Abstract
Objectives
To determine whether there is an association between blood eosinophil count and percentage with the recurrence of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) during Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) maintenance therapy with our preliminary results.
Methods
A total of 53 patients with NMIBC underwent BCG immunotherapy between January 2015 and September 2018, and met our inclusion criteria were included in the study. The parameters age, gender, smoking status, comorbidity, blood neutrophil, lymphocyte and eosinophil counts, blood eosinophil percentage, previous single postoperative intravesical chemotherapy instillation, tumor characteristic, and total and maintenance dose numbers of BCG were extracted from our medical records and compared between patients with response and with recurrence.
Results
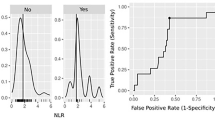
Blood eosinophil count and percentage were significantly higher in patients with recurrence compared to patients with response (0.263 ± 0.37 vs. 0.0134 ± 0.021, p = 0.01 and 0.31 ± 0.29 vs. 0.17 ± 0.27, p = 0.01). Other parameters were similar in patients with recurrence and response. Receiver-operating characteristic analysis showed a considerable diagnostic value of blood eosinophil count and percentage in the prediction of bladder cancer recurrence during BCG immunotherapy.
Conclusion
Blood eosinophil count and percentage in patients with NMIBC can predict the disease recurrence during the BCG immunotherapy. Our research raised new questions and assumptions about the role of eosinophils during BCG immunotherapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
None.
Code availability
None.
References
Kang M, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH (2017) Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio can significantly predict mortality outcomes in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer undergoing transurethral resection of bladder tumor. Oncotarget 8:12891–12901. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14179
Sanli O, Dobruch J, Knowles MA, Burger M, Alemozaffar M, Nielsen ME, Lotan Y (2017) Bladder cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17022. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.22
Arends TJ, Nativ O, Maffezzini M, de Cobelli O, Canepa G, Verweij F, Moskovitz B, van der Heijden AG, Witjes JA (2016) Results of a randomised controlled trial comparing intravesical chemohyperthermia with mitomycin C versus bacillus calmette-guerin for adjuvant treatment of patients with intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 69:1046–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.006
Nunez-Nateras R, Castle EP, Protheroe CA et al (2014) Predicting response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) in patients with carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Urol Oncol 32(45):e23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.06.008
Zlotta AR, Fleshner NE, Jewett MA (2009) The management of BCG failure in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: an update. Can Urol Assoc J 3:S199–205
Kamat AM, Li R, O'Donnell MA et al (2018) Predicting response to intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunotherapy: are we there yet? A systematic review. Eur Urol 73:738–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.10.003
Prakash Babu S, Narasimhan PB, Babu S (2019) Eosinophil polymorphonuclear leukocytes in TB: what we know so far. Front Immunol 10:2639. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02639
Kirman J, Zakaria Z, McCoy K, Delahunt B, Le Gros G (2000) Role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in gamma interferon receptor-deficient mice. Infect Immun 68:2976–2978. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.68.5.2976-2978.2000
Castro AG, Esaguy N, Macedo PM, Aguas AP, Silva MT (1991) Live but not heat-killed mycobacteria cause rapid chemotaxis of large numbers of eosinophils in vivo and are ingested by the attracted granulocytes. Infect Immun 59:3009–3014
Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A (2005) The 2004 WHO classification of bladder tumors: a summary and commentary. Int J Surg Pathol 13:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/106689690501300203
Paner GP, Stadler WM, Hansel DE, Montironi R, Lin DW, Amin MB (2018) Updates in the eighth edition of the tumor-node-metastasis staging classification for urologic cancers. Eur Urol 73:560–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.12.018
Johnston LK, Bryce PJ (2017) Understanding interleukin 33 and its roles in eosinophil development. Front Med 4:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00051
Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD, Foster PS (2013) Eosinophils: changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 13:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3341
Varricchi G, Galdiero MR, Loffredo S, Lucarini V, Marone G, Mattei F, Marone G, Schiavoni G (2018) Eosinophils: the unsung heroes in cancer? Oncoimmunology 7:e1393134. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2017.1393134
Bochner BS (2015) Novel therapies for eosinophilic disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 35:577–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2015.05.007
Lucarini V, Ziccheddu G, Macchia I et al (2017) IL-33 restricts tumor growth and inhibits pulmonary metastasis in melanoma-bearing mice through eosinophils. Oncoimmunology 6:e1317420. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2017.1317420
Horiuchi T, Weller PF (1997) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by human eosinophils: upregulation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.17.1.2796
Folkman J, Shing Y (1992) Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 267:10931–10934
Andersen CL, Siersma VD, Hasselbalch HC, Lindegaard H, Vestergaard H, Felding P, de Fine ON, Bjerrum OW (2014) Eosinophilia in routine blood samples as a biomarker for solid tumor development - a study based on the Copenhagen Primary Care Differential Count (CopDiff) Database. Acta Oncol 53:1245–1250. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2014.887857
Saint F, Patard JJ, Groux Muscatelli B, Lefrere Belda MA, Diez G, de Medina S, Abbou CC, Chopin DK (2001) Evaluation of cellular tumour rejection mechanisms in the peritumoral bladder wall after bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment. BJU Int 88:602–610
Pichler R, Gruenbacher G, Culig Z, Brunner A, Fuchs D, Fritz J, Gander H, Rahm A, Thurnher M (2017) Intratumoral Th2 predisposition combines with an increased Th1 functional phenotype in clinical response to intravesical BCG in bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII 66:427–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1945-z
Miyata Y, Sakai H (2015) Predictive markers for the recurrence of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical therapy. Dis Mark 2015:857416. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/857416
Diny NL, Rose NR, Cihakova D (2017) Eosinophils in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 8:484. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00484
Caldwell JM, Collins MH, Stucke EM, Putnam PE, Franciosi JP, Kushner JP, Abonia JP, Rothenberg ME (2014) Histologic eosinophilic gastritis is a systemic disorder associated with blood and extragastric eosinophilia, TH2 immunity, and a unique gastric transcriptome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 134:1114–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.026
Lowe D, Fletcher CD, Gower RL (1984) Tumour-associated eosinophilia in the bladder. J Clin Pathol 37:500–502
Driss V, Legrand F, Hermann E et al (2009) TLR2-dependent eosinophil interactions with mycobacteria: role of alpha-defensins. Blood 113:3235–3244. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-07-166595
Borelli V, Vita F, Shankar S, Soranzo MR, Banfi E, Scialino G, Brochetta C, Zabucchi G (2003) Human eosinophil peroxidase induces surface alteration, killing, and lysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun 71:605–613
Siracusano S, Vita F, Abbate R, Ciciliato S, Borelli V, Bernabei M, Zabucchi G (2007) The role of granulocytes following intravesical BCG prophylaxis. Eur Urol 51:1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2006.11.045 (discussion 97–99)
Durrington HJ, Gioan-Tavernier GO, Maidstone RJ et al (2018) Time of day affects eosinophil biomarkers in asthma: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 198:1578–1581. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201807-1289LE
Sennels HP, Jorgensen HL, Hansen AL, Goetze JP, Fahrenkrug J (2011) Diurnal variation of hematology parameters in healthy young males: the Bispebjerg study of diurnal variations. Scand J Clin Lab Investig 71:532–541. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365513.2011.602422
Wu HX, Zhuo KQ, Cheng DY (2019) Peripheral blood eosinophil as a biomarker in outcomes of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis 14:3003–3015. https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S226783
Pavord ID, Agusti A (2016) Blood eosinophil count: a biomarker of an important treatable trait in patients with airway disease. Eur Respir J 47:1299–1303. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00055-2016
Bafadhel M, Pavord ID, Russell REK (2017) Eosinophils in COPD: just another biomarker? Lancet Respir Med 5:747–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30217-5
Onesti CE, Josse C, Poncin A, Freres P, Poulet C, Bours V, Jerusalem G (2018) Predictive and prognostic role of peripheral blood eosinophil count in triple-negative and hormone receptor-negative/HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant treatment. Oncotarget 9:33719–33733. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26120
Moreira A, Leisgang W, Schuler G, Heinzerling L (2017) Eosinophilic count as a biomarker for prognosis of melanoma patients and its importance in the response to immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 9:115–121. https://doi.org/10.2217/imt-2016-0138
Sylman JL, Mitrugno A, Atallah M et al (2018) The predictive value of inflammation-related peripheral blood measurements in cancer staging and prognosis. Front Oncol 8:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00078
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZT: conception and design of the work, literature review, drafting manuscript, analysis, and/or interpretation of the data; AC: design of the work, data collection, and/or processing; IU: design of the work, data collection, and/or processing; EK: data collection and/or processing; FP: data collection and/or processing; SS: data collection and/or processing; EY: conception and design of the work, and literature review; EK: supervision and critical review; AS: supervision and critical review; AYM: supervision and critical review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temiz, M.Z., Colakerol, A., Ulus, I. et al. Prediction of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer recurrence during intravesical BCG immunotherapy by use of peripheral blood eosinophil count and percentage: a preliminary report. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 245–252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02673-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02673-x