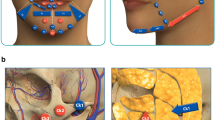
Abstract
Consideration of facial muscle dynamics is underappreciated among clinicians who provide injectable filler treatment. Injectable fillers are customarily used to fill static wrinkles, folds, and localized areas of volume loss, whereas neuromodulators are used to address excessive muscle movement. However, a more comprehensive understanding of the role of muscle function in facial appearance, taking into account biomechanical concepts such as the balance of activity among synergistic and antagonistic muscle groups, is critical to restoring facial appearance to that of a typical youthful individual with facial esthetic treatments. Failure to fully understand the effects of loss of support (due to aging or congenital structural deficiency) on muscle stability and interaction can result in inadequate or inappropriate treatment, producing an unnatural appearance. This article outlines these concepts to provide an innovative framework for an understanding of the role of muscle movement on facial appearance and presents cases that illustrate how modulation of muscle movement with injectable fillers can address structural deficiencies, rebalance abnormal muscle activity, and restore facial appearance.
Level of Evidence V This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn, D.M., Shaw, R.B.: Overview of current thoughts on facial volume and aging. Facial Plast Surg 26(5), 350–355 (2010)
Erickson, B.P., Lee, W.W., Cohen, J., Grunebaum, L.D.: The role of neurotoxins in the periorbital and midfacial areas. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 23(2), 243–255 (2015)
Coleman, K.R., Carruthers, J.: Combination therapy with BOTOX and fillers: the new rejuvenation paradigm. Dermatol Ther 19(3), 177–188 (2006)
Carruthers, J., Carruthers, A., Tezel, A., Kraemer, J., Craik, L.: Volumizing with a 20-mg/mL smooth, highly cohesive, viscous hyaluronic acid filler and its role in facial rejuvenation therapy. Dermatol Surg 36(Suppl 3), 1886–1892 (2010)
Goldberg, R.A., Fiaschetti, D.: Filling the periorbital hollows with hyaluronic acid gel: initial experience with 244 injections. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 22(5), 335–341 (2006)
Callan, P., Goodman, G.J., Carlisle, I., Liew, S., Muzikants, P., Scamp, T., Halstead, M.B., Rogers, J.D.: Efficacy and safety of a hyaluronic acid filler in subjects treated for correction of midface volume deficiency: a 24 month study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 6, 81–89 (2013)
Jones, D., Murphy, D.K.: Volumizing hyaluronic acid filler for midface volume deficit: 2-year results from a pivotal singleblind randomized controlled study. Dermatol Surg 39(11), 1602–1611 (2013)
Carruthers, J.D., Glogau, R.G., Blitzer, A.: Advances in facial rejuvenation: botulinum toxin type A, hyaluronic acid dermal fillers, and combination therapies–consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(Suppl 5), 5S–30S (2008)
Ascher, B., Talarico, S., Cassuto, D., Escobar, S., Hexsel, D., Jaen, P., Monheit, G.D., Rzany, B., Viel, M.: International consensus recommendations on the aesthetic usage of botulinum toxin type A (Speywood Unit)–part I: upper facial wrinkles. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(11), 1278–1284 (2010)
Raspaldo, H., Baspeyras, M., Bellity, P., Dallara, J.M., Gassia, V., Niforos, F.R., Belhaouari, L.: Upper- and mid-face anti-aging treatment and prevention using onabotulinumtoxin A: the 2010 multidisciplinary French consensus–part 1. J Cosmet Dermatol 10(1), 36–50 (2011)
Maas, C., Kane, M.A., Bucay, V.W., Allen, S., Applebaum, D.J., Baumann, L., Cox, S.E., Few, J.W., Joseph, J.H., Lorenc, Z.P., Moradi, A., Nestor, M.S., Schlessinger, J., Wortzman, M., Lawrence, I., Lin, X., Nelson, D.: Current aesthetic use of abobotulinumtoxinA in clinical practice: an evidence-based consensus review. Aesthet Surg J 32(1 Suppl), 8S–29S (2012)
de Maio, M.: Use of botulinum toxin in facial paralysis. J Cosmet Laser Ther 5(3–4), 216–217 (2003)
de Maio, M., Bento, R.F.: Botulinum toxin in facial palsy: an effective treatment for contralateral hyperkinesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(4), 917–927 (2007)
Olson, J.J.: Balanced botox chemodenervation of the upper face: symmetry in motion. Semin Plast Surg 21(1), 47–53 (2007)
Lorenc, Z.P., Smith, S., Nestor, M., Nelson, D., Moradi, A.: Understanding the functional anatomy of the frontalis and glabellar complex for optimal aesthetic botulinum toxin type A therapy. Aesthetic Plast Surg 37(5), 975–983 (2013)
Micheli-Pellegrini, V.: About muscle insertions in man (Proposal for a new nomenclature of striated muscle). Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 31(3), 167–176 (2011)
Goodmurphy, C.W., Ovalle, W.K.: Morphological study of two human facial muscles: orbicularis oculi and corrugator supercilii. Clin Anat 12(1), 1–11 (1999)
Stal, P., Eriksson, P.O., Eriksson, A., Thornell, L.E.: Enzymehistochemical differences in fibre-type between the human major and minor zygomatic and the first dorsal interosseus muscles. Arch Oral Biol 32(11), 833–841 (1987)
Ezure, T., Hosoi, J., Amano, S., Tsuchiya, T.: Sagging of the cheek is related to skin elasticity, fat mass and mimetic muscle function. Skin Res Technol 15(3), 299–305 (2009)
Grelsamer, R.P., Klein, J.R.: The biomechanics of the patellofemoral joint. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 28(5), 286–298 (1998)
Doyle, J.R.: Palmar and digital flexor tendon pulleys. Clin Orthop Relat Res 383, 84–96 (2001)
Aiache, A.E., Ramirez, O.H.: The suborbicularis oculi fat pads: an anatomic and clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 95(1), 37–42 (1995)
Rohrich, R.J., Arbique, G.M., Wong, C., Brown, S., Pessa, J.E.: The anatomy of suborbicularis fat: implications for periorbital rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 124(3), 946–951 (2009)
Gray, H.: The muscles and fasciae. In: Pick, T.P., Howden, R. (eds.) Anatomy, descriptive and surgical, pp. 306–315. Running Press, Philadelphia (1974)
de Maio, M., Rzany, B.: Botulinum toxin in aesthetic medicine. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Ascher, B., Talarico, S., Cassuto, D., Escobar, S., Hexsel, D., Jaen, P., Monheit, G.D., Rzany, B., Viel, M.: International consensus recommendations on the aesthetic usage of botulinum toxin type A (Speywood Unit)–part II: wrinkles on the middle and lower face, neck and chest. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(11), 1285–1295 (2010)
Pessa, J.E., Zadoo, V.P., Garza, P.A., Adrian Jr., E.K., DeWitt, A.I., Garza, J.R.: Double or bifid zygomaticus major muscle: anatomy, incidence, and clinical correlation. Clin Anat 11(5), 310–313 (1998)
Funding
This review was sponsored by Allergan plc, Dublin, Ireland. Writing and editorial assistance was provided to the author by Kathleen M. Dorries, PhD, of Peloton Advantage, Parsippany, NJ, and was funded by Allergan plc. Neither honoraria nor other form of payments was made for authorship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MDM is an Allergan plc consultant for speaking events and medical education.
Additional information
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
This article is being reprinted for ISAPS 50th Anniversary Special Issue.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Maio, M. Myomodulation with Injectable Fillers: An Innovative Approach to Addressing Facial Muscle Movement. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 1300–1316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01825-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01825-9