Abstract
Purpose
Extremely rarely, a persistent hypoglossal artery arises from the external carotid artery; only three cases have been reported in the English-language literature. The purpose of this paper is to report a case of this variation diagnosed by magnetic resonance (MR) angiography.
Methods
A 75-year-old man with sudden-onset right hemiparesis and dysarthria underwent emergency cerebral MR imaging and cerebral MR angiography that included the cervical carotid bifurcation. A 1.5-T scanner was used and MR angiographic images were obtained using the standard three-dimensional time-of-flight technique.
Results
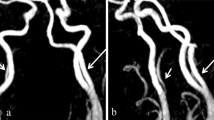
On MR angiography, an anomalous artery arose from the proximal right external carotid artery, ascended just like the ascending pharyngeal artery, entered the hypoglossal canal (anterior condyloid foramen), and finally connected with the terminal segment of the right vertebral artery (VA). The proximal right VA was not visible, probably due to hypoplasia.
Conclusion
We present the first case of this anomaly diagnosed using MR angiography, and we propose the term “type 2 persistent hypoglossal artery” to describe this condition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andoh K, Tanohata K, Moriya N et al (2001) The posterior inferior cerebellar artery arising from the extracranial segment of the internal carotid artery via the hypoglossal canal without an interposed segment of the basilar artery: a persistent primitive hypoglossal artery variant. Clin Imaging 25:86–89
Bohmfalk GL, Story JL (1977) Aneurysms of the persistent hypoglossal artery. Neurosurgery 1:291–296
Brismar J (1976) Persistent hypoglossal artery, diagnostic criteria: report of a case. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 17:160–166
De Caro R, Parenti A, Munari PF (1995) The persistent primitive hypoglossal artery: a rare anatomic variation with frequent clinical implications. Ann Anat 177:193–198
Duffill J, Lang DA, Dwyer N (1996) Subarachnoid haemorrhage in a child from an aneurysm of a persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. Br J Neurosurg 10:607–610
Fujita N, Shimada N, Takimoto H et al (1995) MR appearance of the persistent hypoglossal artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16(4 Suppl):990–992
Gumus T, Onal B, Ilgit ET (2004) Bilateral persistence of type 1 proatlantal arteries: report of a case and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1622–1624
Hacein-Bey L, Daniels DL, Ulmer JL et al (2002) The ascending pharyngeal artery: branches, anastomoses, and clinical significance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1246–1256
Kanai H, Nagai H, Wakabayashi S, Hashimoto N (1992) A large aneurysm of the persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. Neurosurgery 30:794–797
Kim JT, Heo SH, Lee SH et al (2009) An uncommon anastomosis of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery and the external carotid artery with the patent vertebrobasilar system. Br J Radiol 82:e171–e174
Lasjaunias P, Guibert-Tranier F, Braun JP (1981) The pharyngo–cerebellar artery or ascending pharyngeal artery origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. J Neuroradiol 8:317–325
Meguro T, Terada K, Hirotsune N et al (2007) Unusual variant of persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. Br J Radiol 80:e314–e316
Nakamura M, Kobayashi S, Yoshida T et al (2000) Persistent external carotid-vertebrobasilar anastomosis via the hypoglossal canal. Neuroradiology 42:821–823
Uchino A, Sawada A, Takase Y et al (2003) MR angiography of anomalous branches of the internal carotid artery. AJR Am J Roentogenol 181:1409–1414
Vasovic L, Milenkovic Z, Jovanovic I et al (2008) Hypoglossal artery: a review of normal and pathological features. Neurosurg Rev 31:385–396
Welten RJ, Eikelboom BC, Ackerstaff RG et al (1988) A persistent hypoglossal artery arising from the external carotid artery. Eur J Vasc Surg 2:269–272
Yamamoto S, Sunada I, Matsuoka Y et al (1991) Persistent primitive hypoglossal artery aneurysms—report of two cases. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 31:199–202
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchino, A., Saito, N. Persistent hypoglossal artery arising from the external carotid artery diagnosed by MR angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 33, 543–545 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0769-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0769-3