Abstract
Purpose
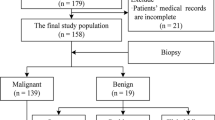
The purpose of this study was to determine the safety and accuracy of aortic and periaortic computed tomography (CT)-guided percutaneous core needle biopsy performed at a single center over 12 years.
Materials and methods
A retrospective review was conducted of cases performed between February 2010 and August 2022 in which the biopsied region was in direct contact with the aorta or great vessels including the pericardium and common iliac arteries. Clinical notes were reviewed for any early or delayed complications following the procedure, which if present were graded using the National Institute of Health’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5.0. Pathology results were compared to subsequent outside biopsy results or follow-up surgical pathology, if available, as well as subsequent clinical decision making and/or clinical course, to determine concordance. Sensitivity, specificity, predictive value, and accuracy (indicative of diagnostic yield) were calculated.
Results
32 core needle biopsies were reviewed from 30 patients (average lesion longest diameter 3.1 cm, range 0.5–10.9 cm; average needle proximity to the vessel endothelium or deep side of the pericardium 1.0 cm, range 0.3–1.8 cm). Complications occurred in 46.9% of cases (15/32), 93.3% (14/15) of which were minor and included small amounts of bleeding or pain. One patient developed a small nonemergent pneumothorax. Of biopsies obtained, 96.9% provided adequate tissue for diagnosis (31/32). When evaluating concordance between pathological and final diagnosis, sensitivity was 94.7% and specificity was 83.3%; positive and negative predictive value were 90.0% and 90.9%, respectively. Accuracy (diagnostic yield) of biopsy was 90.3%.
Conclusion
CT-guided percutaneous aortic and periaortic core needle biopsies are safe and efficacious procedures with high diagnostic yield.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajiah P, Sinha R, Cuevas C, Dubinsky TJ, Bush WH, Kolokythas O. Imaging of Uncommon Retroperitoneal Masses. RadioGraphics Jul 2011;31(4): 949-977. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.314095132
Tomita K, Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Matsui Y, Uka M, Komaki T, Gobara H, Kanazawa S. Computed Tomography Fluoroscopy-guided Core Needle Biopsy of Abdominal Para-aortic Lesions: A Retrospective Evaluation of the Diagnostic Yield and Safety. Interv Radiol (Higashimatsuyama). 2020 Sep 3;5(3):128-133. https://doi.org/10.22575/interventionalradiology.2020-0009. PMID: 36284760; PMCID: PMC9550396.
Casaccia M, Torelli P, Cavaliere D, Panaro F, Nardi I, Rossi E, Spriano M, Bacigalupo A, Gentile R, Valente U. Laparoscopic lymph node biopsy in intra-abdominal lymphoma: high diagnostic accuracy achieved with a minimally invasive procedure. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2007 Jun;17(3):175-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0b013e31804b41c9. PMID: 17581460.
Yasuda I, Tsurumi H, Omar S, Iwashita T, Kojima Y, Yamada T, Sawada M, Takami T, Moriwaki H, Soehendra N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy for lymphadenopathy of unknown origin. Endoscopy. 2006 Sep;38(9):919-24. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-944665. PMID: 16981110.
Nagano T, Nakai Y, Taniguchi F, Suzuki N, Wakutani K, Ohnishi T, Nakayama T, Shibamoto T, Umaoka Y, Ohara A, et al. Diagnosis of paraaortic and pelvic lymph node metastasis of gynecologic malignant tumors by ultrasound-guided percutaneous fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Cancer. 1991 Dec 15;68(12):2571-4. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19911215)68:12<2571::aid-cncr2820681207>3.0.co;2-9. PMID: 1933803.
Aramaki T, Ikeda T, Moriguchi, M, Tsushima T, Endo M, Asakura K, Sawada A, Kimura F. Investigation of the Safety and Usefulness of Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Needle Biopsy of Paraaortic Lymph nodes. Blood 2009;114(22):5027. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V114.22.5027.5027
Burgard C, Stahl R, de Figueiredo GN, Dinkel J, Liebig T, Cioni D, Neri E, Trumm CG. Percutaneous CT Fluoroscopy-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Mediastinal Masses: Technical Outcome and Complications of 155 Procedures during a 10-Year Period. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;11(5):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050781. PMID: 33926046; PMCID: PMC8144979.
Shao H, McCarthy C, Wehrenberg-Klee E, Thabet A, Uppot R, Dawson S, Arellano RS. CT-Guided Percutaneous Needle Biopsy of Retroperitoneal and Pelvic Lymphadenopathy: Assessment of Technique, Diagnostic Yield, and Clinical Value. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018 Oct;29(10):1429-1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Aug 31. PMID: 30174157.
Zangos S, Eichler K, Wetter A, Lehnert T, Hammerstingl R, Diebold T, Reichel P, Herzog C, Hansmann ML, Mack MG, Vogl TJ. MR-guided biopsies of lesions in the retroperitoneal space: technique and results. Eur Radiol. 2006 Feb;16(2):307-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2870-2. Epub 2005 Jul 30. PMID: 16059677.
Anzidei M, Porfiri A, Andrani F, Di Martino M, Saba L, Catalano C, Bezzi M. Imaging-guided chest biopsies: techniques and clinical results. Insights Imaging. 2017 Aug;8(4):419-428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-017-0561-6. Epub 2017 Jun 21. PMID: 28639114; PMCID: PMC5519500.
McGahan, J.P. Challenges in abdominal/pelvic biopsy techniques. Abdom Imaging 2013;38: 1043–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-013-0006-8
National Institutes of Health (NIH). Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0. NIH website. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf. Published Nover 27, 2017. Updated September 2020. Accessed August 28, 2022 [Google Scholar]
Olson MC, Atwell TD, Harmsen WS, Konrad A, King RL, Lin Y, Wall DJ. Safety and Accuracy of Percutaneous Image-Guided Core Biopsy of the Spleen. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Mar;206(3):655-9. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.15.15125. PMID: 26901024.
Tam A, Krishnamurthy S, Pillsbury EP, Ensor JE, Gupta S, Murthy R, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Hicks ME, Madoff DC. Percutaneous image-guided splenic biopsy in the oncology patient: an audit of 156 consecutive cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008 Jan;19(1):80-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2007.08.025. PMID: 18192471.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pitot, M.A., Gu, C.N., Adamo, D.A. et al. Safety and accuracy of aortic and periaortic CT-guided percutaneous core needle biopsy. Abdom Radiol 48, 2148–2156 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03867-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03867-4