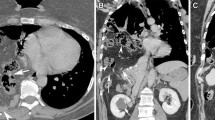
Abstract
Injuries to the diaphragm muscle occur in penetrating and severe blunt trauma and can lead to delayed hernia formation. Computed tomography is the mainstay in the diagnosis of these injuries, which may be subtle at presentation. Imaging findings differ between blunt and penetrating trauma. Key features in blunt trauma include diaphragm fragment distraction and organ herniation because of increased intra-abdominal pressure. In penetrating trauma, herniation is uncommon, and the trajectory of the object is critical in making the diagnosis of diaphragm injury in these patients. Radiologists must keep a high index of suspicion for injury to the diaphragm in cases of trauma to the chest or abdomen.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simpson J, Lobo DN, Shah AB, Rowlands BJ (2000) Traumatic diaphragmatic rupture: associated injuries and outcome. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 82:97–100
Sangster G, Ventura VP, Carbo A, et al. (2007) Diaphragmatic rupture: a frequently missed injury in blunt thoracoabdominal trauma patients. Emerg Radiol 13:225–230. doi:10.1007/s10140-006-0548-y
Feliciano DV, Cruse PA, Mattox KL, et al. (1988) Delayed diagnosis of injuries to the diaphragm after penetrating wounds. J Trauma 28:1135–1144
Clarke DL, Greatorex B, Oosthuizen GV, Muckart DJ (2009) The spectrum of diaphragmatic injury in a busy metropolitan surgical service. Injury 40:932–937. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2008.10.042
Fair KA, Gordon NT, Barbosa RR, et al. (2015) Traumatic diaphragmatic injury in the American College of Surgeons National Trauma Data Bank: a new examination of a rare diagnosis. Am J Surg 209:864–868–869. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2014.12.023
Demetriades D, Kakoyiannis S, Parekh D, Hatzitheofilou C (1988) Penetrating injuries of the diaphragm. Br J Surg 75:824–826. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800750834
Williams M, Carlin AM, Tyburski JG, et al. (2004) Predictors of mortality in patients with traumatic diaphragmatic rupture and associated thoracic and/or abdominal injuries. Am Surg 70:157–162–163
Williams M (2013) Recognition and management of diaphragmatic injury in adults (uptodate)
Chen JC, Wilson SE (1991) Diaphragmatic injuries: recognition and management in sixty-two patients. Am Surg 57:810–815
Shah R, Sabanathan S, Mearns AJ, Choudhury AK (1995) Traumatic rupture of diaphragm. Ann Thorac Surg 60:1444–1449. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(95)00629-Y
Britt LD, Barie PS, Peitzman AB, Jurkovich G (2012) Acute care surgery. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, USA
Murray JA, Demetriades D, Asensio JA, et al. (1998) Occult injuries to the diaphragm: prospective evaluation of laparoscopy in penetrating injuries to the left lower chest. J Am Coll Surg 187:626–630
Murray JA, Demetriades D, Cornwell EE, et al. (1997) Penetrating left thoracoabdominal trauma: the incidence and clinical presentation of diaphragm injuries. J Trauma 43:624–626
Holmes JF, McGahan JP, Wisner DH (2012) Rate of intra-abdominal injury after a normal abdominal computed tomographic scan in adults with blunt trauma. Am J Emerg Med 30:574–579. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2011.02.016
Velmahos GC, Constantinou C, Tillou A, et al. (2005) Abdominal computed tomographic scan for patients with gunshot wounds to the abdomen selected for nonoperative management. J Trauma 59:1155–1160–1161
Bodanapally UK, Shanmuganathan K, Mirvis SE, et al. (2009) MDCT diagnosis of penetrating diaphragm injury. Eur Radiol 19:1875–1881. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1367-9
Stein DM, York GB, Boswell S, et al. (2007) Accuracy of computed tomography (CT) scan in the detection of penetrating diaphragm injury. J Trauma 63:538–543. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e318068b53c
Nchimi A, Szapiro D, Ghaye B, et al. (2005) Helical CT of blunt diaphragmatic rupture. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:24–30. doi:10.2214/ajr.184.1.01840024
Chen H-W, Wong Y-C, Wang L-J, et al. (2010) Computed tomography in left-sided and right-sided blunt diaphragmatic rupture: experience with 43 patients. Clin Radiol 65:206–212. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2009.11.005
Dreizin D, Borja MJ, Danton GH, et al. (2013) Penetrating diaphragmatic injury: accuracy of 64-section multidetector CT with trajectography. Radiology 268:729–737. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121260
Gierada DS, Curtin JJ, Erickson SJ, et al. (1995) Diaphragmatic motion: fast gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging in healthy subjects. Radiology 194:879–884. doi:10.1148/radiology.194.3.7862995
Barbiera F, Nicastro N, Finazzo M, et al. (2003) The role of MRI in traumatic rupture of the diaphragm. Our experience in three cases and review of the literature. Radiol Med (Torino) 105:188–194
Hammer MM, Flagg E, Mellnick VM, et al. (2014) Computed tomography of blunt and penetrating diaphragmatic injury: sensitivity and inter-observer agreement of CT Signs. Emerg Radiol 21:143–149. doi:10.1007/s10140-013-1166-0
Desir A, Ghaye B (2012) CT of blunt diaphragmatic rupture. Radiographics 32:477–498. doi:10.1148/rg.322115082
Murray JG, Caoili E, Gruden JF, et al. (1996) Acute rupture of the diaphragm due to blunt trauma: diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166:1035–1039. doi:10.2214/ajr.166.5.8615237
Rees O, Mirvis SE, Shanmuganathan K (2005) Multidetector-row CT of right hemidiaphragmatic rupture caused by blunt trauma: a review of 12 cases. Clin Radiol 60:1280–1289. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2005.06.013
Desser TS, Edwards B, Hunt S, et al. (2010) The dangling diaphragm sign: sensitivity and comparison with existing CT signs of blunt traumatic diaphragmatic rupture. Emerg Radiol 17:37–44. doi:10.1007/s10140-009-0819-5
Gale ME (1985) Bochdalek hernia: prevalence and CT characteristics. Radiology 156:449–452. doi:10.1148/radiology.156.2.4011909
Mullins ME, Stein J, Saini SS, Mueller PR (2001) Prevalence of incidental Bochdalek’s Hernia in a large adult population. Am J Roentgenol 177:363–366. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.2.1770363
Yeh HC, Halton KP, Gray CE (1990) Anatomic variations and abnormalities in the diaphragm seen with US. Radiogr Rev Publ Radiol Soc N Am Inc 10:1019–1030. doi:10.1148/radiographics.10.6.2259759
Bocchini G, Guida F, Sica G, et al. (2012) Diaphragmatic injuries after blunt trauma: are they still a challenge? Emerg Radiol 19:225–235. doi:10.1007/s10140-012-1025-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not funded.
Conflicts of interest
MMH declares that he has no conflict of interest. DAR declares that he has no conflict of interest. VMM declares that he has no conflict of interest. SB declares that he has no conflict of interest. CAR declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammer, M.M., Raptis, D.A., Mellnick, V.M. et al. Traumatic injuries of the diaphragm: overview of imaging findings and diagnosis. Abdom Radiol 42, 1020–1027 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0908-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0908-3