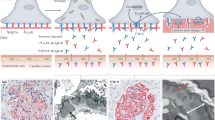
Abstract
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a non-inflammatory organ-specific autoimmune disease which affects the kidney glomerulus, resulting in the formation of immune deposits on the outer aspect of the glomerular basement membrane, complement-mediated proteinuria, and severe renal failure in 30 % of patients. In the last 10 years, substantial advances have been made in the understanding of the molecular bases of MN, with the identification of several antigens and predisposing genes in children and adults. These ground-breaking findings already have a major impact on diagnosis and monitoring and to some extent on therapies. However, there is evidence that the disease is more complex and involves a variety of antigen–antibody systems and genes involved in immune response, progression, recovery, and protective mechanisms. We herein review these recent findings which open new perspectives of research. Understanding the complex pathogenesis of MN will offer many opportunities for future therapeutic interventions and will hopefully have a major impact on patient care. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of MN may also enlighten the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerjaschki D (2000) Pathogenetic concepts of membranous glomerulopathy (MGN). J Nephrol 13:S96–S100
Glassock RJ (2010) The pathogenesis of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a 50-year odyssey. Am J Kidney Dis 56:157–167
Ronco P, Debiec H (2010) Antigen identification in membranous nephropathy moves toward targeted monitoring and new therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:564–569
Simon P, Ramée MP, Autuly V, Laruelle E, Charasse C, Cam G, Ang KS (1994) Epidemiology of primary glomerular diseases in a French region. Variations according to period and age. Kidney Int 46:1192–1198
Maisonneuve P, Agodoa L, Gellert R, Stewart JH, Buccianti G, Lowenfels AB, Wolfe RA, Jones E, Disney AP, Briggs D, McCredie M, Boyle P (2000) Distribution of primary renal diseases leading to end-stage renal failure in the United States, Europe, and Australia/New Zealand: results from an international comparative study. Am J Kidney Dis 35:157–165
Eddy AA, Symons JM (2003) Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 362:629–639
Chen A, Frank R, Vento S, Crosby V, Chandra M, Gauthier B, Valderrama E, Trachtman H (2007) Idiopathic membranous nephropathy in pediatric patients: presentation, response to therapy, and long-term outcome. BMC Nephrol 6:8–11
Polanco N, Gutiérrez E, Covarsí A, Ariza F, Carreño A, Vigil A, Baltar J, Fernández-Fresnedo G, Martín C, Pons S, Lorenzo D, Bernis C, Arrizabalaga P, Fernández-Juárez G, Barrio V, Sierra M, Castellanos I, Espinosa M, Rivera F, Oliet A, Fernández-Vega F, Praga M (2010) Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:697–704
Polanco N, Gutiérrez E, Rivera F, Castellanos I, Baltar J, Lorenzo D, Praga M (2012) Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in membranous nephropathy with chronic renal impairment. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:231–234
Glassock RJ (2003) Diagnosis and natural course of membranous nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 23:324–332
Glassock RJ (2004) The treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a dilemma or a conundrum? Am J Kidney Dis 44:562–566
Hofstra JM, Fervenza FC, Wetzels JF (2013) Treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 9:443–458
Waldman M, Austin HA III (2009) Controversies in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 5:469–479
Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SGF, Hunter JL (1959) Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 100:660–664
Van Damme BJ, Fleuren GJ, Bakker WW, Vernier RL, Hoedemaeker PJ (1978) Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Investig 38:502–510
Couser WG, Steinmuller DR, Stilmant MM, Salant DJ, Lowenstein LM (1978) Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest 62:1275–1287
Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1982) The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79:5557–5561
Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1983) Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (gp330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med 157:667–686
Shah P, Tramontano A, Makker SP (2007) Intramolecular spreading in Heymann nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:3060–3066
Prabakaran T, Nielsen R, Larsen JV, Sørensen SS, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Saleem MA, Petersen CM, Verroust PJ, Christensen EI (2011) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of α-galactosidase A in human podocytes in Fabry disease. PLoS One 6:e25065
Border WA, Ward HJ, Kamil ES, Cohen AH (1982) Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest 69:451–461
Adler SG, Wang H, Ward HJ, Cohen AH, Border WA (1983) Electrical charge. Its role in the pathogenesis and prevention of experimental membranous nephropathy in the rabbit. J Clin Invest 71:487–499
Koyama A, Inage H, Kobayashi M, Nakamura H, Narita M, Tojo S (1986) Effect of chemical cationization of antigen on glomerular localization of immune complexes in active models of serum sickness nephritis in rabbits. Immunology 58:529–534
Bass PS, Drake AF, Wang Y, Thomas JH, Davies DR (1990) Cationization of bovine serum albumin alters its conformation as well as its charge. Lab Investig 62:185–188
Wright NG, Mohammed NA, Eckersall PD, Nash AS (1985) Experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis in dogs receiving cationized bovine serum albumin. Res Vet Sci 38:322–328
Koyama A, Inage H, Kobayashi M, Ohta Y, Narita M, Tojo S, Cameron JS (1986) Role of antigenic charge and antibody avidity on the glomerular immune complex localization in serum sickness of mice. Clin Exp Immunol 64:606–614
Kobayashi M, Muro K, Yoh K, Kondoh M, Iwabuchi S, Hirayama K, Ishizu (1998) Effects of FK506 on experimental membranous glomerulonephritis induced by cationized bovine serum albumin in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:2501–2508
Debiec H, Guigonis V, Mougenot B, Decobert F, Haymann JP, Bensman A, Deschênes G, Ronco PM (2002) Antenatal membranous glomerulonephritis due to anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies. N Engl J Med 346:2053–2060
Ronco P, Debiec H, Guigonis V (2006) Mechanisms of disease: alloimmunization in renal diseases. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2:388–397
Platt JL, Tucker WL, Michael AF (1983) Stages of renal ontogenesis identified by monoclonal antibodies reactive with lymphohematopoietic differentiation antigens. J Exp Med 157:155–172
Appay MD, Mounier F, Gubler MC, Rouchon M, Beziau A, Kazatchkine MD (1985) Ontogenesis of the glomerular C3b receptor (CR1) in fetal human kidney. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 37:103–113
Debiec H, Nauta J, Coulet F, van der Burg M, Guigonis V, Schurmans T, de Heer E, Soubrier F, Janssen F, Ronco P (2004) Role of truncating mutations in MME gene in feto-maternal allo-immunization and neonatal glomerulopathies. Lancet 364:1252–1259
Ronco P, Debiec H (2005) Molecular pathomechanisms of membranous nephropathy: from Heymann nephritis to alloimmunization. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1205–1213
Vivarelli M, Gerken C, Pelle T, Pedicelli S, Diomedi F, Klaus G, Waldegger S, Emma F, Ronco P, Debiec H (2013) Alloimmune membranous nephropathy with anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies: genetic homogeneity but IgG subclass-dependent clinical variability. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28 (suppl 1). ERA-EDTA congress in Istanbul 2013.
Nortier JL, Debiec H, Tournay Y, Mougenot B, Nöel JC, Deschodt-Lanckman MM, Janssen F, Ronco P (2006) Neonatal disease in neutral endopeptidase alloimmunization: lessons for immunological monitoring. Pediatr Nephrol 1:1399–1405
Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, Beck DM, Powell DW, Cummins TD, Klein JB, Salant DJ (2009) M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic MN. N Engl J Med 361:11–21
Stahl R, Hoxha E, Fechner K (2010) PLA2R autoantibodies and recurrent membranous nephropathy after transplantation. N Engl J Med 363:496–498
Blosser CD, Ayalon R, Nair R, Thomas C, Beck LH Jr (2012) Very early recurrence of anti-phospholipase A2 receptor-positive membranous nephropathy after transplantation. Am J Transplant 12:1637–1642
Debiec H, Martin L, Jouanneau C, Dautin G, Mesnard L, Rondeau E, Mousson C, Ronco P (2011) Autoantibodies specific for the phospholipase A(2) receptor in recurrent and de novo membranous nephropathy. Am J Transplant 11:2144–2152
Debiec H, Hanoy M, Francois A, Guerrot D, Ferlicot S, Johanet C, Aucouturier P, Godin M, Ronco P (2012) Recurrent membranous nephropathy in an allograft caused by IgG3κ targeting the PLA2 receptor. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1949–1954
East L, Isacke CM (2002) The mannose receptor family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1572:364–386
Llorca O (2008) Extended and bent conformations of the mannose receptor family. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1302–1310
Behnert A, Fritzler MJ, Teng B, Zhang M, Bollig F, Haller H, Skoberne A, Mahler M, Schiffer M (2013) An anti-phospholipase A2 receptor quantitative immunoassay and epitope analysis in membranous nephropathy reveals different antigenic domains of the receptor. PLoS One 8(4):e61669
Vangelista A, Tazzari R, Bonomini V (1988) Idiopathic membranous nephropathy in twin brothers. Nephron 50:79–80
Bockenhauer D, Debiec H, Sebire N, Barratt M, Warwicker P, Ronco P, Kleta R (2008) Familial membranous nephropathy: an X-linked genetic susceptibility? Nephron Clin Pract 108:10–15
Short CD, Feehally J, Gokal R, Mallick NP (1984) Familial membranous nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289:1500
Vasmant D, Murnaghan K, Bensman A, Muller JY, Mougenot B (1984) Familial idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis. Int J Pediatr Nephrol 5:193–196
Sato K, Oguchi H, Hora K, Furukawa T, Furuta S, Shigematsu H, Yoshizawa S (1987) Idiopathic membranous nephropathy in two brothers. Nephron 46:174–178
Elshihabi I, Kaye CI, Brzowski A (1993) Membranous nephropathy in two human leukocyte antigen-identical brothers. J Pediatr 123:940–942
Chen JS, Chen A, Chang LC, Chang WS, Lee HS, Lin SH, Lin YF (2004) Mouse model of membranous nephropathy induced by cationic bovine serum albumin: antigen dose–response relations and strain differences. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:2721–2728
Bagchus WM, Hoedemaeker PJ, Vos JT, Bakker WW (1989) Thymocytes reacting with heterologous antibodies against GP 330 in autologous immune complex glomerulopathy (AICG) in the rat. The relation between susceptibility for AICG and anti-GP 330-binding thymocytes. Immunobiology 179:432–444
Klouda PT, Manos J, Acheson EJ, Dyer PA, Goldby FS, Harris R, Lawler W, Mallick NP, Williams G (1979) Strong association between idiopathic membranous nephropathy and HLA-DRW3. Lancet 2:770–771
Le Petit JC, Laurent B, Berthoux FC (1982) HLA-DR3 and idiopathic membranous nephritis (IMN) association. Tissue Antigens 20:227–228
Berthoux FC, Alamartine E, Laurent B, Berthoux P, Vacherot C, Lambert C, Le Petit JC (1984) Immunogenetics and immunopathology of human primary membranous glomerulonephritis: HLA-A, B, DR antigens functional activity of splenic macrophage Fc-receptors and peripheral blood T-lymphocyte subpopulations. Clin Nephrol 22:15–20
Vaughan RW, Demaine AG, Welsh KI (1989) A DQA1 allele is strongly associated with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Tissue Antigens 34:261–269
Dyer PA, Short CD, Clarke EA, Mallick NP (1992) HLA antigen and gene polymorphisms and haplotypes established by family studies in membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 7(Suppl 1):42–47
Sacks SH, Warner C, Campbell RD, Dunham I (1993) Molecular mapping of the HLA class II region in HLA-DR3 associated idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 39:S13–S19
Chevrier D, Giral M, Perrichot R, Latinne D, Coville P, Muller JY, Soulillou JP, Bignon JD (1997) Idiopathic and secondary membranous nephropathy and polymorphism at TAP1 and HLA-DMA loci. Tissue Antigens 50:164–169
Stanescu HC, Arcos-Burgos M, Medlar A, Bockenhauer D, Kottgen A, Dragomirescu L, Voinescu C, Patel N, Pearce K, Hubank M, Stephens HA, Laundy V, Padmanabhan S, Zawadzka A, Hofstra JM, Coenen MJ, den Heijer M, Kiemeney LA, Bacq-Daian D, Stengel B, Powis SH, Brenchley P, Feehally J, Rees AJ, Debiec H, Wetzels JF, Ronco P, Mathieson PW, Kleta R (2011) Risk HLA-DQA1 and PLA(2)R1 alleles in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 364:616–626
Kanigicherla D, Gummadova J, McKenzie EA, Roberts SA, Harris S, Nikam M, Poulton K, McWilliam L, Short CD, Venning M, Brenchley PE (2013) Anti-PLA2R antibodies measured by ELISA predict long-term outcome in a prevalent population of patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 83:940–948
Bullich G, Ballarín J, Oliver A, Ayasreh N, Silva I, Santín S, Díaz-Encarnación MM, Torra R, Ars E (2014) HLA-DQA1 and PLA2R1 polymorphisms and risk of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:335–343
Liu YH, Chen CH, Chen SY, Lin YJ, Liao WL, Tsai CH, Wan L, Tsai FJ (2010) Association of phospholipase A2 receptor 1 polymorphisms with idiopathic membranous nephropathy in Chinese patients in Taiwan. J Biomed Sci 17:81–88
Kim S, Chin HJ, Na KY, Kim S, Oh J, Chung W, Noh JW, Lee YK, Cho JT, Lee EK, Chae DW (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the phospholipase A2 receptor gene are associated with genetic susceptibility to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nephron Clin Pract 117:c253–c258
Lv J, Hou W, Zhou X, Liu G, Zhou F, Zhao N, Hou P, Zhao M, Zhang H (2013) Interaction between PLA2R1 and HLA-DQA1 variants associates with anti-PLA2R antibodies and membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1323–1329
Coenen MJ, Hofstra JM, Debiec H, Stanescu HC, Medlar AJ, Stengel B, Boland-Augé A, Groothuismink JM, Bockenhauer D, Powis SH, Mathieson PW, Brenchley PE, Kleta R, Wetzels JF, Ronco P (2013) Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R1) sequence variants in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:677–683
Bantis C, Heering PJ, Aker S, Siekierka M, Kuhr N, Grabensee B, Ivens K (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene G-308A polymorphism is a risk factor for the development of membranous glomerulonephritis. Am Nephrol 26:12–15
Thibaudin D, Thibaudin L, Berthoux P, Mariat C, Filippis JP, Laurent B, Alamartine E, Berthoux F (2007) TNFA2 and d2 alleles of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphism are associated with onset/occurrence of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 71:431–437
Honkanen E, von Willebrand E, Teppo AM, Törnroth T, Grönhagen-Riska C (1998) Adhesion molecules and urinary tumor necrosis factor-alpha in idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 53:909–917
Neale TJ, Rüger BM, Macaulay H, Dunbar PR, Hasan Q, Bourke A, Murray-McIntosh RP, Kitching AR (1995) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is expressed by glomerular visceral epithelial cells in human membranous nephropathy. Am J Pathol 146:1444–1454
Tabibzadeh S, Kong QF, Kapur S et al (1995) TNF-alpha induces dyscohesion of epithelial cells-association with disassembly of actin filaments. Endocrine 3:549–556
Huber TB, Benzing T (2005) The slit diaphragm: a signaling platform to regulate podocyte function. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14:211–216
Lo WY, Chen SY, Wang HJ, Shih HC, Chen CH, Tsai CH, Tsai FJ (2010) Association between genetic polymorphisms of the NPHS1 gene and membranous in the Taiwanese population. Clin Chim Acta 411:714–718
Chen CH, Shu KH, Wen MC, Chen KJ, Cheng CH, Lian JD, Wu MJ, Yu TM, Tsai FJ (2008) Impact of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene polymorphisms on primary membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3166–3173
Luo Y, Wang C, Tu H (2014) Impact of the 4G/5G polymorphism in the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene on primary nephrotic syndrome. Mol Med Rep 9:894–898
Chen SY, Chen CH, Huang YC, Chuang HM, Lo MM, Tsai FJ (2010) Effect of IL-6C-572G polymorphism on idiopathic membranous nephropathy risk in a Han Chinese population. Ren Fail 32:1172–1176
Chen SY, Chen CH, Huang YC, Chan CJ, Hsieh YY, Yu MC, Tsai CH, Tsai FJ (2011) Association of STAT4 polymorphisms with susceptibility to primary membranous glomerulonephritis and renal failure. Clin Chim Acta 412:1899–1904
Chen YT, Wei CC, Ng KL, Chen CH, Chan CJ, Chen XX, Chang YY, Chen SY, Tsai FJ (2013) Toll-like receptor 9 SNPs are susceptible to the development and progression of membranous glomerulonephritis: 27 years follow-up in Taiwan. Ren Fail 35:1370–1375
Debiec H, Ronco P (2011) Nephrotic syndrome: a new specific test for idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:496–498
Hoxha E, Harendza S, Zahner G, Panzer U, Steinmetz O, Fechner K, Helmchen U, Stahl RA (2011) An immunofluorescence test for phospholipase-A2-receptor antibodies and its clinical usefulness in patients with membranous glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:2526–2532
Dähnrich C, Komorowski L, Probst C, Seitz-Polski B, Esnault V, Wetzels JF, Hofstra JM, Hoxha E, Stahl RA, Lambeau G, Stöcker W, Schlumberger W (2013) Development of a standardized ELISA for the determination of autoantibodies against human M-type phospholipase A2 receptor in primary membranous nephropathy. Clin Chim Acta 421:213–218
Qin W, Beck LH Jr, Zeng C, Chen Z, Li S, Zuo K, Salant DJ, Liu Z (2011) Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1137–1143
Knehtl M, Debiec H, Kamgang P, Callard P, Cadranel J, Ronco P, Boffa JJ (2011) A case of phospholipase A2 receptor-positive membranous nephropathy preceding sarcoid-associated granulomatous tubulointerstitial nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 57:140–143
Nawaz FA, Larsen CP, Troxell ML (2013) Membranous nephropathy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Am J Kidney Dis 62:1012–1017
Huang X, Qin W, Zhang M, Zheng C, Zeng C, Liu Z (2013) Detection of anti-PLA2R autoantibodies and IgG subclasses in post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation membranous nephropathy. Am J Med Sci 346:32–37
Svobodova B, Honsova E, Ronco P, Tesar V, Debiec H (2013) Kidney biopsy is a sensitive tool for retrospective diagnosis of PLA2R-related membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:1839–1844
Larsen CP, Messias NC, Silva FG, Messias E, Walker PD (2013) Determination of primary versus secondary membranous glomerulopathy utilizing phospholipase A2 receptor staining in renal biopsies. Mod Pathol 26:709–715
Debiec H, Ronco P (2011) PLA2R autoantibodies and PLA2R glomerular deposits in membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 364:689–690
Hoxha E, Kneißler U, Stege G, Zahner G, Thiele I, Panzer U, Harendza S, Helmchen UM, Stahl RA (2012) Enhanced expression of the M-type phospholipase A2 receptor in glomeruli correlates with serum receptor antibodies in primary membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 82:797–804
Kuroki A, Shibata T, Honda H, Totsuka D, Kobayashi K, Sugisaki T (2002) Glomerular and serum IgG subclasses in diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis, membranous lupus nephritis, and idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Intern Med 41:936–942
Ohtani H, Wakui H, Komatsuda A, Okuyama S, Masai R, Maki N, Kigawa A, Sawada K, Imai H (2004) Distribution of glomerular IgG subclass deposits in malignancy-associated membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:574–579
Segawa Y, Hisano S, Matsushita M, Fujita T, Hirose S, Takeshita M, Iwasaki H (2010) IgG subclasses and complement pathway in segmental and global membranous nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1091–1099
Qu Z, Liu G, Li J, Wu LH, Tan Y, Zheng X, Ao J, Zhao MH (2012) Absence of glomerular IgG4 deposition in patients with membranous nephropathy may indicate malignancy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1931–1937
Hofstra JM, Beck LH Jr, Beck DM, Wetzels JF, Salant DJ (2011) Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies correlate with clinical status in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1286–1291
Beck LH Jr, Fervenza FC, Beck DM, Bonegio RG, Malik FA, Erickson SB, Cosio FG, Cattran DC, Salant DJ (2011) Rituximab-induced depletion of anti-PLA2R autoantibodies predicts response in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1543–1550
Hofstra JM, Debiec H, Short CD, Pellé T, Kleta R, Mathieson PW, Ronco P, Brenchley PE, Wetzels JF (2012) Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1735–1743
Oh YJ, Yang SH, Kim DK, Kang SW, Kim YS (2013) Autoantibodies against phospholipase A2 receptor in Korean patients with membranous nephropathy. PLoS One 8:e62151
Hofstra J, Bech A, Brenchley P, Wetzels J (2013) Measurement of anti PLA2R antibodies predicts relapse rate after immunosuppressive therapy in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy, abstract [OR049] ASN meeting Atlanta 2013
Hu SL, Wang D, Gou WJ, Lei QF, Ma TA, Cheng JZ (2014) Diagnostic value of phospholipase A(2) receptor in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nephrol 27:111–116
Briganti EM, Russ GR, McNeil JJ, Atkins RC, Chadban SJ (2002) Risk of renal allograft loss from recurrent glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med 347:103–109
Dabade TS, Grande JP, Norby SM, Fervenza FC, Cosio FG (2008) Recurrent idiopathic membranous nephropathy after kidney transplantation: a surveillance biopsy study. Am J Transplant 8:1318–1322
Larsen CP, Walker PD (2013) Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) staining is useful in the determination of de novo versus recurrent membranous glomerulopathy. Transplantation 95:1259–1262
Takahashi S, Hiromura K, Tsukida M, Ohishi Y, Hamatani H, Sakurai N, Sakairi T, Ikeuchi H, Kaneko Y, Maeshima A, Kuroiwa T, Yokoo H, Aoki T, Nagata M, Nojima Y (2013) Nephrotic syndrome caused by immune-mediated acquired LCAT deficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1305–1312
Prunotto M, Carnevali ML, Candiano G, Murtas C, Bruschi M, Corradini E, Trivelli A, Magnasco A, Petretto A, Santucci L, Mattei S, Gatti R, Scolari F, Kador P, Allegri L, Ghiggeri GM (2010) Autoimmunity in membranous nephropathy targets aldose reductase and SOD2. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:507–519
Bruschi M, Carnevali ML, Murtas C, Candiano G, Petretto A, Prunotto M, Gatti R, Argentiero L, Magistroni R, Garibotto G, Scolari F, Ravani P, Gesualdo L, Allegri L, Ghiggeri GM (2011) Direct characterization of target podocyte antigens and auto-antibodies in human membranous glomerulonephritis: alfa-enolase and borderline antigens. J Proteomics 74:2008–2017
Murtas C, Bruschi M, Candiano G, Moroni G, Magistroni R, Magnano A, Bruno F, Radice A, Furci L, Argentiero L, Carnevali ML, Messa P, Scolari F, Sinico RA, Gesualdo L, Fervenza FC, Allegri L, Ravani P, Ghiggeri GM (2012) Coexistence of different circulating anti-podocyte antibodies in membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1394–1400
Ronco P, Debiec H, Imai H (2013) Circulating antipodocyte antibodies in membranous nephropathy: pathophysiologic and clinical relevance. Am J Kidney Dis 62:16–19
Debiec H, Lefeu F, Kemper MJ, Niaudet P, Deschênes G, Remuzzi G, Ulinski T, Ronco P (2011) Early childhood membranous nephropathy due to cationic bovine serum albumin. N Engl J Med 364:2101–2110
Sathe SK, Teuber SS, Roux KH (2005) Effects of food processing on the stability of food allergens. Biotechnol Adv 23:423–429
Sanchez C, Fremont S (2003) Consequences of heat treatment and processing of food on the structure and allergenicity of component proteins. Rev Fr Allergol Immunol Clin 43:13–20
van Elburg RM, Fetter WP, Bunkers CM, Heymans HS (2003) Intestinal permeability in relation to birth weight and gestational and postnatal age. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 88:F52–F55
Sreedharan R, Mehta DI (2004) Gastrointestinal tract. Pediatrics 113:1044–1050
Torente F, Murch S (2004) Food allergic enteropathy. In: Walker AW, Goulet O, Kleinman RE et al (eds) Pediatric gastrointestinal disease, 4th edn. BC Decker, Hamilton, pp 944–958
Richards SM (2002) Immunologic considerations for enzyme replacement therapy in the treatment of lysosomal storage disorders. Clin Appl Immunol Rev 2:241–253
Brooks DA (1999) Immune response to enzyme replacement therapy in lysosomal storage disorder patients and animal models. Mol Genet Metab 68:268–275
Koren E, Zuckerman LA, Mire-Sluis AR (2002) Immune responses to therapeutic proteins in humans—clinical significance, assessment and prediction. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 3:349–360
Hunley TE, Corzo D, Dudek M, Kishnani P, Amalfitano A, Chen YT, Richards SM, Phillips JA 3rd, Fogo AB, Tiller GE (2004) Nephrotic syndrome complicating alpha-glucosidase replacement therapy for Pompe disease. Pediatrics 114:e532–e535
Debiec H, Valayannopoulos V, Boyer O, Nöel LH, Callard P, Sarda H, de Lonlay P, Niaudet P, Ronco P (2013) Allo-immune membranous nephropathy and recombinant aryl sulfatase replacement therapy: a need for tolerance induction therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:675–680
Jordan SC, Buckingham B, Sakai R, Olson D (1981) Studies of immune-complex glomerulonephritis mediated by human thyroglobulin. N Engl J Med 304:1212–1215
Hörl WH, Kerjaschki D (2000) Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN). J Nephrol 13:291–316
Bhimma R, Coovadia HM (2004) Hepatitis B virus-associated nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 24:198–211
Nakahara K, Takahashi H, Okuse C, Shigefuku R, Yamada N, Murao M, Matsunaga K, Koike J, Yotsuyanagi H, Suzuki M, Kimura K, Itoh F (2010) Membranous nephropathy associated with chronic hepatitis B occurring in a short period after acute hepatitis B virus infection. Intern Med 49:383–388
Guiard E, Karras A, Plaisier E, Duong Van Huyen JP, Fakhouri F, Rougier JP, Noel LH, Callard P, Delahousse M, Ronco P (2011) Patterns of noncryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis with monoclonal Ig deposits: correlation with IgG subclass and response to rituximab. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1609–1616
de Seigneux S, Bindi P, Debiec H, Alyanakian MA, Aymard B, Callard P, Ronco P, Aucouturier P (2010) Immunoglobulin deposition disease with a membranous pattern and a circulating monoclonal immunoglobulin G with charge-dependent aggregation properties. Am J Kidney Dis 56:117–121
Lundberg K, Venables PJ (2008) Epitope spreading in animal models: array of hope in rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 10:122
Chen L, Hellmark T, Pedchenko V, Hudson BG, Pusey CD, Fox JW, Bolton WK (2006) A nephritogenic peptide induces intermolecular epitope spreading on collagen IV in experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3076–3081
Adler S, Chen X (1992) Anti-Fx1A antibody recognizes a beta 1-integrin on glomerular epithelial cells and inhibits adhesion and growth. Am J Physiol 262:F770–F776
Binstadt BA, Patel PR, Alencar H, Nigrovic PA, Lee DM, Mahmood U, Weissleder R, Mathis D, Benoist C (2006) Particularities of the vasculature can promote the organ specificity of autoimmune attack. Nat Immunol 7:284–292
Spicer ST, Tran GT, Killingsworth MC, Carter N, Power DA, Paizis K, Boyd R, Hodgkinson SJ, Hall BM (2007) Induction of passive Heymann nephritis in complement component 6-deficient PVG rats. J Immunol 179:172–178
Leenaerts PL, Hall BM, Van Damme BJ, Daha MR, Vanrenterghem YF (1995) Active Heymann nephritis in complement component C6 deficient rats. Kidney Int 47:1604–1614
Kerjaschki D, Exner M, Ullrich R, Susani M, Curtiss LK, Witztum JL, Farquhar MG, Orlando RA (1997) Pathogenic antibodies inhibit the binding of apolipoproteins to megalin/gp330 in passive Heymann nephritis. J Clin Invest 100:2303–2309
Turner AJ, Isaac RE, Coates D (2001) The neprilysin (NEP) family of zinc metalloendopeptidases: genomics and function. Bioessays 23:261–269
Ancian P, Lambeau G, Lazdunski M (1995) Multifunctional activity of the extracellular domain of the M-type (180 kDa) membrane receptor for secretory phospholipases A2. Biochemistry 34:13146–13151
Zvaritch E, Lambeau G, Lazdunski M (1996) Endocytic properties of the M-type 180-kDa receptor for secretory phospholipases A2. J Biol Chem 271:250–257
Hanasaki K, Arita H (2002) Phospholipase A2 receptor: a regulator of biological functions of secretory phospholipase A2. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 69:71–82
Lambeau G, Gelb MH (2008) Biochemistry and physiology of mammalian secreted phospholipases A2. Annu Rev Biochem 77:495–520
Augert A, Payré C, de Launoit Y, Gil J, Lambeau G, Bernard D (2009) The M-type receptor PLA2R regulates senescence through the p53 pathway. EMBO Rep 10:271–217
Sis B, Tasanarong A, Khoshjou F, Dadras F, Solez K, Halloran PF (2007) Accelerated expression of senescence associated cell cycle inhibitor p16INK4A in kidneys with glomerular disease. Kidney Int 71:218–226
Cybulsky AV, Quigg RJ, Salant DJ (2005) Experimental membranous nephropathy redux. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F660–F671
Sarma JV, Ward PA (2011) The complement system. Cell Tissue Res 343:227–235
Morgan BP, Haris CL (1999) Regulation in the activation pathways. In: Complement regulatory proteins. Academic, San Diego, pp 41–136
Naik A, Sharma S, Quigg RJ (2013) Complement regulation in renal disease models. Semin Nephrol 33:575–585
Loirat C, Frémeaux-Bacchi V (2011) Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 6:60–90
Hughes AE, Orr N, Esfandiary H, Diaz-Torres M, Goodship T, Chakravarthy U (2006) A common CFH haplotype, with deletion of CFHR1 and CFHR3, is associated with lower risk of age-related macular degeneration. Nat Genet 38:1173–1177
Gold B, Merriam JE, Zernant J, Hancox LS, Taiber AJ, Gehrs K, Cramer K, Neel J, Bergeron J, Barile GR, Smith RT, AMD Genetics Clinical Study Group, Hageman GS, Dean M, Allikmets R (2006) Variation in factor B (BF) and complement component 2 (C2) genes is associated with age-related macular degeneration. Nat Genet 38:458–462
van der Zee JS, van Swieten P, Aalberse RC (1986) Inhibition of complement activation by IgG4 antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol 64:415–422
Aalberse RC, Schuurman J (2002) IgG4 breaking the rules. Immunology 105:9–19
Huang CC, Lehman A, Albawardi A, Satoskar A, Brodsky S, Nadasdy G, Hebert L, Rovin B, Nadasdy T (2013) IgG subclass staining in renal biopsies with membranous glomerulonephritis indicates subclass switch during disease progression. Mod Pathol 26:799–805
Lhotta K, Würzner R, König P (1999) Glomerular deposition of mannose-binding lectin in human glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:881–886
Espinosa-Hernández M, Ortega-Salas R, López-Andreu M, Gómez-Carrasco JM, Pérez-Sáez MJ, Pérez-Seoane C, Aljama-García P (2012) C4d as a diagnostic tool in membranous nephropathy. Nefrologia 32:295–299
Thiel S, Gadjeva M (2009) Humoral pattern recognition molecules: mannan-binding lectin and ficolins. Adv Exp Med Biol 653:58–73
Malhotra R, Wormald MR, Rudd PM, Fischer PB, Dwek RA, Sim RB (1995) Glycosylation changes of IgG associated with rheumatoid arthritis can activate complement via the mannose-binding protein. Nat Med 1:237–243
Bond A, Alavi A, Axford JS, Bourke BE, Bruckner FE, Kerr MA, Maxwell JD, Tweed KJ, Weldon MJ, Youinou P, Hay FC (1997) A detailed lectin analysis of IgG glycosylation, demonstrating disease specific changes in terminal galactose and N-acetylglucosamine. J Autoimmun 10:77–85
Parekh R, Isenberg D, Rook G, Roitt I, Dwek R, Rademacher T (1989) A comparative analysis of disease-associated changes in the galactosylation of serum IgG. J Autoimmun 2:101–114
Ma H, Beck LH Jr, Salant D (2011) J Am Soc Nephrol 22:62A, abstr. ASN congress in 2013.
Rispens T, Ooievaar-De Heer P, Vermeulen E, Schuurman J, van der Neut Kolfschoten M, Aalberse RC (2009) Human IgG4 binds to IgG4 and conformationally altered IgG1 via Fc-Fc interactions. J Immunol 182:4275–4281
Ito T, Kitahara K, Umemura T, Ota M, Shimozuru Y, Kawa S, Bahram S (2010) A novel heterophilic antibody interaction involves IgG4. Scand J Immunol 71:109–114
Nangaku M, Shankland SJ, Couser WG (2005) Cellular response to injury in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1195–1204
Cunningham PN, Quigg RJ (2005) Contrasting roles of complement activation and its regulation in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1214–1222
Tegla CA, Cudrici C, Patel S, Trippe R 3rd, Rus V, Niculescu F, Rus H (2011) Membrane attack by complement: the assembly and biology of terminal complement complexes. Immunol Res 51:45–60
Bohana-Kashtan O, Ziporen L, Donin N, Kraus S, Fishelson Z (2004) Cell signals transduced by complement. Mol Immunol 41:583–597
Moskovich O, Fishelson Z (2000) Live cell imaging of outward and inward vesiculation induced by the complement c5b-9 complex. J Biol Chem 28:29977–29986
Kerjaschki D, Schulze M, Binder S, Kain R, Ojha PP, Susani M, Horvat R, Baker PJ, Couser WG (1989) Transcellular transport and membrane insertion of the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of complement by glomerular epithelial cells in experimental membranous nephropathy. J Immunol 143:546–552
Kon SP, Coupes B, Short CD, Solomon LR, Raftery MJ, Mallick NP, Brenchley PE (1995) Urinary C5b-9 excretion and clinical course in idiopathic human membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 48:1953–1958
Cybulsky AV (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in proteinuric kidney disease. Kidney Int 7:187–193
Cybulsky AV (2013) The intersecting roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress, ubiquitin- proteasome system, and autophagy in the pathogenesis of proteinuric kidney disease. Kidney Int 84:25–33
Wang L, Hong Q, Lv Y, Feng Z, Zhang X, Wu L, Cui S, Hou K, Su H, Huang Z, Wu D, Chen X (2012) Autophagy can repair endoplasmic reticulum stress damage of the passive Heymann nephritis model as revealed by proteomics analysis. J Proteomics 75:3866–3876
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Sievert H, Hoxha E, Sachs M, Klupp EM, Münster S, Balabanov S, Carrier L, Helmchen U, Thaiss F, Stahl RA (2011) Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-l1 activity induces polyubiquitin accumulation in podocytes and increases proteinuria in rat membranous nephropathy. Am J Pathol 178:2044–2057
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Münster S, Klug P, Saleem M, Helmchen U, Stahl RA (2009) A new role for the neuronal ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) in podocyte process formation and podocyte injury in human glomerulopathies. J Pathol 217:452–464
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:89–102
Acknowledgments
Research is supported by European Research Council Grant ERC-2012-ADG_20120314 (Grant Agreement 322947), Agence Nationale pour la Recherche Programme Blanc SVSE1 (2012) Decision ANR-12-BSE1-0002-01, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale Equipe FRM 2012 grant, and 7th Framework Programme of the European Community Contract 2012-305608 (European Consortium for High-Throughput Research in Rare Kidney Diseases).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the special issue on Immunopathology of Glomerular Diseases - Guest Editors: P. Ronco and J. Floege
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debiec, H., Ronco, P. Immunopathogenesis of membranous nephropathy: an update. Semin Immunopathol 36, 381–397 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-014-0423-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-014-0423-y