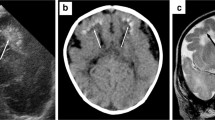
Abstract
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia is a myeloid stem cell disease characterized by an abnormal production and accumulation of monocytic cells in association with other signs of myeloproliferation. Extramedullary manifestations of CMML are common and can affect the spleen, liver skin, and lymph nodes. However, otologic manifestations are extremely rare and could have occurred from either direct leukemic infiltration, hemorrhage of the cochlea, labyrinth, leukostasis, or infection. There is no standard treatment protocol for sensorineural hearing loss in CMML patients. More research is needed to improve the understanding of the pathogenesis of this condition, in order to provide better treatment options.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data used in this manuscript is not publicly available in order to protect patient confidentiality. Reasonable request should be directed to the corresponding author.
Change history
03 November 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05524-8
References
Valent P, Orazi A, Savona MR et al (2019) Proposed diagnostic criteria for classical chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), CMML variants and pre-CMML conditions. Haematologica 104(10):1935–1949
Pudasainee P, Pyakuryal B, Subedi Y et al (2019) Extramedullary manifestation of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: do we treat an acute myeloid leukemia? Case Rep Hematol 2019:8360454. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8360454
Chae SW, Cho JH, Lee JH et al (2002) Sudden hearing loss in chronic myelogenous leukaemia implicating the hyperviscosity syndrome. J Laryngol Otol 116:291–293
Cass ND, Gubbels SP, Portnuff CDF (2018) Sudden bilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo as presenting symptoms of chronic myeloid leukemia. Ann Otology, Rhinol Laryngol 127(10):731–734
Kim HJ, Park EK, Moon IS (2014) A case of sudden hearing loss during treatment with decitabine for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Chinese J Cancer Res 26(1):E1–E4
Kayode AS, Adeleke IA, Oluwatona DA (2018) Sudden sensineural hearing loss in patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia – a case study. Arch Otolaryngol Rhinol 4(4):082–084
Thiel-Klare K, Rogers A, Boston R et al (2022) Mouse model of combination targeted therapy in PTPN11 driven leukemia. Blood 140(Supplement 1):10687–10688. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2022-160358
Greipp PT, Hanson CA, Sharma RG et al (2009) Whole arm duplication of 1q in myeloid neoplasm, with Emphasis On Derivative (1;7)(q10;p10). Blood 114(22):4238. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V114.22.4238.4238
Schreiber BE, Agrup C, Haskard DO et al (2010) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. The Lancet 375:1203–1211
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR et al (2019) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg 161(1_suppl):S1–S45. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599819859885
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RB wrote the manuscript.
MEN corrected and approved the manuscript and provided figures.
YA read and approved manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from patient to publish data.
Conflict of interest
RB has no conflict of interest.
MEN reports stock ownership in 3M, Amgen, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, and Pfizer.
YA has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: This article was originally published with the name of one of the co-authors was inadvertently misspelled. The incorrect spelling "Marc Ellie-Nader" should be corrected to "Marc-Elie Nader."
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babakhanlou, R., Nader, ME. & Alvarado, Y. A case of sudden hearing loss in a patient with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol 102, 3427–3430 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05433-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05433-w