Abstract
Purpose
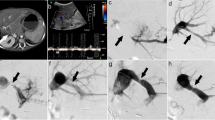
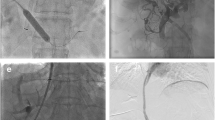
The Habib™ VesOpen Catheter is a new endovascular radiofrequency ablation (RFA) device used to treat malignant portal obstruction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical feasibility and safety of RFA with this device.
Methods
We collected the clinical records and follow-up data of patients with malignant portal obstruction treated with percutaneous endovascular portal RFA using the Habib™ VesOpen Catheter. Procedure-related complications, improvement of symptoms, portal patency, survival, and postoperative biochemical tests were investigated.
Results
The 31 patients enrolled in the study underwent 41 successful endovascular portal RFA procedures. Patients were divided into a portal-stenting (PS) group (n = 13), which underwent subsequent portal stenting with self-expandable metallic stents, and a non-stenting (NS) group (n = 18), which did not undergo stenting. No procedure-related abdominal hemorrhage or portal rupture occurred. Postablation complications included abdominal pain (n = 26), fever (n = 13), and pleural effusion (n = 15). Improvements in clinical manifestations were observed in 27 of the 31 patients. Of the 17 patients experiencing portal restenosis, 10 underwent successful repeat RFA. The rate of successful repeat RFA was significantly higher in the NS group than in the PS group. Median portal patency was shorter in the PS group than in the NS group. No mortality occurred during the 4 weeks after percutaneous endovascular portal RFA.
Conclusions
Percutaneous endovascular portal RFA is a feasible and safe therapeutic option for malignant portal obstruction. Prospective investigations should be performed to evaluate clinical efficacy, in particular, the need to evaluate the necessity for subsequent portal stenting.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monto A, Wright TL. The epidemiology and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2001;28(5):441–9.
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(5 Suppl 1):S35–50.
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J gastroenterol. 2006;12(47):7561–7.
Takizawa D, Kakizaki S, Sohara N, Sato K, Takagi H, Arai H, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: clinical characteristics, prognosis, and patient survival analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52(11):3290–5. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9808-2.
Abdel-Wahab M, El-Ghawalby N, Mostafa M, Sultan A, El-Sadany M, Fathy O, et al. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in lower Egypt Mansoura Gastroenterology Center. Hepato-gastroenterology. 2007;54(73):157–62.
Fujii T, Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, Moriyama N, Wakao F, Kosuge T, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal tumor thrombus: analysis of factors determining prognosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1993;23(2):105–9.
Rabe C, Pilz T, Klostermann C, Berna M, Schild HH, Sauerbruch T, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of a cohort of 101 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7(2):208–15.
Villa E, Moles A, Ferretti I, Buttafoco P, Grottola A, Del Buono M, et al. Natural history of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: estrogen receptors’ status in the tumor is the strongest prognostic factor for survival. Hepatology. 2000;32(2):233–8. doi:10.1053/jhep.2000.9603.
Cohen J, Edelman RR, Chopra S. Portal vein thrombosis: a review. Am J Med. 1992;92(2):173–82.
Macpherson AI. Portal hypertension due to extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. A review of 40 cases. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1984;29(1):4–10.
Witte CL, Brewer ML, Witte MH, Pond GB. Protean manifestations of pylethrombosis. A review of thirty-four patients. Ann Surg. 1985;202(2):191–202.
Sugiura N, Matsutani S, Ohto M, Ebara M, Yoshikawa M, Yamaguchi T, et al. Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in adults detected by ultrasound with frequent lack of portal hypertension signs. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993;8(2):161–7.
Yamakado K, Tanaka N, Nakatsuka A, Matsumura K, Takase K, Takeda K. Clinical efficacy of portal vein stent placement in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading the main portal vein. J Hepatol. 1999;30(4):660–8.
Giorgio A, de Stefano G, Di Sarno A, Farella N, Giorgio V, Scognamiglio U, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma extended into the portal vein: preliminary results. J Ultrasound. 2009;12(1):32–7. doi:10.1016/j.jus.2008.12.004.
Lazoura O, Zacharoulis D, Kanavou T, Rountas C, Katsimboulas M, Tzovaras G, et al. A novel experimental animal model of arterial stenosis based on endovascular radiofrequency energy application. J Investig Surg. 2011;24(3):123–8. doi:10.3109/08941939.2011.557470.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (V2011). J Clin Hepatol. 2011;27(11):1141–59.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53(3):1020–2. doi:10.1002/hep.24199.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL–EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–43. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001.
Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ, Lin SM, Yoshida H, et al. Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2010;4(2):439–74. doi:10.1007/s12072-010-9165-7.
Chuan-Xing L, Xu H, Bao-Shan H, Yong L, Pei-Jian S, Xian-Yi Y, et al. Efficacy of therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: chemoembolization and stent combined with iodine-125 seed. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;12(10):865–71. doi:10.4161/cbt.12.10.17676.
Mizandari M, Ao G, Zhang Y, Feng X, Shen Q, Chen M, et al. Novel percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of portal vein tumor thrombus: safety and feasibility. Cardiovasc Interven Radiol. 2013;36(1):245–8. doi:10.1007/s00270-012-0451-8.
Wu TT, Li HC, Li WM, Ao GK, Lin H, Zheng F, et al. Percutaneous intraluminal radiofrequency ablation for malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction: a safe and feasible method. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(7):2158–63. doi:10.1007/s10620-015-3547-6.
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Tanaka N, Fujii A, Isaji S, Kawarada Y, et al. Portal venous stent placement in patients with pancreatic and biliary neoplasms invading portal veins and causing portal hypertension: initial experience. Radiology. 2001;220(1):150–6. doi:10.1148/radiology.220.1.r01jl03150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest or current funding sources for this study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Hu-Cheng Li is the co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, TT., Li, HC., Zheng, F. et al. Percutaneous Endovascular Radiofrequency Ablation for Malignant Portal Obstruction: An Initial Clinical Experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 994–1000 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1317-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1317-2