Abstract Purpose:
We aimed to determine the immunological effects of low doses of recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) and recombinant interferon-α (rIFN-α) in patients bearing advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Methods: Twenty-seven patients received therapeutic cycles consisting of subcutaneous rIL-2 for 5 days per week and intramuscular rIFN-α twice weekly, for 4 consecutive weeks. The cycle was repeated indefinitely at regular 4-month intervals, for all patients. rIL-2 (1 × 106 IU/m2) was administered every 12 h on days 1 and 2 and once a day on days 3–5 of each week; rIFN-α (1.8 × 106 IU/m2) was given on days 3 and 5.
In the enrolled patients, total and differential white blood cell counts, phenotypic analysis of some lymphocyte subsets, and soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R), were investigated before and after each of the first six cycles of therapy (about 24 months of follow-up).
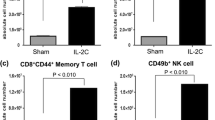
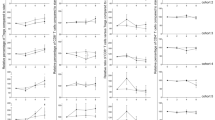
Results: The cycles of immunotherapy induced a significant increase of total lymphocytes (37%, P < 0.001), eosinophils (222%, P < 0.001), CD25+ cells (27%, P=0.004), sIL-2R (174%, P < 0.001) and natural killer (NK) cells (CD3-CD56+) (61%, P < 0.001); the subset that expresses CD56 with high density (CD56+ bright) expanded more (233%, P < 0.001) than the subset expressing the same marker with low density (CD56+ dimmer) (15%, P=0.043). Unlike the previous subsets, the treatment decreased significantly T-lymphocytes with NK cell marker (CD3+ CD56+) (28%, P=0.011).
No significant differences of effectiveness were found among the subsequent treatment cycles, except for CD25+ cells and sIL-2R (P=0.036 and P=0.005, respectively): the increase induced by immunotherapy was maximum after the first cycle and decreased progressively thereafter.
Conclusions: Long-term repeated cycles of low-dose immunotherapy induced repeated and significant expansion of one of the most important lymphocyte subsets for the non-MHC-restricted immune response to the tumour mass: CD3–CD56+ cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 November 2000 / Accepted: 11 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavone, L., Andrulli, S., Santi, R. et al. Long-term treatment with low doses of interleukin-2 and interferon-α: immunological effects in advanced renal cell cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 50, 82–86 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620100175
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620100175