Abstract
Purpose
Gemcitabine resistance is the main problem in pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. Hence, we aimed to identify the correlation between expression of RRM1 and CDA as the resistance genes and their predicted targeting miR-608 in the resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines to gemcitabine.
Methods
Dual luciferase assay was performed to determine whether both RRM1 and CDA are targeted by miR-608 in 293T and pancreatic cancer cell lines. AsPC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cell lines became gradually resistant to gemcitabine by exposing to the increasing doses of gemcitabine. After RNA and miRNAs extraction and cDNA conversion, the expressions of RRM1, CDA and miR-608 in all cell lines were studied by quantitative PCR. Pre-miR-608 transfection to the cell lines was done by calcium phosphate method. MTT assay was performed for analyzing the chemo sensitivity of different cell lines to gemcitabine.
Results
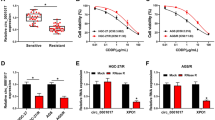
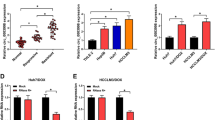
Luciferase assays showed that miR-608 targeted RRM1 and CDA genes in 293T, AsPC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cell lines. Compared to parental cell line, resistant MIA PaCa-2 and AsPC-1 cells demonstrated increased expression of RRM1 and CDA. On the other hand the expression of miR-608 in resistant MIA PaCa-2 and AsPC-1 cells was lower than parental cells. Furthermore, transfection of MIA PaCa-2 and AsPC-1 cells by miR-608 lead to decreased expression of RRM1 and CDA and lowered viability of the cells in comparison with scrambled microRNA transfected cells.
Conclusion
During resistance induction in pancreatic cancer cells, miR-608 which is targeting RRM1 and CDA is downregulated which leads to upregulation of these genes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- GEM:
-
Gemcitabine
- CDA:
-
Cytidine deaminase
- RRM1:
-
Ribonucleotide reductase M1
- dNTP:
-
Deoxynucleoside triphosphate
- miR:
-
miRNA, microRNA
- dFdU:
-
2′2′-Difluorodeoxyuridine
- IC:
-
Inhibitory concentration
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Di methylthiazole-2-yl)-2, 5-biphenyl tetrazolium bromide
References
Long J, Zhang Y, Yu X, Yang J, LeBrun DG, Chen C, Yao Q, Li M (2011) Overcoming drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15(7):817–828
Valsecchi ME, Holdbrook T, Leiby BE, Pequignot E, Littman SJ, Yeo CJ, Brody JR, Witkiewicz AK (2012) Is there a role for the quantification of RRM1 and ERCC1 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma? BMC Cancer 12(1):1
Fujita H, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Itaba S, Ito T, Nakata K, Yu J, Kayashima T, Souzaki R, Tajiri T (2010) Gene expression levels as predictive markers of outcome in pancreatic cancer after gemcitabine-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Neoplasia 12(10):807–808
Hagmann W, Jesnowski R, Löhr JM (2010) Interdependence of gemcitabine treatment, transporter expression, and resistance in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Neoplasia 12(9):740–747
Rajabpour A, Rajaei F, Teimoori-Toolabi L (2016) Molecular alterations contributing to pancreatic cancer chemoresistance. Pancreatology 17(2):310–320
Rukov JL, Shomron N (2011) MicroRNA pharmacogenomics: post-transcriptional regulation of drug response. Trends Mol Med 17(8):412–423
Bhutia YD, Hung SW, Patel B, Lovin D, Govindarajan R (2011) CNT1 expression influences proliferation and chemosensitivity in drug-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Can Res 71(5):1825–1835
Ueno H, Kiyosawa K, Kaniwa N (2007) Pharmacogenomics of gemcitabine: Can genetic studies lead to tailor-made therapy? Br J Cancer 97(2):145–151
Nakano Y, Tanno S, Koizumi K, Nishikawa T, Nakamura K, Minoguchi M, Izawa T, Mizukami Y, Okumura T, Kohgo Y (2007) Gemcitabine chemoresistance and molecular markers associated with gemcitabine transport and metabolism in human pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer 96(3):457–463
Souglakos J, Boukovinas I, Taron M, Mendez P, Mavroudis D, Tripaki M, Hatzidaki D, Koutsopoulos A, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V (2008) Ribonucleotide reductase subunits M1 and M2 mRNA expression levels and clinical outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with docetaxel/gemcitabine. Br J Cancer 98(10):1710–1715
Jordheim LP, Dumontet C (2013) Do hENT1 and RRM1 predict the clinical benefit of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer? Biomarkers 7(4):663–671
Jordheim LP, Sève P, Trédan O, Dumontet C (2011) The ribonucleotide reductase large subunit (RRM1) as a predictive factor in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol 12(7):693–702
Elnaggar M, Giovannetti E, Peters GJ (2012) Molecular targets of gemcitabine action: rationale for development of novel drugs and drug combinations. Curr Pharm Des 18(19):2811–2829
Carpi FM, Vincenzetti S, Ubaldi J, Pucciarelli S, Polzonetti V, Micozzi D, Mignini F, Napolioni V (2013) CDA gene polymorphisms and enzyme activity: genotype–phenotype relationship in an Italian-Caucasian population. Pharmacogenomics 14(7):769–781
Sugiyama E, Kaniwa N, Kim S-R, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Hasegawa R, Maekawa K, Saito Y, Ozawa S, J-i Sawada, Kamatani N (2006) Pharmacokinetics of gemcitabine in Japanese cancer patients: the impact of a cytidine deaminase polymorphism. J Clin Oncol 25(1):32–42
Funamizu N, Okamoto A, Kamata Y, Misawa T, Uwagawa T, Gocho T, Yanaga K, Manome Y (2010) Is the resistance of gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer settled only by overexpression of deoxycytidine kinase? Oncol Rep 23(2):471
Rukov JL, Wilentzik R, Jaffe I, Vinther J, Shomron N (2013) Pharmaco-miR: linking microRNAs and drug effects. Brief Bioinform 15:648–659
Hashimoto Y, Akiyama Y, Yuasa Y (2013) Multiple-to-multiple relationships between microRNAs and target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62589
Zhang XJ, Ye H, Zeng CW, He B, Zhang H, Chen YQ (2010) Dysregulation of miR-15a and miR-214 in human pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol 3(1):1
Hwang J-H, Voortman J, Giovannetti E, Steinberg SM, Leon LG, Kim Y-T, Funel N, Park JK, Kim MA, Kang GH (2010) Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10630
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L, Xiang D, DeSano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D (2009) MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6816
Li Y, VandenBoom TG, Kong D, Wang Z, Ali S, Philip PA, Sarkar FH (2009) Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Can Res 69(16):6704–6712
Park J-K, Lee EJ, Esau C, Schmittgen TD (2009) Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or-221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 38(7):e190–e199
Nakahira S, Nakamori S, Tsujie M, Takahashi Y, Okami J, Yoshioka S, Yamasaki M, Marubashi S, Takemasa I, Miyamoto A (2007) Involvement of ribonucleotide reductase M1 subunit overexpression in gemcitabine resistance of human pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120(6):1355–1363
Azizi M, Teimoori-Toolabi L, Arzanani MK, Azadmanesh K, Fard-Esfahani P, Zeinali S (2014) MicroRNA-148b and microRNA-152 reactivate tumor suppressor genes through suppression of DNA methyltransferase-1 gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther 15(4):419–427
Gheidari F, Bakhshandeh B, Teimoori-Toolabi L, Mehrtash A, Ghadir M, Zeinali S (2014) TCF4 silencing sensitizes the colon cancer cell line to oxaliplatin as a common chemotherapeutic drug. Anticancer Drugs 25(8):908–916
Davidson JD, Ma L, Flagella M, Geeganage S, Gelbert LM, Slapak CA (2004) An increase in the expression of ribonucleotide reductase large subunit 1 is associated with gemcitabine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Can Res 64(11):3761–3766
Bengala C, Guarneri V, Giovannetti E, Lencioni M, Fontana E, Mey V, Fontana A, Boggi U, Del Chiaro M, Danesi R (2005) Prolonged fixed dose rate infusion of gemcitabine with autologous haemopoietic support in advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 93(1):35–40
Liu X, Wang W, Lin L, Song S (2010) Expression of Gemcitabine-resistance-related gene and polymorphism of ribonucleotide reductase M1 gene promoter in Gemcitabine-resistant A549/Gem and NCI-H460/Gem cell lines. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi [Chin J Oncol] 32(1):17–21
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D, Abbruzzesse JL, Frazier ML, Killary AM, Sen S (2009) MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res 2(9):807–813
Zheng J, Deng J, Xiao M, Yang L, Zhang L, You Y, Hu M, Li N, Wu H, Li W (2013) A sequence polymorphism in miR-608 predicts recurrence after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Can Res 73(16):5151–5162
Ma X-P, Yu G, Chen X, Xiao Q, Shi Z, Zhang L-Y, Chen H, Zhang P, Ding D-L, Huang H-X (2016) MiR-608 rs4919510 is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol 37(7):9931–9942
Ryan BM, McClary AC, Valeri N, Robinson D, Paone A, Bowman ED, Robles AI, Croce C, Harris CC (2012) rs4919510 in hsa-mir-608 is associated with outcome but not risk of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 7(5):e36306
Huang A-J, Yu K-D, Li J, Fan L, Shao Z-M (2012) Polymorphism rs4919510: C > G in mature sequence of human microRNA-608 contributes to the risk of HER2-positive breast cancer but not other subtypes. PLoS ONE 7(5):e35252
Alves R, Antunes F, Salvador A (2006) Tools for kinetic modeling of biochemical networks. Nat Biotechnol 24(6):667–672
Wang S, Raghavachari S (2011) Quantifying negative feedback regulation by micro-RNAs. Phys Biol 8(5):055002
Raj A, van Oudenaarden A (2008) Nature, nurture, or chance: stochastic gene expression and its consequences. Cell 135(2):216–226
Pedraza JM, van Oudenaarden A (2005) Noise propagation in gene networks. Science 307(5717):1965–1969
Bhardwaj V, Bhushan A, Lai JC, Tadinada SM (2012) Failure of pancreatic cancer chemotherapy: consequences of drug resistance mechanisms. INTECH Open Access Publisher, Rijeka
Azmi AS, Beck FW, Bao B, Mohammad RM, Sarkar FH (2011) Aberrant epigenetic grooming of miRNAs in pancreatic cancer:a systems biology perspective. Epigenomics 3(6):747–759
Achiwa H, Oguri T, Sato S, Maeda H, Niimi T, Ueda R (2004) Determinants of sensitivity and resistance to gemcitabine: the roles of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 and deoxycytidine kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci 95(9):753–757
Samulitis BK, Pond KW, Pond E, Cress AE, Patel H, Wisner L, Patel C, Dorr RT, Landowski TH (2015) Gemcitabine resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines acquire an invasive phenotype with collateral hypersensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Biol Ther 16(1):43–51
Kasinski AL, Slack FJ (2011) MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: progress in validating and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 11(12):849–864
Funding
This research was funded by Qazvin University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 28/20/10563) and Pasteur Institute of Iran (Grant Number: 94/0201/1405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Azam Rajabpour declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ali Afgar declares that he has no conflict of interest. Habibollah Mahmoodzadeh declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jalal-e-Din Radfar declares that he has no conflict of interest. Farzad Rajaei declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ladan Teimoori-Toolabi declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajabpour, A., Afgar, A., Mahmoodzadeh, H. et al. MiR-608 regulating the expression of ribonucleotide reductase M1 and cytidine deaminase is repressed through induced gemcitabine chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 765–775 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3418-2