Abstract
Purpose
The goal of our study is to compare hepatic stiffness measures using gradient-recalled echo (GRE) versus spin-echo echo planar imaging (SE-EPI)-based MR Elastography (MRE) at 3T used to measure hepatic stiffness in a patients with suspected liver diseases.
Materials and methods
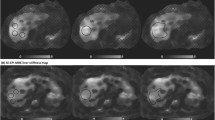
This retrospective study included 52 patients with liver disease who underwent a 3T MRE exam including both an investigational SE-EPI-based technique and a product GRE-based technique. Regions of interest (ROI) were placed on the elastograms to measure elastography-derived liver stiffness as well as the area included within the ROIs. The mean liver stiffness values and area of ROIs were compared.
Results
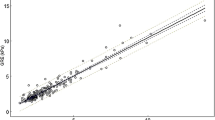
The mean liver stiffness was 3.72 kilopascal (kPa) ± 1.29 using GRE MRE and 3.78 kPa ± 1.13 using SE-EPI MRE. Measurement of liver stiffness showed excellent agreement between the two pulse sequences with a mean bias of − 0.1 kPa (range − 1.8 to 1.7 kPa) between sequences. The mean measurable ROI area was higher with SE-EPI (313.8 cm2 ± 213.8) than with the GRE technique (208.6 cm2 ± 114.8), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our data shows excellent agreement of measured liver stiffness between GRE and SE-EPI-based sequences at 3T. Our results show the advantage of a SE-EPI MRE sequence in terms of image quality, ROI size and acquisition time with equivalent liver stiffness measurements as compared to GRE-MRE sequence.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhole, S.D., et al., Chronic Liver Diseases in Children: Clinical Profile and Histology. J Clin Diagn Res, 2015. 9(7): p. SC04-7.
Lobstein, T., et al., Child and adolescent obesity: part of a bigger picture. Lancet, 2015. 385(9986), p. 2510-20
Wallihan, D.B., et al., Relationship of MR elastography determined liver stiffness with cardiac function after Fontan palliation. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2014. 40(6), p. 1328-35
Serai, S.D., et al., Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver in patients status-post fontan procedure: feasibility and preliminary results. Congenit Heart Dis, 2014. 9(1), p. 7-14
Gunay-Aygun, M., et al., Characteristics of congenital hepatic fibrosis in a large cohort of patients with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Gastroenterology, 2013. 144(1), p. 112-121.e2
Rockey, D.C., et al., Liver biopsy. Hepatology, 2009. 49(3), p. 1017-44
Cunha, G.M., et al., Feasibility and agreement of stiffness measurements using gradient-echo and spin-echo MR elastography sequences in unselected patients undergoing liver MRI. Br J Radiol, 2018. 91(1087), p. 20180126
German, A.L., et al., Can reference images improve interobserver agreement in reporting liver fibrosis?. J Clin Pathol, 2018. 71(4), p. 368-371
Jung, E.S., et al., Interobserver Agreement on Pathologic Features of Liver Biopsy Tissue in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Pathol Transl Med, 2016. 50(3), p. 190-6
Pournik, O., et al., Inter-observer and Intra-observer Agreement in Pathological Evaluation of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Suspected Liver Biopsies. Hepat Mon, 2014. 14(1), p. e15167
Maharaj B Fau - Maharaj, R.J., et al., Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. (0140-6736 (Print)).
Ratziu, V., et al., Survival, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma in obesity-related cryptogenic cirrhosis. Hepatology, 2002. 35(0270-9139 (Print)): p. 1485-93.
Bedossa, P., V. Dargere D Fau - Paradis, and V. Paradis, Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology, 2003. 38(0270-9139 (Print)): p. 1449-57.
Regev, A., et al., Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol, 2002. 97(0002-9270 (Print)): p. 2614-8.
Cadranel, J.F., F. Rufat P Fau - Degos, and F. Degos, Practices of liver biopsy in France: results of a prospective nationwide survey. For the Group of Epidemiology of the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF). Hepatology, 2000. 32(0270-9139 (Print)): p. 477-81.
Froehlich, F., et al., Practice and complications of liver biopsy. Results of a nationwide survey in Switzerland. Dig Dis Sci, 1993. 38(0163-2116 (Print)): p. 1480-4.
Piccinino F Fau - Sagnelli, E., et al., Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy. A multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. (0168-8278 (Print)).
Perrault J Fau - McGill, D.B., et al., Liver biopsy: complications in 1000 inpatients and outpatients. (0016-5085 (Print)).
Bravo, A.A., Sheth, S.G., Chopra, S., Liver Biopsy. New England Journal of Medicine, 2001. 344(7), p. 495-500
Watanabe, A., et al., Magnetic resonance imaging of the cirrhotic liver: An update. World J Hepatol, 2015. 7(3). p. 468-87
Serai, S.D., Towbin, A.J., Podberesky, D.J, Pediatric liver MR elastography. Dig Dis Sci, 2012. 57(10), p. 2713-9
Trout, A.T., et al., Diagnostic Performance of MR Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Children and Young Adults with a Spectrum of Liver Diseases. Radiology, 2018: p. 172099.
Xanthakos, S.A., et al., Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease. J Pediatr, 2014. 164(1), p. 186-8
Serai, S.D., spin-echo echo-planar imaging Mr elastography versus gradient-echo Mr elastography for assessment of liver stiffness in children and Young adults suspected of having liver Disease. Radiology, 2016.
Chang, W., liver Fibrosis staging with Mr elastography: Comparison of Diagnostic Performance between Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B and Those with Other Etiologic Causes. Radiology, 2016.
Singh, S, et al., Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a diagnostic accuracy systematic review and individual participant data pooled analysis. Eur Radiol, 2016. 26(5), p. 1431-40
Shi, Y., Mr elastography for the assessment of hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: Does Histologic Necroinflammation Influence the Measurement of Hepatic Stiffness? Radiology, 2014.
Loomba, R., et al., Magnetic resonance elastography predicts advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study. Hepatology, 2014. 60(6), p. 1920-8
Yin, M., et al., Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017. 5(10), p. 1207-1213.e2
DeLaPaz, R.L., Echo-planar imaging. Radiographics, 1994. 14(5), p. 1045-58
Serai, S.D., et al., Cross-vendor validation of liver magnetic resonance elastography. Abdom Imaging, 2015. 40(4). p. 789-94
Amatya, P., et al., Clinical and ultrasonographic measurement of liver size in normal children. Indian J Pediatr, 2014.0 81(5), p. 441-5
Hallgren, K.A., Computing Inter-Rater Reliability for Observational Data: An Overview and Tutorial. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol, 2012.8(1), p. 2
Trout, A.T., et al., Prospective Assessment of Correlation between US Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse and MR Elastography in a Pediatric Population: Dispersion of US Shear-Wave Speed Measurement Matters. Radiology, 2016. 281(2), p. 544–552
Serai S.D, et al.,Correlating liver stiffness with disease severity scoring system (DS3) values in Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) patients. Mol Genet Metab, 2018. 123(3), p. 357-363
Serai, S.D., Trout, A.T., Sirlin, C.B., Elastography to assess the stage of liver fibrosis in children: Concepts, opportunities, and challenges. Clinical Liver Disease, 2017. 9(1). p. 5-10
Serai, S.D., spin-echo echo-planar imaging Mr elastography versus gradient-echo Mr elastography for assessment of liver stiffness in children and Young adults suspected of having liver Disease. Radiology, 2016. 0000, p. 10
Trout, A.T., et al., Liver Stiffness Measurements with MR Elastography: Agreement and Repeatability across Imaging Systems, Field Strengths, and Pulse Sequences. Radiology, 2016. 281(3), p. 793-804
Herzka, D.A., et al., Magnetic resonance elastography in the liver at 3 Tesla using a second harmonic approach. Magn Reson Med, 2009. 62(2), p. 284-91
Bae, J.S., et al., Magnetic resonance elastography of healthy livers at 3.0 T: Normal liver stiffness measured by SE-EPI and GRE. European Journal of Radiology, 2018. 107: p. 46-53.
Suraj, S., spin-echo echo-planar imaging Mr elastography versus gradient-echo Mr elastography for assessment of liver stiffness in children and Young adults suspected of having liver Disease. Radiology, 2016.
Wood R Fau - Bassett, K., et al.
Felker, E.R., et al., Liver MR Elastography at 3 T: Agreement Across Pulse Sequences and Effect of Liver R2* on Image Quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol, (2018). 211(3), p. 588-594
Acknowledgements
We thank Carolina Maya MD (study coordinator), and Robert Carson BSRT (lead MRI technologist), of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia; Richard L. Ehman, MD, PhD, and Scott Kruse, BS, of Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN); and Christianne Leidecker, PhD, from Siemens Healthineers for their support and technical assistance related to 2D SE-EPI MRE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calle-Toro, J.S., Serai, S.D., Hartung, E.A. et al. Magnetic resonance elastography SE-EPI vs GRE sequences at 3T in a pediatric population with liver disease. Abdom Radiol 44, 894–902 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1884-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1884-6