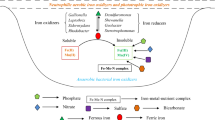
Abstract
The iron-reducing capability of anammox bacteria was examined in this study using Percoll purified anammox bacteria. Anammox bacteria could reduce Fe(III) to Fe(II) with organic matters as the electron donor. The activity of anammox iron-reducing process was dependent on different electron donor, acceptor and pH. The highest iron-reducing activity of anammox bacteria was achieved with Fe(III)-NTA (nitrilotriacetic acid) as electron acceptor and formate as the electron donor at pH7. Similar to other iron reducers, 80 % of the iron reductase in anammox bacteria was located in the membrane fraction. Due to the chemical oxidant of NO2 − and the NO3 − dependent ferrous iron oxidation by anammox bacteria, the iron-reducing activity of anammox bacteria could be severely inhibited when iron-reducing pathway and the anammox process were coupled. However, the total nitrogen removal efficiency was not significantly affected in the presence of Fe(III). The iron-reducing capability of anammox bacteria could influence both N and Fe cycle on earth, and it is a potential way for wastewater treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(6):1919–1925
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. United Book Press, Baltimore
Arrigo KR (2004) Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature 437:349–355
Bonneville S, Van Cappellen P, Behrends T (2004) Microbial reduction of iron (III) oxyhydroxides: effects of mineral solubility and availability. Chem Geol 212:255–268
Chistyakova N, Rusakov V, Nazarova K, Koksharov YA, Zavarzina D, Greneche JM (2008) Iron minerals formed by dissimilatory iron-and sulfur reducing bacteria studied by Mössbauer spectrometry. Hyperfine Interact 182:55–63
Clément JC, Shrestha J, Ehrenfeld JG, Jaffé PR (2005) Ammonium oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron under anaerobic conditions in wetland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2323–2328
Coby AJ, Picardal FW (2005) Inhibition of NONO3 − and NO2 − reduction by microbial Fe(III) reduction: Evidence of a reaction between NO2 − and cell surface-bound Fe2 +. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5267–5274
Cummings DE, March AW, Bostick B, Spring S, Caccavo F, Fendorf S, Rosenzweig RF (2000) Evidence for microbial Fe(III) reduction in anoxic, mining-impacted lake sediments (Lake Coeur d’Alene, Idaho). Appl Environ Microbiol 66:154–162
den Camp O, Kartal B, Guven D et al (2006) Global impact and application of the anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Biochem Soc Trans 34:174–178
DiCHRISTINA TJ (1992) Effects of nitrate and nitrite on dissimilatory iron reduction by Shewanella putrefaciens 200. J Bacteriol 174:1891–1896
Dobbin PS, Butt JN, Powell AK, Reid GA, Richardson DJ (1999) Characterization of a flavocytochrome that is induced during the anaerobic respiration of Fe3 + by Shewanella frigidimarina NCIMB400. Biochem J 342:439
Emerson D, Fleming EJ, McBeth JM (2010) Iron-oxidizing bacteria: an environmental and genomic perspective. Annu Rev Microbiol 64:561–583
Fredrickson JK, Zachara JM, Balkwill DL, Kennedy D, Li SW, Kostandarithes HM, Daly MJ, Romine MF, Brockman FJ (2004) Geomicrobiology of high-level nuclear waste-contaminated vadose sediments at the Hanford Site, Washington state. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4230–4241
Güven D, Dapena A, Kartal B et al (2005) Propionate oxidation by and methanol inhibition of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1066–1071
Gaspard S, Vazquez F, Holliger C (1998) Localization and solubilization of the iron (III) reductase of Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3188–3194
Greene AC, Patel BKC, Sheehy AJ (1997) Deferribacter thermophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel thermophilic manganese-and iron-reducing bacterium isolated from a petroleum reservoir. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:505–509
Haas JR, Dichristina TJ (2002) Effects of Fe(III) chemical speciation on dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction by Shewanella putrefaciens. Environ Sci Technol 36:373–380
Hu B, Shen L, Xu X, Zheng P (2011) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in different natural ecosystems. Biochem Soc Trans 39:1811
Inoue K, Qian X, Morgado L, Kim BC, Mester T, Izallalen M, Salgueiro CA, Lovley DR (2010) Purification and characterization of OmcZ, an outer-surface, octaheme c-type cytochrome essential for optimal current production by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3999–4007
Jetten M, Schmid M, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Sinninghe Damsté J, Strous M (2005) Anammox organisms: enrichment, cultivation, and environmental analysis. Methods Enzymol 397:34–57
Jetten MSM, Niftrik L, Strous M, Kartal B, Keltjens JT, Op den Camp HJM (2009) Biochemistry and molecular biology of anammox bacteria. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 44:65–84
Kampschreur MJ, Kleerebezem R, de Vet WWJM, van Loosdrecht M (2011) Reduced iron induced nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emission. Water Res 45:5945–5952
Karlsson R, Karlsson A, Bäckman O, Johansson BR, Hulth S (2009) Identification of key proteins involved in the anammox reaction. FEMS Microbiol Lett 297:87–94
Kartal B, Geerts W, Jetten MS (2011) Cultivation, detection, and ecophysiology of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Methods Enzymol 486:89–108
Kartal B, Almeida NM, Maalcke WJ, Camp HJ, Jetten MS, Keltjens JT (2013) How to make a living from anaerobic ammonium oxidation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:428–461
Kartal B, Maalcke WJ, de Almeida NM et al (2011) Molecular mechanism of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Nature 479:127–130
Liu S, Gong Z, Yang F, Zhang H, Shi L, Furukawa K (2008) Combined process of urea nitrogen removal in anaerobic Anammox co-culture reactor. Bioresour Technol 99:1722–1728
Lovley DR (2000) Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Environmental microbe-metal interactions. ASM Press, Washington, pp 3–30
Myers CR, Myers JM (1992) Localization of cytochromes to the outer membrane of anaerobically grown Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol 174:3429–3438
Myers CR, Myers JM (1993) Ferric reductase is associated with the membranes of anaerobically grown Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 108:15–22
Nielsen JL, Juretschko S, Wagner M, Nielsen PH (2002) Abundance and phylogenetic affiliation of iron reducers in activated sludge as assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4629–4636
Oshiki M, Ishii S, Yoshida K, Fujii N, Ishiguro M, Satoh H, Okabe S (2013) Nitrate-dependent ferrous iron oxidation by anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4087–4093
Park W, Nam Y-K, Lee M-J, Kim T-H (2009) Anaerobic ammonia-oxidation coupled with Fe3 + reduction by an anaerobic culture from a piggery wastewater acclimated to NH4 +/Fe3 + medium. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 14:680–685
Pepper S, Borkowski M, Richmann M, Reed D (2010) Determination of ferrous and ferric iron in aqueous biological solutions. Anal Chim Acta 663:172–177
Pernthaler J, Glöckner FO, Schönhuber W, Amann R (2001) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Methods microbiol 30:207–226
Ruebush SS, Brantley SL, Tien M (2006) Reduction of soluble and insoluble iron forms by membrane fractions of Shewanella oneidensis grown under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2925–2935
Schmid M, Schmitz-Esser S, Jetten M, Wagner M (2001) 16S–23S rDNA intergenic spacer and 23S rDNA of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria: implications for phylogeny and in situ detection. Environ Microbiol 3:450–459
Schmid MC, Maas B, Dapena A et al (2005) Biomarkers for in situ detection of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1677–1684
Schouten S, Strous M, Kuypers MMM, Rijpstra WIC, Baas M, Schubert CJ, Jetten MSM, Damsté JSS (2004) Stable carbon isotopic fractionations associated with inorganic carbon fixation by anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3785–3788
Stein LY, La Duc MT, Grundl TJ, Nealson KH (2002) Bacterial and archaeal populations associated with freshwater ferromanganous micronodules and sediments. Environ Microbiol 3:10–18
Stookey LL (1970) Ferrozine—a new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal Chem 42:779–781
Strous M, Fuerst JA, Kramer EH, Logemann S, Muyzer G, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Webb R, Kuenen JG, Jetten MS (1999) Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 400:446–449
Strous M, Pelletier E, Mangenot S et al (2006) Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anammox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 440:790–794
Van de Graaf AA, de Bruijn P, Robertson LA, Jetten MSM, Kuenen JG (1996) Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing micro-organisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 142:2187–2196
van Niftrik L, Geerts WJC, van Donselaar EG, Humbel BM, Yakushevska A, Verkleij AJ, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2008) Combined structural and chemical analysis of the anammoxosome: a membrane-bounded intracytoplasmic compartment in anammox bacteria. J Struct Biol 161:401–410
Van Niftrik L, Geerts WJC, Van Donselaar EG, Humbel BM, Webb RI, Fuerst JA, Verkleij AJ, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2008) Linking ultrastructure and function in four genera of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria: cell plan, glycogen storage, and localization of cytochrome C proteins. J Bacteriol 190:708–717
Vargas M, Kashefi K, Blunt-Harris EL, Lovley DR (1998) Microbiological evidence for Fe(III) reduction on early earth. Nature 395:65–67
Vorhies JS, Gaines RR (2009) Microbial dissolution of clay minerals as a source of iron and silica in marine sediments. Nat Geosci 2(3)
Wang Z, Liu C, Wang X et al (2008) Kinetics of reduction of Fe(III) complexes by outer membrane cytochromes MtrC and OmcA of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6746–6755
Yang WH, Weber KA, Silver WL (2012) Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction. Nat Geosci 5:538–541
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to show our deepest gratitude to the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20110041110002) and Major State Science and Technology Water Projects (No.2013ZX07202010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Zhang, H., Li, Y. et al. Research of Iron Reduction and the Iron Reductase Localization of Anammox Bacteria. Curr Microbiol 69, 880–887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0668-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0668-7