Abstract
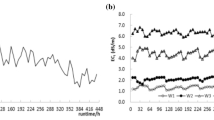
Drip irrigation is the most effective and reliable method for reclaimed water irrigation. The water usually contains a lot of suspended particles, metal salt ions, organisms and microbial communities, which will enhance the possibility of emitter clogging or more complex clogging mechanism. Emitter clogging has become one of the key problems to the application and popularization of the drip irrigation technology. In this paper, we selected four kinds of pressure-compensating emitters and four kinds of non-pressure-compensating emitters, and executed the experiment of drip irrigation with on-site reclaimed water treated with cyclic activated sludge system (CASS). The emitter discharge ratio variation (Dra), coefficient of uniformity (CU) and clogging rate distribution were analyzed to evaluate the emitter clogging characteristics after eliminating the effect of temperature and pressure on the emitter outflow by data correction. The results showed that Dra and CU varied in three periods as system operation. The beginning of experiment was the fluctuated balance period, Dra and CU recurrent fluctuated in 5 %, and the emitters clogged at some spots after the system run 36–48 h. Then the two parameters varied linearly in 60–108 h, tuning into the initiate linear period, as the non-pressure-compensating emitters got an obvious linear change than the pressure-compensating ones with the gradient changed from −0.094 to 0.042 and −0.073 to 0.047, respectively. Some of the emitters have a significant difference on these two parameters at this stage. After the restarting in the second year, Dra and CU decreased sharply. The maximum decrement was, respectively, 9.6 and 10.7 %. Then they varied in line with a greater slope degree as all emitters reached the significant level, the gradient ranges were −0.176 to 0.115 and −0.216 to 0.117, respectively. This stage was called the accelerated linear period. Seriously clogged and completely clogged emitters appeared, and both Dra and CU dropped down to 38.7 and 41.5 %. Various degrees of clogged emitters often emerged in the end part of lateral at first then propelled to the head gradually, the completely clogged emitters in the end accounted for more than 73.0 % when the system run 540 h. Comprehensively considered, the pressure-compensating emitters and cusp-shaped saw-tooth non-pressure-compensating emitters with short flow path are recommended in reclaimed water drip irrigation. These researches are aimed to provide references explaining the emitter clogging mechanism of reclaimed water drip irrigation as well as its technological application and popularization.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adin A, Sacks M (1991) Dripper clogging factor in wastewater irrigation. J Irrig Drain Eng 117(6):813–826
Ahmed BAO, Yamamoto T, Fujiyama H, Miyamoto K (2007) Assessment of emitter discharge in microirrigation system as affected by polluted water. Irrig Drain Syst 21(2):97–107
Asano T, Burton F, Leverenz H, Tsuchihashi R, Tchobanoglous G (2007) Water reuse: issues, technologies and applications. McGraw Hill Inc, New York
Bucks DA, Nakayama FS, Gilbert RG (1979) Trickle irrigation water quality and preventive maintenance. Agric Water Manag 2:149–162
Capra A, Scicolone B (2004) Emitter and filter tests for wastewater reuse by drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 68:135–149
Chen QC, Zheng YQ (1994) The estimation of local head loss in emitters. Inner Mongolia Water Resources 4:52–54
Duran-Ros M, Puig-Bargues J, Arbat G, Barragan J, Cartagena FR (2009) Effect of filter, emitter, and location on clogging when using effluents. Agric Water Manag 96:67–79
Gilbert RG, Nakayama FS, Bucks DA, French OF, Adamson KC (1981) Trickle irrigation: emitter clogging and other flow problems. Agric Water Manag 3(3):159–178
Li YK, Yang PL, Ren SM, Yang L, Wu XB (2005) Hydraulic performance and its mechanism of liquid flow in gravity drip irrigation emitter. Transact Chin Soc Agric Mach 36(10):54–57
Li YK, Yang PL, Ren SM, Xu TW (2006) Hydraulic characterizations of tortuous flow in path drip irrigation emitter. J Hydrodyn Ser B 18(4):449–457
Li JS, Chen L, Li Y (2009) Comparison of clogging in drip emitters during application of sewage effluent and groundwater. Trans ASABE 52(4):1203–1211
Li GB, Li YK, Xu TW, Liu YZ, Jin H, Yang PL, Yan DZ, Ren SM, Tian ZF (2012a) Effects of average velocity on the growth and surface topography of biofilms attached on the reclaimed wastewater drip irrigation system laterals. Irrig Sci 30:103–113
Li JS, Li YF, Zhang H (2012b) Tomato yield and quality and emitter clogging as affected by chlorination schemes of drip irrigation systems applying sewage effluent. J Integr Agric 11(10):1744–1754
Li YK, Liu YZ, Li GB, Xu TW, Liu HS, Ren SM, Yan DZ, Yang PL (2012c) Surface topographic characteristics of suspended particulates in reclaimed wastewater and effects on clogging in labyrinth drip irrigation emitters. Irrig Sci 30:43–56
Liu HJ, Huang GH (2009) Laboratory experiment on drip emitter clogging with fresh water and treated sewage effluent. Agric Water Manag 96:745–756
Nakayama FS, Bucks DA (1991) Water quality in drip/trickle irrigation: a review. Irrig Sci 12:187–192
Provenzano G, Pumo G (2004) Experiment analysis of local pressure losses for microirrigation laterals. J Irrig Drain Eng 130(4):318–324
Puig-Bargues J, Arbat G, Barragan J, Cartagena FR (2005) Hydraulic performance of drip irrigation subunits using WWTP effluents. Agric Water Manag 77(1–3):249–262
Puig-Bargues J, Arbat G, Elbana M, Duran-Ross M, Barragan J, Ramire CF, Lamm FR (2010) Effect of flushing frequency on emitter clogging in microirrigation with effluents. Agric Water Manag 97(6):883–891
Ravina I, Paz E, Sofer Z, Marcu A, Shisha A, Sagi G (1992) Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 13(3):129–139
Ravina I, Paz E, Sofer Z, Marcu A, Shisha A, Sagi G, Yechialy Z, Lev Y (1997) Control of clogging in drip irrigation with stored treated municipal sewage effluent. Agric Water Manag 33(2):127–137
Scott CA, Faruqui NI, Raschid-Sally L (2004) Wastewater use in irrigated agriculture-confronting and the livelihood and environmental realities. CABI Publication, Cambridge, MA
Taylor HD, Bastos RKX, Pearson HW, Mara DD (1995) Drip irrigation with waste stabilization pond effluents: solving the problem of emitter fouling. Water Resour 29(4):1069–1078
Wu XB (2006) Experimental study on anti-clogging performance of emitters for reclaimed wastewater irrigation. China Agriculture University, Beijing
Wu XB, Wu WY, Liu HL, Hao ZY, Ma ZJ (2008) Experimental study on anti-clogging performance of emitters for reclaimed water irrigation. Trans CSAE 24(5):61–64
Yan DZ, Yang PL, Rowan M, Ren SM, Pitts D (2010) Biofilm accumulation and structure in the flow path of drip emitters using reclaimed wastewater. Trans ASABE 53(3):751–758
Yan DZ, Yang PL, Li YK, Ren SM (2011) Evaluation of drip emitter clogging with reclaimed water irrigation. Trans CSAE 27(5):19–24
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 51321001, 51339007, 51179190), New Century Excellent Researcher Award Program of Chinese Ministry of Education (NETC-10-0780) and Beijing Science and Technology Plan (D13110500070000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Stone.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, Y., Li, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Eight emitters clogging characteristics and its suitability under on-site reclaimed water drip irrigation. Irrig Sci 32, 141–157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-013-0420-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-013-0420-2