Abstract
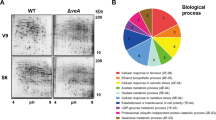
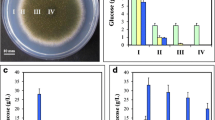
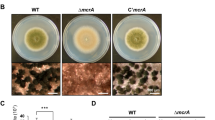
Aspergillus nidulans produces cleistothecia as sexual reproductive organs in a process affected by genetic and external factors. To gain a deeper insight into A. nidulans sexual development, we performed comparative proteome analyses based on the wild type developmental periods. We identified sexual development-specific proteins with a more than twofold increase in production during hypoxia or the sexual period compared to the asexual period. Among the sexual development-specific proteins analyzed by gene-deletion experiments and functional assays, MpdA, a putative mannitol-1-phosphate 5-dehydrogenase, plays multiple roles in growth and differentiation of A. nidulans. The most distinct mpdA-deletion phenotype was ascosporogenesis failure. Genetic mpdA deletion resulted in small cleistothecia with no functional ascospores. Transcriptional analyses indicated that MpdA modulates the expression of key development- and meiosis-regulatory genes during sexual development. The mpdA deletion increased hyphal branching and decreased conidial heat resistance. Mannitol production in conidia showed no difference, whereas it was decreased in mycelia and sexual cultures. Addition of mannitol during vegetative growth recovered the defects in conidial heat resistance and ascospore genesis. Taken together, these results indicate that MpdA plays an important role in sexual development, hyphal branching, and conidial heat resistance in Aspergillus nidulans.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams TH, Wieser JK, Yu JH (1998) Asexual sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:35–54
Albrecht D, Guthke R, Brakhage AA, Kniemeyer O (2010) Integrative analysis of the heat shock response in Aspergillus fumigatus. BMC Genomics 11:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-32
Baltussen TJH, Coolen JPM, Zoll J et al (2018) Gene co-expression analysis identifies gene clusters associated with isotropic and polarized growth in Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Fungal Genet Biol 116:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2018.04.013
Bayram Ö, Braus GH (2012) Coordination of secondary metabolism and development in fungi: The velvet family of regulatory proteins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00285.x
Bayram ÖS, Bayram Ö, Valerius O et al (2010) LaeA control of velvet family regulatory proteins for light-dependent development and fungal cell-type specificity. PLoS Genet 6:e1001226. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001226
Bok JW, Keller NP (2004) LaeA, a regulator of secondary metabolism in Aspergillus spp. Eukaryot Cell 3:527–535. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.3.2.527
Busch S, Eckert SE, Krappmann S, Braus GH (2003) The COP9 signalosome is an essential regulator of development in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 49:717–730. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03612.x
Chaturvedi V, Bartiss A, Wong B (1997) Expression of bacterial mtlD in Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in mannitol synthesis and protects a glycerol-defective mutant from high-salt and oxidative stress. J Bacteriol 179:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.1.157-162.1997
Corina DL, Munday KA (1971) Studies on polyol function in Aspergillus clavatus: a role for mannitol and ribitol. J Gen Microbiol 69:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-69-2-221
Deng WW, Sasamoto H, Ashihara H (2015) Effect of caffeine on the expression pattern of water-soluble proteins in rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Nat Prod Commun 10:733–736
Dijksterhuis J, Teunissen PGM (2004) Dormant ascospores of talaromyces macrosporus are activated to germinate after treatment with ultra high pressure. J Appl Microbiol 96:162–169
Dulermo T, Rascle C, Billon-Grand G et al (2010) Novel insights into mannitol metabolism in the fungal plant pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Biochem J 427:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20091813
Dyer PS, O’Gorman CM (2012) Sexual development and cryptic sexuality in fungi: insights from Aspergillus species. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:165–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00308.x
Gerke J, Braus GH (2014) Manipulation of fungal development as source of novel secondary metabolites for biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8443–8455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5997-8
Han KH (2009) Molecular genetics of Emericella nidulans sexual development. Mycobiology 37:171–182. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2009.37.3.171
Han KH, Han KY, Yu JH et al (2001) The nsdD gene encodes a putative GATA-type transcription factor necessary for sexual development of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 41:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02472.x
Han KH, Lee DB, Kim JH et al (2003) Environmental factors affecting development of Aspergillus nidulans. J Microbiol 41:34–40
Han KH, Kim JH, Moon H et al (2008) The Aspergillus nidulans esdC (early sexual development) gene is necessary for sexual development and is controlled by veA and a heterotrimeric G protein. Fungal Genet Biol 45:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2007.09.008
Horikoshi K, Iida S, Keda Y (1965) Mannitol and mannitol dehydrogenases in conidia of Aspergillus oryzae. J Bacteriol 89:326–330
Horio T, Oakley BR (2005) The role of microtubules in rapid hyphal tip growth of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 16:918–926. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E04-09-0798
Hult K, Veide A, Gatenbeck S (1980) The distribution of the NADPH regenerating mannitol cycle among fungal species. Arch Microbiol 128:253–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00406168
Kim HS, Han KY, Kim KJ et al (2002) The veA gene activates sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 37:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00029-4
Kim Y, Nandakumar MP, Marten MR (2007) Proteome map of Aspergillus nidulans during osmoadaptation. Fungal Genet Biol 44:886–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2006.12.001
Kim HR, Chae KS, Han KH, Han DM (2009) The nsdC gene encoding a putative C2H2-type transcription factor is a key activator of sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 182:771–783. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.109.101667
Kim YJ, Yeong Man Y, Maeng PJ (2017) Differential control of asexual development and sterigmatocystin biosynthesis by a novel regulator in Aspergillus nidulans. Sci Rep 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46340
Kong Q, Wang L, Liu Z et al (2013) Gβ-Like CpcB plays a crucial role for growth and development of Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 8:e70355. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070355
Krappmann S, Jung N, Medic B et al (2006) The Aspergillus nidulans F-box protein GrrA links SCF activity to meiosis. Mol Microbiol 61:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05215.x
Lauter FR, Marchfelder U, Russo VE et al (1998) Photoregulation of cot-1, a kinase-encoding gene involved in hyphal growth in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 23:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.1998.1038
Lee SY, Lee KO (2011) Proteomic analysis of RNA interference induced knockdown plant. Methods Mol Biol 744:211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-123-9_15
Lee MK, Kwon NJ, Choi JM et al (2014) NsdD is a key repressor of asexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 197:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.114.161430
Lesk AM (1995) NAD-binding domains of dehydrogenases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 5:775–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-440X(95)80010-7
Lim JY, Kang EH, Park YH et al (2020) Survival factor SvfA plays multiple roles in differentiation and is essential for completion of sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Sci Rep 10:5586. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62455-4
Lima JF, Malavazi I, Fagundes VZKMR et al (2005) The csnD/csnE signalosome genes are involved in the Aspergillus nidulans DNA damage response. Genetics 171:1003–1015. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.041376
Lin X, Momany M (2004) Identification and complementation of abnormal hyphal branch mutants ahbA1 and ahbB1 in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 41:998–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2004.07.005
Markham P, Robson GD, Bainbridge BW, Trinci AP (1993) Choline: Its role in the growth of filamentous fungi and the regulation of mycelial morphology. FEMS Microbiol Lett 104:287–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05872.x
Mogilevsky K, Glory A, Bachewich C (2012) The polo-like kinase PLKA in Aspergillus nidulans is not essential but plays important roles during vegetative growth and development. Eukaryot Cell 11:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.05130-11
Momany M, Westfall PJ, Abramowsky G (1999) Aspergillus nidulans swo mutants show defects in polarity establishment, polarity maintenance and hyphal morphogenesis. Genetics 151:557–567
Ni M, Yu JH (2007) A novel regulator couples sporogenesis and trehalose biogenesis in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000970
Oakley BR, Kirsch DR, Morris NR (1980) A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 105:361–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4
Palmer JM, Theisen JM, Duran RM et al (2013) Secondary metabolism and development is mediated by LlmF control of VeA subcellular localization in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS Genet 9:e1003193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003193
Park HS, Yu JH (2016) Velvet regulators in Aspergillus spp. Microbiol Biotechnol Lett 44:409–419. https://doi.org/10.4014/mbl.1607.07007
Park HS, Ni M, Jeong KC et al (2012) The Role, interaction and regulation of the velvet regulator VelB in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 7:e45935. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045935
Park HS, Nam TY, Han KH et al (2014) VelC positively controls sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 9:e89883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089883
Park DS, Yu YM, Kim YJ, Maeng PJ (2015) Negative regulation of the vacuole-mediated resistance to K+ stress by a novel C2H2 zinc finger transcription factor encoded by aslA in Aspergillus nidulans. J Microbiol 53:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-4701-8
Pera LM, Baigorí MD, Callieri D (1999) Influence of environmental conditions on hyphal morphology in pellets of Aspergillus niger: Role of β-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase. Curr Microbiol 39:65–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900419
Riquelme M, Reynaga-Peña CG, Gierz G, Bartnicki-García S (1998) What determines growth direction in fungal hyphae? Fungal Genet Biol 24:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.1998.1074
Rocha MC, De Godoy KF, De Castro PA et al (2015) The Aspergillus fumigatus pkcAG579R mutant is defective in the activation of the cell wall integrity pathway but is dispensable for virulence in a neutropenic mouse infection model. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0135195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0135195
Rocha MC, Fabri JHTM, Franco de Godoy K et al (2016) Aspergillus fumigatus MADS-Box transcription factor rlmA is required for regulation of the cell wall integrity and virulence. G3 (Bethesda) 6:2983–3002. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.116.031112
Ruijter GJG, Bax M, Patel H et al (2003) Mannitol is required for stress tolerance in Aspergillus niger conidiospores. Eukaryot Cell 2:690–698
Schier N, Liese R, Fischer R (2001) A Pcl-like cyclin of Aspergillus nidulans is transcriptionally activated by developmental regulators and is involved in sporulation. Mol Cell Biol 21:4075–4088. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.12.4075-4088.2001
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Singh M, Scrutton NS, Scrutton MC (1988) NADPH generation in Aspergillus nidulans: is the mannitol cycle involved? J Gen Microbiol 134:643–654. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-134-3-643
Sohn KT, Yoon KS (2002) Ultrastructural study on the cleistothecium development in Aspergillus nidulans. Mycobiology 30:117–127. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2002.30.3.117
Solomon PS, Waters ODC, Jörgens CI et al (2006) Mannitol is required for asexual sporulation in the wheat pathogen Stagonospora nodorum (glume blotch). Biochem J 399:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20060891
Solomon PS, Waters ODC, Oliver RP (2007) Decoding the mannitol enigma in filamentous fungi. Trends Microbiol 15:257–262
Steele GC, Trinci APJ (1977) Effect of temperature and temperature shifts on growth and branching of a wild type and a temperature sensitive colonial mutant (Cot 1) of Neurospora crassa. Arch Microbiol 113:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428578
Stinnett SM, Espeso EA, Cobeño L et al (2007) Aspergillus nidulans VeA subcellular localization is dependent on the importin α carrier and on light. Mol Microbiol 63:242–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05506.x
Suzuki G, Yanagawa Y, Kwok SF et al (2002) Arabidopsis COP10 is a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme variant that acts together with COP1 and the COP9 signalosome in repressing photomorphogenesis. Genes Dev 16:554–559. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.964602
Szewczyk E, Nayak T, Oakley CE et al (2006) Fusion PCR and gene targeting in Aspergillus nidulans. Nat Protoc 1:3111–3120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.405
Teertstra WR, Tegelaar M, Dijksterhuis J et al (2017) Maturation of conidia on conidiophores of Aspergillus niger. Fungal Genet Biol 98:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2016.12.005
Trinci APJ (1974) A study of the kinetics of hyphal extension and branch initiation of fungal mycelia. J Gen Microbiol 81:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-81-1-225
Uhm YK, Jung KH, Bu HJ et al (2010) Effects of Machilus thunbergii Sieb et Zucc on UV-induced photoaging in hairless mice. Phyther Res 24:1339–1346. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3117
Vallim MA, Miller KY, Miller BL (2000) Aspergillus SteA (sterile12-like) is a homeodomain-C2/H2-Zn+2 finger transcription factor required for sexual reproduction. Mol Microbiol 36:290–301
Van der Veen P, Ruijter GJG, Visser J (1995) An extreme creA mutation in Aspergillus nidulans has severe effects on D-glucose utilization. Microbiology 141:2301–2306. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-141-9-2301
Vélëz H, Glassbrook NJ, Daub ME (2007) Mannitol metabolism in the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. Fungal Genet Biol 44:258–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2006.09.008
Wang ZL, Lu J, Feng MG (2012) Primary roles of two dehydrogenases in the mannitol metabolism and multi-stress tolerance of entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Environ Microbiol 14:2139–2150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02654.x
Wartenberg D, Vödisch M, Kniemeyer O et al (2012) Proteome analysis of the farnesol-induced stress response in Aspergillus nidulans—the role of a putative dehydrin. J Proteom 75:4038–4049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2012.05.023
Witteveen CFB, Visser J (1995) Polyol pools in Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol Lett 134:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07914.x
Wyatt TT, van Leeuwen MR, Wösten HAB, Dijksterhuis J (2014) Mannitol is essential for the development of stress-resistant ascospores in Neosartorya fischeri (Aspergillus fischeri). Fungal Genet Biol 64:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2013.12.010
Yelton MM, Hamer JE, Timberlake WE (1984) Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by using a trpC plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 20:1470–1474. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.81.5.1470
Yu JH, Hamari Z, Han KH et al (2004) Double-joint PCR: a PCR-based molecular tool for gene manipulations in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 41:973–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2004.08.001
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Chungnam National University (CNU) (Grant No. 2019-0852-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all authors. We understand that the corresponding author is the sole contact for the editorial process. He is responsible for communicating with the other authors regarding progress, submissions of revisions, and final approval of proofs. All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Michael Polymenis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, JY., Jang, SH. & Park, HM. Mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase, MpdA, is required for mannitol production in vegetative cells and involved in hyphal branching, heat resistance of conidia and sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Genet 67, 613–630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-021-01163-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-021-01163-6