS) hospitals, adding to the complexity of access to effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Greece. The aim of this paper was to assess the barriers to access RA treatment, by recording patients’, rheumatologists’ and EOPYY pharmacists’ experiences. One twenty-three patients, 12 rheumatologists and 27 pharmacists from Athens and other urban areas in Greece participated in the study. Three types of standardized questionnaires were used to elicit information from each group of respondents using the method of personal interview for patients and the method of postal survey for doctors and pharmacists. During the last year, 26 % of patients encountered problems in accessing their rheumatologist and 49 % of patients experienced difficulties in accessing their medication. Ninety-two percent of rheumatologists and 96 % of pharmacists confirmed that patients experience difficulties in accessing RA medication. The most commonly reported reasons for reduced access to medical treatment were travel difficulties and long distance from doctor’s clinic, as well as delays in booking an appointment. The most frequently reported barriers to access pharmaceutical treatment were difficulties in the prescription process, distance from EOPYY pharmacies and medicine shortages in NHS hospitals. The study showed that RA patients are facing increased barriers to access timely and effective treatment. Redesign of the current system of distribution ensuring the operation of additional points of sale is deemed necessary.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
These include (a) presence of RF and/or anti-CCP antibodies (particularly at high titers), (b) erosions in hands and/or feet detected by radiographs and (c) high disease activity (according to Disease Activity Index, number of swollen joints or the presence of acute-phase proteins).
References
Donabedian A (1992) Defining and measuring the quality in health care, in Assessing Quality Health Care. In: Wenzel RP (ed) Perspectives for Clinicians. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Hoebert JM, Mantel-Teeuwisse AK, van Dijk L, Bijlsma JWJ, Leufkens HGM (2012) Do rheumatoid arthritis patients have equal access to treatment with new medicines? Tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors use in four European countries. Health Policy 104(1):76–83
Miltenburger C, Günther OH, Justo N, Karampampa K, Texier-Richard B, Schweikert B. (2009) A survey of barriers to treatment access in rheumatoid arthritis in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK. Available from:http://www.comparatorreports.se/RA%20Barrier%20Report_FINAL_050110.pdf
Garneau KL, Iversen MD, Tsao H, Solomon DH (2011) Primary care physicians’ perspectives towards managing rheumatoid arthritis: room for improvement. Arthr Res Ther 13:R189
Hagglund KJ, Clark MJ, Hilton SA, Hewett JE (2005) Access to healthcare services among persons with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 84(9):702–711
Bernatsky S, Feldman D, De Civita M, Haggerty J, Tousignant P, Legaré J, Zummer M, Meagher T, Mill C, Roper M, Lee J (2010) Optimal care for rheumatoid arthritis: a focus group study. Clin Rheumatol 29(6):645–657
Westhoff G, Schneider M, Raspe H, Zeidler H, Runge C, Volmer T, Zink A (2009) Advance and unmet need of health care for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the German population—results from the German rheumatoid arthritis population survey (GRAPS). Rheumatology 48:650–657
Põlluste K, Kallikorm R, Meiesaar K, Lember M (2012) Satisfaction with access to health services: the perspective of Estonian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci W J 2012:257569
de Boer D, Delnoij D, Rademakers J (2010) Do patient experiences on priority aspects of health care predict their global rating of quality of care? A study in five patient groups. Health Expect 13(3):285–297
Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, vander Horst-Bruinsma IE, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM (2001) Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med 111(6):446–451
Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS (2004) Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 43(7):906–914
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gorter S, Knevel R, Nam J, Schoels M, Aletaha D, Buch M, Gossec L, Huizinga T, Bijlsma JW, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, Gabay C, Gomez-Reino J, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Martin-Mola E, McInnes I, Pavelka K, van Riel P, Scholte M, Scott DL, Sokka T, Valesini G, van Vollenhoven R, Winthrop KL, Wong J, Zink A, van der Heijde D (2010) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):964–975
Pugner KM, Scott DI, Holmes JW, Hieke K (2000) The costs of rheumatoid arthritis: an international long-term view. Sem Arthr Rheum 29:305–320
Callahan LF (1998) The burden of rheumatoid arthritis: facts and figures. J Rheumatol Suppl 53:8–12
Irvine S, Munro R, Porter D (1999) Early referral, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for changing medical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 58(8):510–513
Boonen A, Severens JL (2011) The burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 1:S3–S8
Doan QV, Chiou CF, Dubois RW (2006) Review of eight pharmacoeconomic studies of the value of biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. J Manag Care Pharm 12(7):555–569
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, Paulus HE, Mudano A, Pisu M, Elkins-Melton M, Outman R, Allison JJ, Suarez Almazor M, Bridges SL Jr, Chatham WW, Hochberg M, MacLean C, Mikuls T, Moreland LW, O’Dell J, Turkiewicz AM, Furst DE, American College of Rheumatology (2008) American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59(6):762–784
Athanasakis K, Detsis M, Souliotis K, Golna C, Kyriopoulos J (2012) Greek NHS capacity constraints regarding intravenous treatment for rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int 32(4):921–926
National Organization for Medicine, available from: http://www.eof.gr/web/guest/protocols?p_p_id=20&p_p_lifecycle=0&p_p_state=maximized&p_p_mode=view&p_p_col_id=column-1&p_p_col_count=1&_20_struts_action=%2Fdocument_library%2Fview&_20_folderId=34627. Accessed at 25 August 2013
Hernandez AC, Boumpas D, Drosos D, Galanopoulos N, Sakas L, Setas L, Sidiropoulos P, Christaki S, Tzioufas A, Athanasakis K, Vitsou E, Petrakis I (2012) Rheumatoid arthritis in Greece: the economic burden and impact on quality of life; interim analysis of the HORA study. Hell Rheumatol 23(4):28
Tountas Y, Oikonomou N, Pallikarona G, Dimitrakaki C, Tzavara C, Souliotis K, Mariolis A, Pappa E, Kontodimopoulos N, Niakas D (2011) Sociodemographic and socioeconomic determinants of health services utilization in Greece: the Hellas Health I study. Health Serv Manag Res 24(1):8–18
Welsing PM, Landewé RB, van Riel PL, Boers M, van Gestel AM, van der Linden S, Swinkels HL, van der Heijde DM (2004) The relationship between disease activity and radiologic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal analysis. Arth Rheum 50(7):2082–2093
Laires PA, Exposto F, Mesquita R, Martins AP, Cunha-Miranda L, Fonseca JE (2012) Patients’ access to biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison between Portugal and other European countries. Eur J Health Econ 1-11
Putrik P, Ramiro S, Kvien TK, Sokka T, Pavlova M, Uhlig T, Boonen A (2013) Working Group ‘Equity in access to treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Europe’. Inequities in access to biologic and synthetic DMARDs across 46 European countries. Ann Rheum Dis
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Vassiliki Alexiou, Eleni Alexopoulou, Stamo Georgala and Aikaterini Pournaropoulou for their valuable assistance in collecting the data for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souliotis, K., Papageorgiou, M., Politi, A. et al. Barriers to accessing biologic treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in Greece: the unseen impact of the fiscal crisis—the Health Outcomes Patient Environment (HOPE) study. Rheumatol Int 34, 25–33 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2866-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2866-1