Abstract
Background
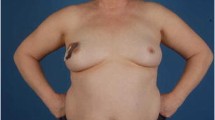
Microvascular reconstruction provides natural, lasting breasts that can be integrated easily into body image but most thin patients are often not ideal candidates because of inadequate donor-site volume. The purpose of this study was to present our experience in delayed augmented DIEP flaps with large fat-volume transfer.
Methods
From 2010 to 2014, 20 consecutive patients were prospectively enrolled for delayed fat-graft-augmented DIEP flaps (active group, AG) and matched with a control group (CG) submitted to the same procedure without fat-injection. Patient’s age, mastectomy and flap weight, number of take-backs to the theater for secondary procedures, total treatment period (TTP), and complications were collected and analyzed. Patient and surgeon surveys rated aesthetic outcomes. Continuous and categorical variables were analyzed using student t test and Kruskal–Wallis test, respectively. A value of p ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The groups did not differ in age and mastectomy weight (p > 0.05). The AG had a smaller BMI and flap weight (p < 0.05). Comparison of the mean number of take-backs (1.5 in AG vs. 1.4 in CG) and mean TTP (8.6 months in AG vs. 8.9 months in CG) did not show a significant difference (p > 0.05) between groups. Volume, upper/lower-pole shapes, projection, breast mound placement, IMF, symmetry, overall appearance, and general satisfaction sub-items obtained high-score evaluation without a significant difference between groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
Delayed fat-graft-augmented DIEP flaps can be offered to patients with insufficient donor-site volume and medium/large breasts. In comparison with the same technique without fat grafting, no additional take-backs and no prolonged TTP were required to achieve pleasing aesthetic results.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderman AK, Wilkins EG, Lowery JC, Kim M, Davis JA (2000) Determinants of patient satisfaction in postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstruct Surg 106:769–776
Craft RO, Colakoglu S, Curtis MS et al (2011) Patient satisfaction in unilateral and bilateral breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstruct Surg 127:1417–1424
Tykkä E, Asko Seljavaara S, Hietanen H (2002) Patient satisfaction with delayed breast reconstruction: a prospective study. An Plast Surg 49:258–263
Wilkins EG, Cederna PS, Lowery JC et al (2000) Prospective analysis of psychosocial outcomes in breast reconstruction: one-year postoperative results from the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcome Study. Plast Reconstruct Surg 106:1014–1025 discussion 26–27
Coleman SR, Saboeiro AP (2007) Fat grafting to the breast revisited: safety and efficacy. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:775–785 discussion 786–777
Delay E, Gosset J, Toussoun G et al (2008) Efficacy of lipomodelling for the management of sequelae of breast cancer conservative treatment. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 53:153–168
ELFadl D, Garimella V, Mahapatra TK et al (2010) Lipomodelling of the breast: a review. Breast 19:202–209
Delay E (2006) Lipomodeling of the reconstructed breast. In: Spear SL, Willey SC, Robb GL et al (eds) Surgery of the breast: principles and art. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 930–946
Kling RE, Mehrara BJ, Pusic AL, Young VL, Hume KM, Crotty CA, Rubin JP (2013) Trends in autologous fat grafting to the breast: a national survey of the american society of plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:35–46
Holm C, Mayr M, Höfter E et al (2006) Perfusion zones of the DIEP flap revisited: a clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:37–43
Cohen M, Evanoff B, George LT et al (2005) A subjective rating scale for evaluating the appearance outcome of autologous breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:440–449
Cohen J (1960) A coefficient of agreement for nominal scale. Educat Psychol Measure 20:37–46
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Hodgson EL, Malata CM (2002) Implant-based breast reconstruction following mastectomy. Breast Dis 16:47–63
Abdalla HM, Shalaan MA, Fouad FA et al (2006) Immediate breast reconstruction with expander assisted latissimus dorsi flap after skin sparing mastectomy. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 18:134–140
Moore TS, Farrell LD (1992) Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap for breast reconstruction: long-term results. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:666–672 discussion 673-664
Tarantino I, Banic A, Fischer T (2006) Evaluation of late results in breast reconstruction by latissimus dorsi flap and prosthesis implantation. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1387–1394
Woerdeman LA, Hage JJ, Hofland MM et al (2007) A prospective assessment of surgical risk factors in 400 cases of skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with implants to establish selection criteria. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:455–463
Kim B, Roth C, Chung KC et al (2011) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma and breast implants: a systemic review. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:2141–2150
Kim B, Roth C, Vl Young et al (2011) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma and breast implants: results from a structured expert consultation process. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:629–663
Blondeel PN (1999) One hundred free DIEP flap breast reconstructions: a personal experience. Br J Plast Surg 52:104–111
Koshima I, Soeda S (1989) Inferior epigastric artery skin flap without rectus abdominis muscle. Br J Plast Surg 42:645–648
Allen RJ, Treece P (1994) Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 32:32–38
Santanelli F, Longo B, Angelini M, Laporta R, Paolini G (2011) Prospective computerized analyses of sensibility in breast reconstruction with non-reinnervated DIEP flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:1790–1795
Santanelli F, Longo B, Cagli B, Pugliese P, Sorotos M, Paolini G (2013) Predictive and protective factors for partial necrosis in DIEP flap breast reconstruction: does nulliparity bias flap viability. Ann Plast Surg 74:47–51
Colakoglu S, Khansa I, Curtis MS et al (2011) Impact of complications on patient satisfaction in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:1428–1436
Zhong T, McCarthy C, Min S et al (2012) Patient satisfaction and health-related quality of life after autologous tissue breast reconstruction: a prospective analysis of early postoperative outcomes. Cancer 118:1701–1709
DellaCroce FJ, Sullivan SK (2005) Application and refinement of the superior gluteal artery perforator free flap for bilateral simultaneous breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:97–103 discussion 104–105
Santanelli di Pompeo F, Laporta R, Sorotos M, Pagnoni M, Falesiedi F, Longo B (2014) Latissimus dorsi flap for total autologous immediate breast reconstruction without implant. Plast Reconstr Surg 134:871e–879e
Agarwal JP, Gottlieb LJ (2007) Double pedicle deep inferior epigastric perforator/muscle sparing TRAM flaps for unilateral breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 58:359–363
Della Croce FJ, Sullivan SK, Trahan C (2011) Stacked deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: a review of 110 flaps in 55 cases over 3 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:1093–1099
Delay E, Garson S, Tousson G et al (2009) Fat injection to the breast: technique, results, and indications based on 880 procedures over 10 years. Aesthet Surg J 29:360–376
Missana MC, Laurent I, Barreau L, Balleyguier C (2007) Autologous fat transfer in reconstructive breast surgery: indications, technique and results. Eur J Surg Oncol 33:685–690
Rubino C, Ramakrishnan V, Figus A, Bulla A, Coscia V, Cavazzuti MA (2009) Flap size/flow rate relationship in perforator flaps and its importance in DIEAP flap drainage. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:1666–1670
Khouri RK, Khouri RK Jr, Rigotti G, Marchi A, Cardoso E, Rotemberg SC, Biggs TM (2014) Aesthetic applications of brava-assisted megavolume fat grafting to the breasts: a 9-year, 476-patient, multicenter experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 133:796–807
Del Vecchio DA, Del Vecchio SJ (2014) The graft-to-capacity ratio: volumetric planning in large-volume fat transplantation. Plast Reconstr Surg 133:561–569
Choi YD, Shin HS, Mok JO (2014) Impaired survival of autologous fat grafts by diabetes mellitus in an animal model: a pilot study. Aesthet Surg J 34:168–174
Maillard GF (1994) Liponecrotic cysts after augmentation mammaplasty with fat injections. Aesthetic Plast Surg 18:405–406
Montanana Vizcaino J, Baena Montilla P, Benito Ruiz J (1990) Complications of autografting fat obtained by liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg 85:638–639
Kwak JY, Lee SH, Park HL et al (2004) Sonographic findings in complications of cosmetic breast augmentation with autologous fat obtained by liposuction. J Clin Ultrasound 32:299–301
Weichman KE, Broer PN, Tanna N, Wilson SC, Allan A, Levine JP, Ahn C, Choi M, Karp NS, Allen R (2013) The role of autologous fat grafting in secondary microsurgical breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 71:24–30
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laporta, R., Longo, B., Sorotos, M. et al. Breast Reconstruction with Delayed Fat-Graft-Augmented DIEP Flap in Patients with Insufficient Donor-Site Volume. Aesth Plast Surg 39, 339–349 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0475-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0475-y