Abstract
Purpose
The heart rate response (HRR, percentage change from baseline) to regadenoson during myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) can provide incremental prognostic value in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease. Our purpose was to evaluate the variability and prognostic value of HRR on serial measurements.
Methods
We studied 648 consecutive patients (61 ± 11 years, 48 % with diabetes) who underwent two regadenoson MPI studies (16 ± 9 months between studies). HRR <30 % was defined as abnormal. All-cause mortality was determined by chart review and verified using the US Social Security Death Master File.
Results
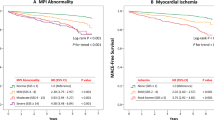
HRR was well correlated between the two studies (intraclass correlation coefficient 0.72, 95 % CI 0.67 – 0.76) with no systematic bias (mean difference 0.88 %, p = 0.2) or proportional bias (p = 0.5) by Bland-Altman analysis in all patients and in those with normal MPI on both studies. Of the 308 patients (48 %) with normal baseline HRR (HRR-1), 33 % had developed a blunted HRR on the second MPI study (HRR-2). Older age, male gender, end-stage renal disease, and abnormal baseline left ventricular ejection fraction were independent predictors of a new-onset abnormal HRR. During a mean follow-up of 2.4 ± 1.2 years, 55 patients (8.5 %) died. Patients with a blunted HRR-1 had increased mortality risk irrespective of their HRR-2 (p = 0.9, log-rank test). Among patients with normal HRR-1, a blunted HRR-2 was an independent predictor of all-cause mortality beyond clinical and traditional MPI data (hazard ratio 2.83, 95 % CI 1.14 – 7.03). Finally, patients with a normal HRR-1 and HRR-2 had the lowest event rate, while those with any abnormal HRR had an increased risk of death (hazard ratio 2.5, 95 % CI 1.2 – 5.4).
Conclusion
There was good correlation in the HRR to regadenoson on serial measurements without systematic or proportional biases. Patients with consistently normal HRR had the best prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- HRR:
-
Heart rate response
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- MPI:
-
Myocardial perfusion imaging
- PCI:
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention
- PDS:
-
Perfusion defect size
- SPECT:
-
Single photon emission computed tomography
References
Klocke FJ, Baird MG, Lorell BH, Bateman TM, Messer JV, Berman DS, et al. ACC/AHA/ASNC guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imaging – executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASNC Committee to Revise the 1995 Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Cardiac Radionuclide Imaging). Circulation. 2003;108:1404–18.
Hage FG, Ghimire G, Lester D, Mckay J, Bleich S, El-Hajj S, et al. The prognostic value of regadenoson myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015;22:1214–21.
Hachamovitch R, Berman DS, Kiat H, Cohen I, Lewin H, Amanullah A, et al. Incremental prognostic value of adenosine stress myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography and impact on subsequent management in patients with or suspected of having myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol. 1997;80:426–33.
Shaw LJ, Hage FG, Berman DS, Hachamovitch R, Iskandrian A. Prognosis in the era of comparative effectiveness research: where is nuclear cardiology now and where should it be? J Nucl Cardiol. 2012;19:1026–43.
Hage FG, Dean P, Bhatia V, Iqbal F, Heo J, Iskandrian AE. The prognostic value of the heart rate response to adenosine in relation to diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Am Heart J. 2011;162:356–62.
Hage FG, Dean P, Iqbal F, Heo J, Iskandrian AE. A blunted heart rate response to regadenoson is an independent prognostic indicator in patients undergoing myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2011;18:1086–94.
Hage FG, Wackers FJ, Bansal S, Chyun DA, Young LH, Inzucchi SE, et al. The heart rate response to adenosine: a simple predictor of adverse cardiac outcomes in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:2952–7.
AlJaroudi W, Campagnoli T, Fughhi I, Wassouf M, Ali A, Doukky R. Prognostic value of heart rate response during regadenoson stress myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with end stage renal disease. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0234-0.
Andrikopoulou E, Hage FG. Heart rate response to regadenoson: making the case for its value in clinical practice. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0269-2.
Iskandrian AE, Hage FG, Shaw LJ, Mahmarian JJ, Berman DS. Serial myocardial perfusion imaging: defining a significant change and targeting management decisions. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7:79–96.
El-Hajj S, AlJaroudi WA, Farag A, Bleich S, Manaoragada P, Iskandrian AE, et al. Effect of changes in perfusion defect size during serial regadenoson myocardial perfusion imaging on cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk patients. J Nucl Cardiol. 2016;23:101–12.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001;285:2486–97.
Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Hansen CL, Taillefer R, Yao SS. ASNC imaging guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures: stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol. 2009;16:331. doi:10.1007/s12350-009-9062-4.
Al Jaroudi W, Iskandrian AE. Regadenoson: a new myocardial stress agent. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1123–30.
Ficaro EP, Lee BC, Kritzman JN, Corbett JR. Corridor4DM: the Michigan method for quantitative nuclear cardiology. J Nucl Cardiol. 2007;14:455–65.
Germano G, Kiat H, Kavanagh PB, Moriel M, Mazzanti M, Su HT, et al. Automatic quantification of ejection fraction from gated myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:2138–47.
Hage FG, Heo J, Franks B, Belardinelli L, Blackburn B, Wang W, et al. Differences in heart rate response to adenosine and regadenoson in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Am Heart J. 2009;157:771–6.
Bangalore S. Stress testing in patients with chronic kidney disease: the need for ancillary markers for effective risk stratification and prognosis. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0264-7
Myocardial Study Market Guide, January–June 2012. Malvern, PA: Arlington Medical Resources, Inc; 2012.
Lexiscan. Northbrook, IL: Astellas Pharma US; 2015.
Ben Bouallegue F, Roubille F, Lattuca B, Cung TT, Macia JC, Gervasoni R, et al. SPECT myocardial perfusion reserve in patients with multivessel coronary disease: correlation with angiographic findings and invasive fractional flow reserve measurements. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1712–7.
Katz JS, Ruisi M, Giedd KN, Rachko M. Assessment of transient ischemic dilation (TID) ratio in gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) using regadenoson, a new agent for pharmacologic stress testing. J Nucl Cardiol. 2012;19:727–34.
Lester D, El-Hajj S, Farag AA, Bhambhvani P, Tauxe L, Heo J, et al. Prognostic value of transient ischemic dilation with regadenoson myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0272-7
AlJaroudi W, Aggarwal H, Venkataraman R, Heo J, Iskandrian AE, Hage FG. Impact of left ventricular dyssynchrony by phase analysis on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Nucl Cardiol. 2010;17:1058–64.
AlJaroudi W, Alraies MC, Menon V, Brunken RC, Cerqueira MD, Jaber WA. Predictors and incremental prognostic value of left ventricular mechanical dyssynchrony response during stress-gated positron emission tomography in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Cardiol. 2012;19:958–69.
Dhalla AK, Wong MY, Wang WQ, Biaggioni I, Belardinelli L. Tachycardia caused by A2A adenosine receptor agonists is mediated by direct sympathoexcitation in awake rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:695–702.
Iqbal FM, Al Jaroudi W, Sanam K, Sweeney A, Heo J, Iskandrian AE, et al. Reclassification of cardiovascular risk in patients with normal myocardial perfusion imaging using heart rate response to vasodilator stress. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111:190–5.
Bellam N, Veledar E, Dorbala S, Di Carli MF, Shah S, Eapen D, et al. Prognostic significance of impaired chronotropic response to pharmacologic stress Rb-82 PET. J Nucl Cardiol. 2014;21:233–44.
Williams BA, Merhige ME. Comparing changes in severe versus mild perfusion defect size in patients who underwent serial rubidium-82 positron emission tomography myocardial perfusion imaging. Am J Cardiol. 2014;114:1512–7.
Shaw LJ, Cerqueira MD, Brooks MM, Althouse AD, Sansing VV, Beller GA, et al. Impact of left ventricular function and the extent of ischemia and scar by stress myocardial perfusion imaging on prognosis and therapeutic risk reduction in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: results from the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation 2 Diabetes (BARI 2D) trial. J Nucl Cardiol. 2012;19:658–69.
Farzaneh-Far A, Phillips HR, Shaw LK, Starr AZ, Fiuzat M, O'Connor CM, et al. Ischemia change in stable coronary artery disease is an independent predictor of death and myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol Img. 2012;5:715–24.
Zellweger MJ, Maraun M, Osterhues HH, Keller U, Muller-Brand J, Jeger R, et al. Progression to overt or silent CAD in asymptomatic patients with diabetes mellitus at high coronary risk: main findings of the prospective multicenter BARDOT trial with a pilot randomized treatment substudy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7:1001–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
None.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Hage reports grant funding from Astellas Pharma USA. Dr. Iskandrian is scientific advisor for Rapidscan Pharma. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not describe any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Efstathia Andrikopoulou and Wael A. AlJaroudi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrikopoulou, E., AlJaroudi, W.A., Farag, A. et al. The reproducibility and prognostic value of serial measurements of heart rate response to regadenoson during myocardial perfusion imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 1493–1502 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3380-y