Abstract
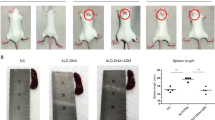
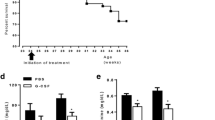
We observed the distribution of monocyte’s changes in damage to renal tissue and the expression of macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC) in MRL/lpr mice. The 8-week-old MRL/lpr mice were randomly assigned to receive either MDC antibodies (n = 6) or placebo (n = 6) at a once-every-other-day dose of 300 μl from week 4. We then quantified the differences in 24-h urine protein and serum creatinine concentrations, performed a histological evaluation of renal tissue and assessed the expression of MDC protein and mRNA between the two groups 4 weeks after treatment was initiated. Antibody-treated mice demonstrated significantly lower urine protein and serum creatinine concentrations and had fewer renal lesions compared with control mice. The expression of MDC protein and mRNA in renal tissues was significantly lower in the antibody-treated mice than in control mice, suggesting that the elevated expression of MDC, which led to monocyte infiltration in the kidney, may play an important role in the development of lupus nephritis. Furthermore, the anti-MDC antibodies may act to alleviate the renal lesions of murine lupus nephritis by inhibiting the infiltration of monocytes in the renal tissue of the lupus mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imai T, Nagira M, Takagi S, Kakizaki M, Nishimura M, Wang J, Gray PW, Matsushima K, Yoshie O (1999) Selective recruitment of CCR4-bearing Th2 cells toward antigen-presenting cells by the CC chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int Immunol 11:81–88
Bonecchi R, Sozzani S, Stine JT, Luini W, D’Amico G, Allavena P, Chantry D, Mantovani A (1998) Divergent effects of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma on macrophage-derived chemokine production: an amplification circuit of polarized T helper 2 responses. Blood 92:2668–2671
Andrew DP, Chang MS, McNinch J, Wathen ST, Rihanek M, Tseng J, Spellberg JP, Elias CG 3rd (1998) STCP-1 (MDC) CC chemokine acts specifically on chronically activated Th2 lymphocytes and is produced by monocytes on stimulation with Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. J Immunol 161:5027–5038
Imai T, Chantry D, Raport CJ, Wood CL, Nishimura M, Godiska R, Yoshie O, Gray PW (1998) Macrophage-derived chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 273:1764–1768
Imai T, Baba M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Yoshie O (1997) The T cell-directed CC chemokine TARC is a highly specific biological ligand for CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 272:15036–15042
Vestergaard C, Yoneyama H, Murai M, Nakamura K, Tamaki K, Terashima Y, Imai T, Yoshie O, Irimura T, Mizutani H, Matsushima K (1999) Overproduction of Th2-specific chemokines in NC/Nga mice exhibiting atopic dermatitis-like lesions. J Clin Invest 104:1097–1105
Lloyd CM, Delaney T, Nguyen T, Tian J, Martinez AC, Coyle AJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (2000) CC chemokine receptor (CCR)3/eotaxin is followed by CCR4/monocyte-derived chemokine in mediating pulmonary T helper lymphocyte type 2 recruitment after serial antigen challenge in vivo. J Exp Med 191:265–274
Caligaris-Cappio F, Bertero MT, Converso M, Stacchini A, Vinante F, Romagnani S, Pizzolo G (1995) Circulating levels of soluble CD30, a marker of cells producing Th2-type cytokines, are increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and correlate with disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol 13:339–343
Garcia GE, Xia Y, Harrison J, Wilson CB, Johnson RJ, Bacon KB, Feng L (2003) Mononuclear cell-infiltrate inhibition by blocking macrophage-derived chemokine results in attenuation of developing crescentic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol 162:1061–1073
Kim SH, Cleary MM, Fox HS, Chantry D, Sarvetnick N (2002) CCR4-bearing T cells participate in autoimmune diabetes. J Clin Invest 110:1675–1686
Cuzic S, Ritz E, Waldherr R (1992) Dendritic cells in glomerulonephritis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 62:357–363
Atkins RC, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Song Q, Lan HY (1996) Modulators of crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:2271–2278
Kulkarni O, Pawar RD, Purschke W, Eulberg D, Selve N, Buchner K, Ninichuk V, Segerer S, Vielhauer V, Klussmann S, Anders HJ (2007) Spiegelmer inhibition of CCL2/MCP-1 ameliorates lupus nephritis in MRL-(Fas)lpr mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2350–2358
Tian S, Li J, Wang L, Liu T, Liu H, Cheng G, Liu D, Deng Y, Gou R, Wan Y, Jia J, Chen C (2007) Urinary levels of RANTES and M-CSF are predictors of lupus nephritis flare. Inflamm Res 56:304–310
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Kexu research funds of Higher Education of Liaoning Educational Committee (No. 202013141).
Conflicts of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Diao, C., Wu, C. et al. Anti-macrophage-derived chemokine antibody relieves murine lupus nephritis. Rheumatol Int 31, 1459–1464 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1499-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1499-x