Abstract
Purpose
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2), epidermal growth factor receptor-1 (EGFR), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) stimulate key processes involved in tumor progression and are important targets for cancer drugs. 18F-FDG maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) is a marker of tumor metabolic activity. The purpose of this study was to measure SUVmax combined with VEGFR-2, EGFR and COX-2 proteins in pretreatment tumor biopsies from patients with locally advanced rectal cancer receiving intensive neoadjuvant treatment and to correlate the findings with clinical outcome.
Methods
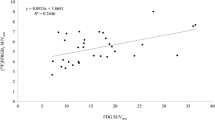
VEGFR-2, EGFR and COX-2 were measured using the immunoreactive score (IRS). SUVmax (median 8.4) was quantified in tumors with molecular overexpression (IRS ≥3 + SUVmax ≥ 8.4 indicating active tumors; SUVmax <8.4 indicating inactive tumors). The Cox proportional hazards model was used to explore associations between tumor markers, disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results
The study group comprised 38 patients with a median follow-up of 69.3 months (range 4.5 – 92 months). Multivariate analysis showed that active tumors (overexpressing VEGFR-2, high SUVmax) were associated with worse DFS (HR 4.73, 95 % CI 1.18 – 22.17; p = 0.04) and OS (HR 4.28, 95 % CI 1.04 – 20.12; p = 0.05).
Conclusion
Active tumors overexpressing VEGFR-2 are associated with a worse overall outcome in patients with rectal cancer treated with induction chemotherapy followed by pelvic chemoradiation and surgery. The optimal diagnostic cut-off level for this novel biomarker association should be investigated. Evaluation in a clinical trial is required to determine whether selected patients could benefit from a VEGFR-targeting drug.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heald RJ, Ryall RD. Recurrence and survival after total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Lancet. 1986;1:1479–82.
Smith N, Brown G. Preoperative staging of rectal cancer. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:20–31.
Nagtegaal ID, van Krieken JH. The role of pathologists in the quality control of diagnosis and treatment of rectal cancer – an overview. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:964–72.
Bosset JF, Collette L, Calais G, Mineur L, Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L, et al. Chemotherapy with preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1114–23.
van Gijn W, Marijnen CA, Nagtegaal ID, Kranenbarg EM, Putter H, Wiggers T, et al. Preoperative radiotherapy combined with total mesorectal excision for resectable rectal cancer: 12-Year follow-up of the multicentre, randomised controlled TME trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:575–82.
Bujko K, Nowacki MP, Nasierowska-Guttmejer A, Michalski W, Bebenek M, Pudełko M, et al. Sphincter preservation following preoperative radiotherapy for rectal cancer: report of a randomised trial comparing short-term radiotherapy vs. conventionally fractionated radiochemotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2004;72:15–24.
Blomqvist L, Glimelius B. The “good”, the “bad”, and the “ugly” rectal cancers. Acta Oncol. 2008;47:5–8.
Roth AD, Delorenzi M, Tejpar S, Yan P, Klingbiel D, Fiocca R, et al. Integrated analysis of molecular and clinical prognostic factors in stage II/III colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1635–46.
Kuremsky JG, Tepper JE, McLeod HL. Biomarkers for response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation for rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:673–88.
McShane L, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM, et al. REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:1690–6.
Altman DG, McShane LM, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE. Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK): explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2012;9:e1001216.
Ali HR, Dawson SJ, Blows FM. A Ki67/BCL2 index based on immunohistochemistry is highly prognostic in ER-positive breast cancer. J Pathol. 2012;226:97–107.
Calvo FA, Sole CV, de la Mata D, Cabezón L, Gómez-Espí M, Alvarez E, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT-based treatment response evaluation in locally advanced rectal cancer: a prospective validation of long-term outcomes. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:657–67.
Calvo FA, Cabezón L, González C, Soria A, de la Mata D, Gómez-Espí M, et al. 18F-FDG PET bio-metabolic monitoring of neoadjuvant therapy effects in rectal cancer: focus on nodal disease characteristics. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97:212–6.
Calvo FA, Serrano FJ, Diaz-González JA, Gomez-Espi M, Lozano E, Garcia R, et al. Improved incidence of pT0 downstaged surgical specimens in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) treated with induction oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil and preoperative chemoradiation. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:1103–10.
Quirke P, Durdey P, Dixon MF, Williams NS. Local recurrence of rectal adenocarcinoma due to inadequate surgical resection. Histopathological study of lateral tumor spread and surgical excision. Lancet. 1986;2:996–9.
American Joint Committee on Cancer. General information on cancer staging and end-results reporting. In: Cancer Staging Handbook. Seventh edition, Heidelberg: Springer; 2007. p.1–39.
Rödel C, Martus P, Papadoupolos T, Füzesi L, Klimpfinger M, Fietkau R, et al. Prognostic significance of tumor regression after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8688–96.
Beaulieu S, Kinahan P, Tseng J, Dunnwald LK, Schubert EK, Pham P, et al. SUV varies with time after injection in (18)F-FDG PET of breast cancer: characterization and method to adjust for time differences. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1044–50.
Boellaard R, Krak NC, Hoekstra OS, Lammertsma AA. Effects of noise, image resolution, and ROI definition on the accuracy of standard uptake values: a simulation study. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1519–27.
Remmele W, Stegner HE. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe. 1987;8:138–40.
Shields AF. Positron emission tomography measurement of tumor metabolism and growth: its expanding role in oncology. Mol Imaging Biol. 2006;8:141–50.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–57.
Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996;86:353–64.
Bouck N, Stellmach V, Hsu S. How tumors become angiogenic. Adv Cancer Res. 1996;69:135–74.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(21):4368–80.
Veeravagu A, Hsu AR, Cai W, Hou LC, Tse VC, Chen X. Vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents in cancer therapy. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 2007;2:59–71.
Longo R, Gasparini G. Challenges for patient selection with VEGF inhibitors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007;60:151–70.
Mandrekar SJ, Sargent DJ. Clinical trial designs for predictive biomarker validation: theoretical considerations and practical challenges. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4027–34.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S, et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3584–90.
Hurwitz HI, Fehrenbacher L, Hainsworth JD, Heim W, Berlin J, Holmgren E, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin: an active regimen for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3502–8.
Chen Z, Duldulao MP, Li W, Lee W, Kim J, Garcia-Aguilar J. Molecular diagnosis of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:1008–17.
Glynne-Jones R, Anyamene N. Just how useful an endpoint is complete pathological response after neoadjuvant chemoradiation in rectal cancer? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:319–20.
Sanghera P, Wong DW, McConkey CC, Geh JI, Hartley A. Chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer: an updated analysis of factors affecting pathological response. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2008;20:176–86.
Glynne-Jones R, Hughes R. Critical appraisal of the ‘wait and see’ approach in rectal cancer for clinical complete responders after chemoradiation. Br J Surg. 2012;99:897–909.
Valentini V, van Stiphout R, Lammering G, Gambacorta MA, Barba MC, Bebenek M, et al. Nomograms for predicting local recurrence, distant metastases, and overall survival for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer on the basis of European randomized clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3163–72.
Acknowledgments
This study was financed in part by a research grant from Mutua Madrileña Biomedical, Foundation Institute Health Research Marañon, study code CMF, FMM 06–02.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 85 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sole, C.V., Calvo, F.A., Alvarez, E. et al. Clinical significance of VEGFR-2 and 18F-FDG PET/CT SUVmax pretreatment score in predicting the long-term outcome of patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40, 1635–1644 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2479-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2479-7