Abstract
Background
The non-invasive three-dimensional (3D) stereophotogrammetry is widely used in anthropometry for medical purpose. Yet, few studies have assessed its reliability on measuring the perioral region.
Objectives
This study aimed to provide a standardized 3D anthropometric protocol for the perioral region.
Methods
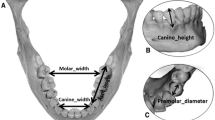
38 female and 12 male Asians were recruited (mean age 31.6 ± 9.6 years). Two sets of 3D images using the VECTRA 3D imaging system were acquired for each subject, and two measurement sessions for each image were performed independently by two raters. 25 landmarks were identified, and 28 linear, 2 curvilinear, 9 angular and 4 areal measurements were evaluated for intrarater, interrater, and intramethod reliability.
Results
Our results showed high reliability of 3D imaging-based perioral anthropometry by mean absolute difference (0.57 and 0.57 unit), technical error measurement (0.51 and 0.55 unit), relative error of measurement (2.18% and 2.44%), relative technical error of measurement (2.02% and 2.34%), and intraclass correlation coefficient (0.98 and 0.98) for intrarater 1 and intrarater 2 reliability; respectively 0.78 unit, 0.74 unit, 3.26%, 3.06% and 0.97 for interrater reliability; and respectively 1.01 unit, 0.97 unit, 4.74%, 4.57% and 0.95 for intramethod reliability.
Conclusions
This standardized protocol utilizing 3D surface imaging technologies are feasible and highly reliable in perioral assessment. It could be further applied for diagnostic purpose, surgical planning and therapeutic effect evaluation in clinical practice in relation to perioral morphologies.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu SQ, Pan BL, An Y et al (2019) Lip morphology and aesthetics: study review and prospects in plastic surgery. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(3):637–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1268-x
Naini FB, Gill DS (2008) Facial aesthetics: 1. Concepts and canons. Dent Update 35(2):102–104, 106–107. https://doi.org/10.12968/denu.2008.35.2.102
Werschler WP, Fagien S, Thomas J et al (2015) Development and validation of a photographic scale for assessment of lip fullness. Aesthet Surg J 35(3):294–307. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sju025
Kim H, Lee M, Park SY et al (2019) Age-related changes in lip morphological and physiological characteristics in Korean women. Skin Res Technol 25(3):277–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/srt.12644
Gibelli D, Pucciarelli V, Cappella A et al (2018) Are portable stereophotogrammetric devices reliable in facial imaging? A validation study of VECTRA H1 device. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 76(8):1772–1784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2018.01.021
Guo Y, Rokohl AC, Schaub F et al (2019) Reliability of periocular anthropometry using three-dimensional digital stereophotogrammetry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 257(11):2517–2531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04428-6
Patel AA, Schreiber JE, Gordon AR et al (2022) Three-dimensional perioral assessment following subnasal lip lift. Aesthet Surg J 42(7):733–739. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjac070
Gibelli D, Codari M, Rosati R et al (2015) A quantitative analysis of lip aesthetics: the influence of gender and aging. Aesthetic Plast Surg 39(5):771–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0495-7
Tsai LC, Lin ET, Chang CC et al (2022) Quantitative and objective measurements of facial aging process with anatomical landmarks. J Cosmet Dermatol 21(3):1317–1320. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14221
Weinberg SM (2022) 3D Facial Norms Database. https://www.facebase.org/facial_norms/summary/
Sawyer AR, See M, Nduka C (2009) 3D stereophotogrammetry quantitative lip analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 33(4):497–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9191-1
Sforza C, Grandi G, Binelli M et al (2010) Age- and sex-related changes in three-dimensional lip morphology. Forensic Sci Int 200(1–3):182.e1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.04.050
Chong Y, Dong R, Liu X et al (2021) Stereophotogrammetry to reveal age-related changes of labial morphology among Chinese women aging from 20 to 60. Skin Res Technol 27(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/srt.12906
Othman SA, Saffai L, Wan Hassan WN (2020) Validity and reproducibility of the 3D VECTRA photogrammetric surface imaging system for the maxillofacial anthropometric measurement on cleft patients. Clin Oral Investig 24(8):2853–2866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03150-1
Weinberg SM, Scott NM, Neiswanger K et al (2004) Digital three-dimensional photogrammetry: evaluation of anthropometric precision and accuracy using a Genex 3D camera system. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 41(5):507–518. https://doi.org/10.1597/03-066.1
Andrade LM, Rodrigues da Silva AMB, Magri LV et al (2017) Repeatability study of angular and linear measurements on facial morphology analysis by means of stereophotogrammetry. J Craniofac Surg 28(4):1107–1111. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000003554
Camison L, Bykowski M, Lee WW et al (2018) Validation of the vectra H1 portable three-dimensional photogrammetry system for facial imaging. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47(3):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2017.08.008
de Menezes M, Rosati R, Ferrario VF et al (2010) Accuracy and reproducibility of a 3-dimensional stereophotogrammetric imaging system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68(9):2129–2135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.09.036
De Stefani A, Barone M, Hatami Alamdari S et al (2022) Validation of vectra 3D imaging systems: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148820
Zhao XG, Hans MG, Palomo JM et al (2013) Comparison of Chinese and white Bolton standards at age 13. Angle Orthod 83(5):809–816. https://doi.org/10.2319/110412-849.1
Funding
The work was supported by National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding, Grant Nos. 2022-PUMCH-B-041, 2022-PUMCH-A-210, 2022-PUMCH-C-025 and Major Collaborative Innovation Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Grant No. 2021-I2M-1-068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
All participants provided written consent for the use of their 3D facial images.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Peking Union Medical College Hospital (Reference Number I-22PJ693) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.





Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Chi, Y., Jin, L. et al. Development and Validation of a Comprehensive Perioral Evaluation Method Using Three-Dimensional Stereophotogrammetry. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 2389–2400 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03473-1