Abstract
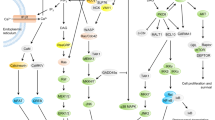
Linker for activation of T cells (LAT) is a membrane adaptor protein that is expressed in T cells and coordinates the assembly of a multiprotein complex—the LAT signalosome—that links the T cell-specific and the ubiquitous components of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling pathway. The present review focuses on recent LAT knock-in mice that were found to develop lymphoproliferative disorders involving polyclonal CD4+ T cells that produced excessive amounts of T helper-type 2 cytokines. These mouse models revealed that LAT constitutes more than just a positive regulator of TCR signaling and plays a negative regulatory role that contributes to terminate antigen-driven T cell responses by exerting a repressive function on components of the TCR signaling cassette that lie upstream of LAT or function independently of LAT. In the absence of such a LAT-operated negative regulatory loop that is intrinsic to conventional CD4+ T cells and of no lesser importance than the extrinsic regulatory mechanisms mediated by regulatory T cells, physiologic, antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses evolve into chronic pro-inflammatory responses that perpetuate themselves in a manner that does not depend on engagement of the TCR and that induce the production of massive amounts of antibodies and autoantibodies in a major histocompatibility complex-II-independent, “quasi-mitogenic” mode. As discussed, these data underscore that a novel immunopathology proper to defective LAT signalosomes is likely taking shape, and we propose to call it “LAT signaling pathology.”
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altan-Bonnet G (2005) Germain RN: modeling T cell antigen discrimination based on feedback control of digital ERK responses. PLoS Biol 3:e356
Mingueneau M, Roncagalli R, Gregoire C, Kissenpfennig A, Miazek A, Archambaud C, Wang Y, Perrin P, Bertosio E, Sansoni A et al (2009) Loss of the LAT adaptor converts antigen-responsive T cells into pathogenic effectors that function independently of the T cell receptor. Immunity 31:197–208
Finco TS, Kadlecek T, Zhang W, Samelson LE, Weiss A (1998) LAT is required for TCR-mediated activation of PLCgamma1 and the Ras pathway. Immunity 9:617–626
Zhang W, Irvin BJ, Trible RP, Abraham RT, Samelson LE (1999) Functional analysis of LAT in TCR-mediated signaling pathways using a LAT-deficient Jurkat cell line. Int Immunol 11:943–950
Aguado E, Richelme S, Nunez-Cruz S, Miazek A, Mura AM, Richelme M, Guo XJ, Sainty D, He HT, Malissen B et al (2002) Induction of T helper type 2 immunity by a point mutation in the LAT adaptor. Science 296:2036–2040
Sommers CL, Park CS, Lee J, Feng C, Fuller CL, Grinberg A, Hildebrand JA, Lacana E, Menon RK, Shores EW et al (2002) A LAT mutation that inhibits T cell development yet induces lymphoproliferation. Science 296:2040–2043
Genton C, Wang Y, Izui S, Malissen B, Delsol G, Fournie GJ, Malissen M, Acha-Orbea H (2006) The Th2 lymphoproliferation developing in LatY136F mutant mice triggers polyclonal B cell activation and systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol 177:2285–2293
Wang Y, Kissenpfennig A, Mingueneau M, Richelme S, Perrin P, Chevrier S, Genton C, Lucas B, DiSanto JP, Acha-Orbea H et al (2008) Th2 lymphoproliferative disorder of LatY136F mutant mice unfolds independently of TCR-MHC engagement and is insensitive to the action of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 180:1565–1575
Lahl K, Loddenkemper C, Drouin C, Freyer J, Arnason J, Eberl G, Hamann A, Wagner H, Huehn J, Sparwasser T (2007) Selective depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induces a scurfy-like disease. J Exp Med 204:57–63
Kim JM, Rasmussen JP, Rudensky AY (2007) Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice. Nat Immunol 8:191–197
Liston A, Enders A, Siggs OM (2008) Unravelling the association of partial T-cell immunodeficiency and immune dysregulation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:545–558
Wang Y, Horvath O, Hamm-Baarke A, Richelme M, Gregoire C, Guinamard R, Horejsi V, Angelisova P, Spicka J, Schraven B et al (2005) Single and combined deletions of the NTAL/LAB and LAT adaptors minimally affect B-cell development and function. Mol Cell Biol 25:4455–4465
Malissen M, Gillet A, Ardouin L, Bouvier G, Trucy J, Ferrier P, Vivier E, Malissen B (1995) Altered T cell development in mice with a targeted mutation of the CD3-epsilon gene. Embo J 14:4641–4653
Sommers CL, Lee J, Steiner KL, Gurson JM, Depersis CL, El-Khoury D, Fuller CL, Shores EW, Love PE, Samelson LE (2005) Mutation of the phospholipase C-gamma1-binding site of LAT affects both positive and negative thymocyte selection. J Exp Med 201:1125–1134
Lin SY, Ardouin L, Gillet A, Malissen M, Malissen B (1997) The single positive T cells found in CD3-zeta/eta−/− mice overtly react with self-major histocompatibility complex molecules upon restoration of normal surface density of T cell receptor-CD3 complex. J Exp Med 185:707–715
Surh CD, Sprent J (2008) Homeostasis of naive and memory T cells. Immunity 29:848–862
Martin B, Banz A, Bienvenu B, Cordier C, Dautigny N, Becourt C, Lucas B (2004) Suppression of CD4+ T lymphocyte effector functions by CD4+CD25+ cells in vivo. J Immunol 172:3391–3398
Nunez-Cruz S, Aguado E, Richelme S, Chetaille B, Mura AM, Richelme M, Pouyet L, Jouvin-Marche E, Xerri L, Malissen B et al (2003) LAT regulates gammadelta T cell homeostasis and differentiation. Nat Immunol 4:999–1008
Archambaud C, Sansoni A, Mingueneau M, Devilard E, Delsol G, Malissen B, Malissen M (2009) STAT6 deletion converts the Th2 inflammatory pathology afflicting Lat(Y136F) mice into a lymphoproliferative disorder involving Th1 and CD8 effector T cells. J Immunol 182:2680–2689
Houtman JC, Houghtling RA, Barda-Saad M, Toda Y, Samelson LE (2005) Early phosphorylation kinetics of proteins involved in proximal TCR-mediated signaling pathways. J Immunol 175:2449–2458
Chiang YJ, Sommers CL, Jordan MS, Gu H, Samelson LE, Koretzky GA, Hodes RJ (2004) Inactivation of c-Cbl reverses neonatal lethality and T cell developmental arrest of SLP-76-deficient mice. J Exp Med 200:25–34
Bunnell SC, Singer AL, Hong DI, Jacque BH, Jordan MS, Seminario MC, Barr VA, Koretzky GA, Samelson LE (2006) Persistence of cooperatively stabilized signaling clusters drives T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol 26:7155–7166
Yamasaki S, Nishida K, Sakuma M, Berry D, McGlade CJ, Hirano T, Saito T (2003) Gads/Grb2-mediated association with LAT is critical for the inhibitory function of Gab2 in T cells. Mol Cell Biol 23:2515–2529
Yasuda T, Bundo K, Hino A, Honda K, Inoue A, Shirakata M, Osawa M, Tamura T, Nariuchi H, Oda H et al (2007) Dok-1 and Dok-2 are negative regulators of T cell receptor signaling. Int Immunol 19:487–495
Dong S, Corre B, Foulon E, Dufour E, Veillette A, Acuto O, Michel F (2006) T cell receptor for antigen induces linker for activation of T cell-dependent activation of a negative signaling complex involving Dok-2, SHIP-1, and Grb-2. J Exp Med 203:2509–2518
Seddon B, Tomlinson P, Zamoyska R (2003) Interleukin 7 and T cell receptor signals regulate homeostasis of CD4 memory cells. Nat Immunol 4:680–686
Shen S, Zhu M, Lau J, Chuck M, Zhang W (2009) The essential role of LAT in thymocyte development during transition from the double-positive to single-positive stage. J Immunol 182:5596–5604
Prinz I, Gregoire C, Mollenkopf H, Aguado E, Wang Y, Malissen M, Kaufmann SH, Malissen B (2005) The type 1 cysteinyl leukotriene receptor triggers calcium influx and chemotaxis in mouse alpha beta- and gamma delta effector T cells. J Immunol 175:713–719
Koonpaew S, Shen S, Flowers L, Zhang W (2006) LAT-mediated signaling in CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cell development. J Exp Med 203:119–129
Roufosse F, Schandene L, Sibille C, Kennes B, Efira A, Cogan E, Goldman M (1999) T-cell receptor-independent activation of clonal Th2 cells associated with chronic hypereosinophilia. Blood 94:994–1002
Dunleavy K, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES (2007) Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma: pathobiological insights and clinical implications. Curr Opin Hematol 14:348–353
Nijnik A, Ferry H, Lewis G, Rapsomaniki E, Leung JC, Daser A, Lambe T, Goodnow CC, Cornall RJ (2006) Spontaneous B cell hyperactivity in autoimmune-prone MRL mice. Int Immunol 18:1127–1137
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Acha-Orbea for discussion. This study is supported by CNRS, INSERM, European Communities (MASTERSWITCH and SYBILLA Integrating Projects), ANR (Plate-forme Technologique du Vivant IBISA), ARC, FRM, and by doctoral fellowships from Ecole Normale Supérieure and ARC (MiM) and postdoctoral fellowships from FNRS (CL) and the European Communities SYBILLA Integrating Project (RR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roncagalli, R., Mingueneau, M., Grégoire, C. et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders involving T helper effector cells with defective LAT signalosomes. Semin Immunopathol 32, 117–125 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-009-0195-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-009-0195-y