Abstract
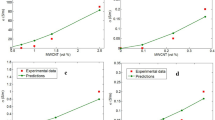
A new version of the semi-empirical Halpin–Tsai (H–T) model is presented to evaluate the effective thermal conductivity of general carbon nanotubes (CNTs)-reinforced polymer nanocomposites. The model captures the influences of the CNTs alignment, random orientation, aggregation, waviness, length, diameter and the CNT/polymer interfacial thermal resistance parameters. In order to verify the suitability of the new H–T model, the numerically calculated thermal conductivities are compared with existing experimentally measured ones. An excellent predictability is found of the modified H–T model over a wide range of the tests. The consideration of the CNT waviness and the interfacial thermal resistance parameters is seriously essential for a more realistic prediction in all conditions. For aligned CNT-reinforced polymer nanocomposites, considering the alignment factor seems to be very important. Moreover, in the case of well-dispersed CNTs into the matrix, it is necessary to incorporate the CNT random orientation parameter. Additionally, when CNTs are not well dispersed, the CNT aggregation and random orientation parameters must be incorporated in the analysis. The effects of the CNT volume fraction, length, diameter and non-straight shape on the nanocomposite thermal conducting behavior are estimated in details. The results clearly expose that it is needed to eliminate the aggregation, use the straight CNTs and form a strong interface if the full potential of CNT reinforcement is to be realized. Finally, the thermal conductivities of CNT-shape-memory polymer nanocomposites at different temperatures are obtained.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doudou BB, Vivet A, Chen J, Laachachi A, Falher T, Poilâne C (2014) Hybrid carbon nanotube—silica/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites films: preparation and characterisation. J Polym Res 21(4):420
Hassanzadeh-Aghdam MK, Ansari R, Darvizeh A (2017) Micromechanical modeling of thermal expansion coefficients for unidirectional glass fiber-reinforced polyimide composites containing silica nanoparticles. Compos Part A 96:110–121
Chaudhary B, Panwar V, Roy T, Pal K (2019) Thermomechanical behaviour of zirconia-multiwalled carbon nanotube-reinforced polypropylene hybrid composites. Polym Bull 76(1):511–521
Bui K, Papavassiliou DV (2013) Numerical calculation of the effective thermal conductivity of nanocomposites. Numer Heat Transf Part A: Appl 63(8):590–603
Kochetov R, Korobko AV, Andritsch T, Morshuis PHF, Picken SJ, Smit JJ (2011) Modelling of the thermal conductivity in polymer nanocomposites and the impact of the interface between filler and matrix. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(39):395401
Omidi M, Milani AS, Seethaler RJ, Arasteh R (2010) Prediction of the mechanical characteristics of multi-walled carbon nanotube/epoxy composites using a new form of the rule of mixtures. Carbon 48(11):3218–3228
Philip B, Xie J, Abraham JK, Varadan VK (2005) Polyaniline/carbon nanotube composites: starting with phenylamino functionalized carbon nanotubes. Polym Bull 53(2):127–138
Bakshi SR, Patel RR, Agarwal A (2010) Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composites: a multi-scale study using object oriented finite element method. Comput Mater Sci 50(2):419–428
Bryning MB, Milkie DE, Islam MF, Kikkawa JM, Yodh AG (2005) Thermal conductivity and interfacial resistance in single-wall carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Appl Phys Lett 87(16):161909
Xu Y, Ray G, Abdel-Magid B (2006) Thermal behavior of single-walled carbon nanotube polymer–matrix composites. Compos Part A 37(1):114–121
Bonnet P, Sireude D, Garnier B, Chauvet O (2007) Thermal properties and percolation in carbon nanotube-polymer composites. Appl Phys Lett 91(20):201910
Kim YA, Kamio S, Tajiri T, Hayashi T, Song SM, Endo M, Dresselhaus MS (2007) Enhanced thermal conductivity of carbon fiber/phenolic resin composites by the introduction of carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 90(9):093125
Haggenmueller R, Guthy C, Lukes JR, Fischer JE, Winey KI (2007) Single wall carbon nanotube/polyethylene nanocomposites: thermal and electrical conductivity. Macromolecules 40(7):2417–2421
Guthy C, Du F, Brand S, Winey KI, Fischer JE (2007) Thermal conductivity of single-walled carbon nanotube/PMMA nanocomposites. J Heat Transf 129(8):1096–1099
Marconnet AM, Yamamoto N, Panzer MA, Wardle BL, Goodson KE (2011) Thermal conduction in aligned carbon nanotube-polymer nanocomposites with high packing density. ACS Nano 5(6):4818–4825
Ji T, Feng Y, Qin M, Feng W (2016) Thermal conducting properties of aligned carbon nanotubes and their polymer composites. Compos Part A 91:351–369
Bouchard J, Cayla A, Devaux E, Campagne C (2013) Electrical and thermal conductivities of multiwalled carbon nanotubes-reinforced high performance polymer nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 86:177–184
Kwon SY, Kwon IM, Kim YG, Lee S, Seo YS (2013) A large increase in the thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube/polymer composites produced by percolation phenomena. Carbon 55:285–290
Kim HS, Jang JU, Yu J, Kim SY (2015) Thermal conductivity of polymer composites based on the length of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos Part B 79:505–512
Yu K, Liu Y, Liu Y, Peng HX, Leng J (2014) Mechanical and shape recovery properties of shape memory polymer composite embedded with cup-stacked carbon nanotubes. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25(10):1264–1275
Behl M, Lendlein A (2007) Shape-memory polymers. Mater Today 10(4):20–28
Dastgerdi JN, Marquis G, Salimi M (2013) The effect of nanotubes waviness on mechanical properties of CNT/SMP composites. Compos Sci Technol 86:164–169
Yang QS, He XQ, Liu X, Leng FF, Mai YW (2012) The effective properties and local aggregation effect of CNT/SMP composites. Compos Part B 43(1):33–38
Kundalwal SI, Ray MC (2014) Estimation of thermal conductivities of a novel fuzzy fiber reinforced composite. Int J Therm Sci 76:90–100
Hassanzadeh-Aghdam MK, Ansari R, Darvizeh A (2017) A new micromechanics approach for predicting the elastic response of polymer nanocomposites reinforced with randomly oriented and distributed wavy carbon nanotubes. J Compos Mater 51(20):2899–2912
Jia Y, Peng K, Gong XL, Zhang Z (2011) Creep and recovery of polypropylene/carbon nanotube composites. Int J Plast 27(8):1239–1251
Kumlutas D, Tavman IH (2006) A numerical and experimental study on thermal conductivity of particle filled polymer composites. J Therm Compos Mater 19(4):441–455
Nan CW, Liu G, Lin Y, Li M (2004) Interface effect on thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube composites. Appl Phys Lett 85(16):3549–3551
Ginga NJ, Chen W, Sitaraman SK (2014) Waviness reduces effective modulus of carbon nanotube forests by several orders of magnitude. Carbon 66:57–66
Yeh MK, Tai NH, Liu JH (2006) Mechanical behavior of phenolic-based composites reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 44(1):1–9
Aliev AE, Lima MH, Silverman EM, Baughman RH (2009) Thermal conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotube sheets: radiation losses and quenching of phonon modes. Nanotechnology 21(3):035709
Weidenfeller B, Anhalt M (2014) Polyurethane-magnetite composite shape-memory polymer: thermal properties. J Therm Compos Mater 27(7):895–908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safi, M., Hassanzadeh-Aghdam, M.K. & Mahmoodi, M.J. A semi-empirical model for thermal conductivity of polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes. Polym. Bull. 77, 6577–6590 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03082-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03082-6