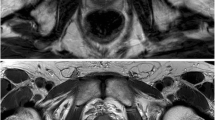
Abstract
Purpose
To compare the diagnostic performance of high-resolution 3D T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) with compressed sensing (CS) sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution (SPACE) to that of conventional T2WI with turbo spin echo (TSE) in prostate MRI.
Materials and methods
This study evaluated 179 patients (mean age 69.1 ± 9.3) who underwent prostate biopsy after prostate prebiopsy MRI, including two sets of three-plane T2WI with TSE (thickness: 3 mm, scan time: 10 min 4 s) and CS SPACE (thickness: 0.6 mm, scan time: 4 min 55 s). Two radiologists evaluated two sets of images with the Prostate Imaging—Reporting and Data System (PIRADS) classification and determined the extraprostatic extension (EPE) of the lesion. The diagnostic performance to detect prostate cancer (PIRADS classification) and EPE was compared between the two T2WI sets.
Results
Clinically significant cancer (CSC) was diagnosed in 103 patients (57.5%). Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the PIRADS classification on both image sets with T2 TSE and T2 CS SPACE were higher than 0.7 and did not show significant differences for either radiologist (p > 0.05). EPE was confirmed in 25 of 70 patients underwent prostatectomy. For evaluating EPE on MRI, the sensitivity and specificity did not differ between the two T2WI sequences (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
High-resolution 3D T2WI using CS SPACE, which was acquired within a shorter acquisition time than three-plane T2 TSE, showed comparable diagnostic performance to conventional T2 TSE for detecting CSC and evaluating EPE.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed HU, El-Shater Bosaily A, Brown LC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet. 2017;389:815-22.
Kasivisvanathan V, Rannikko AS, Borghi M, et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1767-77.
Rouviere O, Puech P, Renard-Penna R, et al. Use of prostate systematic and targeted biopsy on the basis of multiparametric MRI in biopsy-naive patients (MRI-FIRST): a prospective, multicentre, paired diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:100-9.
van der Leest M, Cornel E, Israel B, et al. Head-to-head Comparison of Transrectal Ultrasound-guided Prostate Biopsy Versus Multiparametric Prostate Resonance Imaging with Subsequent Magnetic Resonance-guided Biopsy in Biopsy-naive Men with Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen: A Large Prospective Multicenter Clinical Study. Eur Urol. 2019;75:570-8.
Mottet N, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur Urol. 2021;79:243–62.
Giganti F, Kasivisvanathan V, Kirkham A, et al. Prostate MRI quality: a critical review of the last 5 years and the role of the PI-QUAL score. Br J Radiol. 2022;95:20210415.
Karanasios E, Caglic I, Zawaideh JP, Barrett T. Prostate MRI quality: clinical impact of the PI-QUAL score in prostate cancer diagnostic work-up. Br J Radiol. 2022;95:20211372.
Giganti F, Allen C. Progress in Prostate MRI Quality. Acad Radiol. 2022;29:15-6.
Potsch N, Rainer E, Clauser P, et al. Impact of PI-QUAL on PI-RADS and cancer yield in an MRI-TRUS fusion biopsy population. Eur J Radiol. 2022;154:110431.
Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging - Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur Urol. 2016;69:16-40.
Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur Urol. 2019;76:340-51.
Polanec SH, Lazar M, Wengert GJ, et al. 3D T2-weighted imaging to shorten multiparametric prostate MRI protocols. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:1634-41.
Rosenkrantz AB, Neil J, Kong X, et al. Prostate cancer: Comparison of 3D T2-weighted with conventional 2D T2-weighted imaging for image quality and tumor detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194:446-52.
Almansour H, Weiland E, Kuehn B, et al. Accelerated Three-dimensional T2-Weighted Turbo-Spin-Echo Sequences with Inner-Volume Excitation and Iterative Denoising in the Setting of Pelvis MRI at 1.5T: Impact on Image Quality and Lesion Detection. Acad Radiol. 2022.
Lim KK, Noe G, Hornsey E, Lim RP. Clinical applications of 3D T2-weighted MRI in pelvic imaging. Abdominal imaging. 2014;39:1052-62.
Jaspan ON, Fleysher R, Lipton ML. Compressed sensing MRI: a review of the clinical literature. Br J Radiol. 2015;88:20150487.
Yoon JH, Nickel MD, Peeters JM, Lee JM. Rapid Imaging: Recent Advances in Abdominal MRI for Reducing Acquisition Time and Its Clinical Applications. Korean J Radiol. 2019;20:1597-615.
Wong OL, Poon DMC, Kam MKM, et al. 3D-T2W-TSE radiotherapy treatment planning MRI using compressed sensing acceleration for prostate cancer: Image quality and delineation value. Asia-Pacific journal of clinical oncology. 2022.
Lojanapiwat B, Anutrakulchai W, Chongruksut W, Udomphot C. Correlation and diagnostic performance of the prostate-specific antigen level with the diagnosis, aggressiveness, and bone metastasis of prostate cancer in clinical practice. Prostate Int. 2014;2:133-9.
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, et al. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:244–52.
Caglic I, Povalej Brzan P, Warren AY, Bratt O, Shah N, Barrett T. Defining the incremental value of 3D T2-weighted imaging in the assessment of prostate cancer extracapsular extension. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:5488-97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary video 1. Conventional T2-weighted imaging of the prostate gland using 2D turbo spin echo (AVI 645 kb)
Supplementary video 2. High-resolution 3D T2-weighted imaging of the prostate gland using CS SPACE (AVI 1976 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, M.H., Lee, Y.J., Jung, S.E. et al. High-resolution 3D T2-weighted SPACE sequence with compressed sensing for the prostate gland: diagnostic performance in comparison with conventional T2-weighted images. Abdom Radiol 48, 1090–1099 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03777-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03777-x