Abstract
Purpose
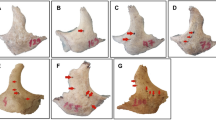
Anatomical knowledge of the zygomatic region is important, because the zygomatic nerve and its branches may suffer lesions during surgical procedures in the periorbital region. The position and frequency of zygomaticofacial foramina (ZFF) may vary between individuals, and between one side and the other in the same individual. In the present study, we analysed the presence and location of ZFF, as well as the distance between them and the orbital cavity, in macerated skulls of adult individuals.
Methods
We examined 287 macerated skulls, of individuals of both sexes, analysing the frequency and location of ZFF and the distance from the ZFF to the margin of the orbital cavity (OC).
Results
Zygomaticofacial foramina are very frequent structures which tend to appear singly. They are generally located in the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, but in many cases, they may be located in the mid portion of the bone. They also tend to appear at the same distance from the OC when left and right sides are compared. Sex was an important factor in determining differences in ZFF; the distance from the ZFF to the margin of the OC was greater in males than in females. Sex, age, side and skin colour did not affect the frequency and location of the ZFF.
Conclusion
We consider that the mid portion of the zygomatic bone is the safest place to anchor zygomatic implants (ZI), since ZFF are less frequently located there than in the temporal process of the zygomatic bone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu F, Ceri NG, Arman C et al (2009) Location and incidence of the zygomaticofacial foramen: an anatomic study. Clin Anat 22:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20805
Alves N (2013) Morphometric analysis of anatomic landmarks involved in surgical technique of zygomatic implants placement. Int J Morphol 31:986–990. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022013000300035
Alves N, Cândido P (2016) Anatomia para o curso de odontologia geral e específica, 4th edn. Editora Santos, São Paulo
Alves N, Deana NF (2016) Evaluation of bony structures involved in surgical technique for installation of zygomatic implants in edentulous macerated skulls. Av Periodoncia 28:29–33
Aparicio C, Ouazzani W, Aparicio A et al (2010) Extrasinus zygomatic implants: three year experience from a new surgical approach for patients with pronounced buccal concavities in the edentulous maxilla. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 12:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2008.00130.x
Aparicio C, Ouazzani W, Hatano N (2008) The use of zygomatic implants for prosthetic rehabilitation of the severely resorbed maxilla. Periodontology 47:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2008.00259.x
Bedrossian E (2010) Rehabilitation of the edentulous maxilla with the zygoma concept: a 7-year prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 25:1213–1221
Bernardi S, Gatto R, Severino M et al (2018) Short versus longer implants in mandibular alveolar ridge augmented using osteogenic distraction: one year follow-up of a randomized split-mouth trial. J Oral Implantol 44:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-D-16-00216
Chrcanovic BR, Abreu MHNG (2013) Survival and complications of zygomatic implants: a systematic review. Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-012-0331-z
Chrcanovic BR, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2016) Survival and complications of zygomatic implants: an updated systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74:1949–1964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2016.06.166
Del Neri NB, Araujo-Pires AC, Andreo JC, Rubira-Bullen IR, Ferreira Júnior O (2014) Zygomaticofacial foramen location accuracy and reliability in cone-beam computed tomography. Acta Otontol Scand 72:157–160. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016357.2013.814804
Ferro A, Basyuni S, Brassett C, Santhanam V (2017) Study of anatomical variations of the zygomaticofacial foramen and calculation of reliable reference points for operation. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.10.016
González José R, Dahinten S, Hernández M (2001) The settlement of patagonia: a matrix correlation study. Hum Biol 73:233–248. https://doi.org/10.1353/hub.2001.0019
Hwang SH, Jin S, Hwang K (2007) Location of the zygomaticofacial foramen related to malar reduction. J Craniofac Surg 18:872–874. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0b013e3180a03353
Kaur J, Choudhry R, Raheja S, Dhissa NC (2012) Non metric traits of the skull and their role in anthropological studies. J Morphol Sci 29:189–194
Kim HS, Oh JH, Choi DY et al (2013) Three-dimensional courses of zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemporal canals using micro-computed tomography in Korean. J Craniofac Surg 24:1565–1568. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e318299775d
Lone M, Telang A, Rajgopal L, Bhuiyan PS (2016) Location and incidence of the zygomatico-facial foramen in dry human skulls: an anatomical study. J Anat Soc India 65:164–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasi.2017.01.001
Malevez C, Abarca M, Durdu F, Daelemans P (2004) Clinical outcome of 103 consecutive zygomatic implants: a 6–48 months follow-up study. Clin Oral Implants Res 15:18–22
Mangal A, Choudhry R, Tuli A et al (2004) Incidence and morphological study of zygomaticofacial and zygomatico-orbital foramina in dry adult human skulls: the non-metrical variants. Surg Radiol Anat 26:96–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0198-7
Nkenke E, Hahn M, Lell M et al (2003) Anatomic site evaluation of the zygomatic bone for dental implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res 14:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.2003.140110.x
Ongeti K, Hassanali J, Ogeng’o J, Saidi H (2008) Biometric features of facial foramina in adult Kenyan skulls. Eur J Anat 12:89–95
Pi Urgell J, Revilla Gutiérrez V, Gay Escoda CG (2008) Rehabilitation of atrophic maxilla: a review of 101 zygomatic implants. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 13:E363–E370
Rigolizzo MB, Camilli JA, Francischone CE et al (2005) Zygomatic bone: anatomic bases for osseointegrated implant anchorage. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 20:441–447
Williams JV (2002) Transblepharoplasty endoscopic subperiosteal midface lift. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1769–1775. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000033904.92556.BA. (discussion 1776–1777)
Williams PL, Bannister LH, Berry MM et al (1995) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine and surgery, 38th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Zhao Y, Chundury R, Blandford A, Perry J (2018) Anatomic description of zygomatic foramina in African American skulls. Ophtal Plast Reconstr Surg 34:167–171. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000905
Acknowledgements
Universidad de La Frontera. Ministerio de Educación, Programa MECE Educación Superior. Department of Morphology and Genetics of UNIFESP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NA: project development, data collection and manuscript writing. NFD: data collection, data analysis and manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deana, N.F., Alves, N. Frequency and location of the zygomaticofacial foramen and its clinical importance in the placement of zygomatic implants. Surg Radiol Anat 42, 823–830 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02455-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02455-1