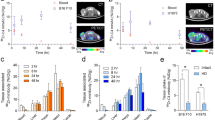
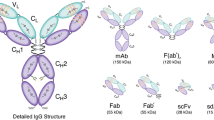
Abstract
Imaging of gene expression in vivo has many potential uses for biomedical research and drug discovery, ranging from the study of gene regulation and cancer to the non-invasive assessment of gene therapies. To streamline the development of imaging marker gene technologies for nuclear medicine, we propose a new approach to the design of reporter/probe pairs wherein the reporter is a cell surface-expressed single chain antibody variable fragment that has been raised against a low molecular weight imaging probe with optimized pharmacokinetic properties. Proof of concept of the approach was achieved using a single chain antibody variable fragment that binds with high affinity to fluorescein and an imaging probe consisting of fluorescein isothiocyanate coupled to the chelator diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid labeled with the gamma-emitter 111In. We demonstrate specific high-affinity binding of this probe to the cell surface-expressed reporter in vitro and assess the in vivo biodistribution of the probe both in wild-type mice and in mice harboring tumor xenografts expressing the reporter. Specific uptake of the probe by, and in vivo imaging of, tumors expressing the reporter are shown. Since ScFvs with high affinities can be raised to almost any protein or small molecule, the proposed methodology may offer a new flexibility in the design of imaging tracer/reporter pairs wherein both probe pharmacokinetics and binding affinities can be readily optimized.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissleder R, Mahmood U. Molecular imaging. Radiology 2001; 219:316–333.
Yu Y, Annala AJ, Barrio JR, Toyokuni T, Satyamurthy N, Namavari M, Cherry SR, Phelps ME, Herschman HR, Gambhir SS. Quantification of target gene expression by imaging reporter gene expression in living animals. Nat Med 2000; 6:933–937.
Contag PR, Olomu IN, Stevenson DK, Contag CH. Bioluminescent indicators in living mammals. Nat Med 1998; 4:245–247.
Tjuvajev JG, Chen SH, Joshi A, Joshi R, Guo ZS, Balatoni J, Ballon D, Koutcher J, Finn R, Woo SL, Blasberg RG. Imaging adenoviral-mediated herpes virus thymidine kinase gene transfer and expression in vivo. Cancer Res 1999; 59:5186–5193.
Yaghoubi SS, Wu L, Liang Q, Toyokuni T, Barrio JR, Namavari M, Satyamurthy N, Phelps ME, Herschman HR, Gambhir SS. Direct correlation between positron emission tomographic images of two reporter genes delivered by two distinct adenoviral vectors. Gene Ther 2001; 8:1072–1080.
Tjuvajev JG, Avril N, Oku T, Sasajima T, Miyagawa T, Joshi R, Safer M, Beattie B, DiResta G, Daghighian F, Augensen F, Koutcher J, Zweit J, Humm J, Larson SM, Finn R, Blasberg R. Imaging herpes virus thymidine kinase gene transfer and expression by positron emission tomography. Cancer Res 1998; 58:4333–4341.
Gambhir SS, Barrio JR, Phelps ME, Iyer M, Namavari M, Satyamurthy N, Wu L, Green LA, Bauer E, MacLaren DC, Nguyen K, Berk AJ, Cherry SR, Herschman HR. Imaging adenoviral-directed reporter gene expression in living animals with positron emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999; 96:2333–2338.
Iyer M, Barrio JR, Namavari M, Bauer E, Satyamurthy N, Nguyen K, Toyokuni T, Phelps ME, Herschman HR, Gambhir SS. 8-[18F]Fluoropenciclovir: an improved reporter probe for imaging HSV1-tk reporter gene expression in vivo using PET. J Nucl Med 2001; 42:96–105.
MacLaren DC, Gambhir SS, Satyamurthy N, Barrio JR, Sharfstein S, Toyokuni T, Wu L, Berk AJ, Cherry SR, Phelps ME, Herschman HR. Repetitive, non-invasive imaging of the dopamine D2 receptor as a reporter gene in living animals. Gene Ther 1999; 6:785–791.
Zinn KR, Buchsbaum DJ, Chaudhuri TR, Mountz JM, Grizzle WE, Rogers BE. Noninvasive monitoring of gene transfer using a reporter receptor imaged with a high-affinity peptide radiolabeled with99mTc or 188Re. J Nucl Med 2000; 41:887–895.
Weissleder R, Moore A, Mahmood U, Bhorade R, Benveniste H, Chiocca EA, Basilion JP. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of transgene expression. Nat Med 2000; 6:351–355.
Louie AY, Huber MM, Ahrens ET, Rothbacher U, Moats R, Jacobs RE, Fraser SE, Meade TJ. In vivo visualization of gene expression using magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Biotechnol 2000; 18:321–325.
Vaughan TJ, Williams AJ, Pritchard K, Osbourn JK, Pope AR, Earnshaw JC, McCafferty J, Hodits RA, Wilton J, Johnson KS. Human antibodies with sub-nanomolar affinities isolated from a large non-immunized phage display library. Nat Biotechnol 1996; 14:309–314.
Lin AY, Devaux B, Green A, Sagerstrom C, Elliott JF, Davis MM. Expression of T cell antigen receptor heterodimers in a lipid-linked form. Science 1990; 249:677–679.
Wrighton NC, Farrell FX, Chang R, Kashyap AK, Barbone FP, Mulcahy LS, Johnson DL, Barrett RW, Jolliffe LK, Dower WJ. Small peptides as potent mimetics of the protein hormone erythropoietin. Science 1996; 273:458–464.
Koller KJ, Whitehorn EA, Tate E, Ries T, Aguilar B, Chernov-Rogan T, Davis AM, Dobbs A, Yen M, Barrett RW. A generic method for the production of cell lines expressing high levels of 7-transmembrane receptors. Anal Biochem 1997; 15:51–60.
Mattheakis LC, Olivan SE, Dias JM, Northrop JP. Expression of cre recombinase as a reporter of signal transduction in mammalian cells. Chem Biol 1999; 6:835–844.
Northrop JP, Pustelnik MJ, Lu AT, Grove JR. Characterization of the roles of SH2 domain-containing proteins in T-lymphocyte activation by using dominant negative SH2 domains. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16:2255–2263.
McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, Chriswell DJ. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 1990; 348:552–554.
Winter G, Griffiths AD, Hawkins RE, Hoogenbloom HR. Making antibodies by phage display technology. Annu Rev Immunol 1994; 12:433–455.
Winthrop MD, Denardo GL, Denardo SJ. Antibody phage display applications for nuclear medicine imaging and therapy. Q J Nucl Med 2000; 44:284–295.
Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G, Dorsch-Hasler K, Fleckenstein B, Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell 1985; 41:521–530.
MacLaren DC, Toyokuni T, Cherry SR, Barrio JR, Phelps ME, Herschman HR, Gambhir SS. PET imaging of transgene expression. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48:337–348.
Begent RH, Verhaar MJ, Chester KA, Casey JL, Green AJ, Napier MP, Hope-Stone LD, Cushen N, Keep PA, Johnson CJ, Hawkins RE, Hilson AJ, Robson L. Clinical evidence of efficient tumor targeting based on single-chain Fv antibody selected from a combinatorial library. Nat Med 1996; 2:979–984.
Adams GP, Schier R, McCall AM, Crawford RS, Wolf EJ, Weiner LM, Marks JD Prolonged in vivo tumour retention of a human diabody targeting the extracellular domain of human HER2/neu. Br J Cancer 1998; 77:1405–1412.
Viti F, Tarli L, Giovannoni L, Zardi L, Neri D. Increased binding affinity and valence of recombinant antibody fragments lead to improved targeting of tumoral angiogenesis. Cancer Res 1999; 59:347–352.
Willuda J, Honegger A, Waibel R, Schubiger PA, Stahel R, Zangemeister-Wittke U, Pluckthun A. High thermal stability is essential for tumor targeting of antibody fragments: engineering of a humanized anti-epithelial glycoprotein-2 (epithelial cell adhesion molecule) single-chain Fv fragment. Cancer Res 1999; 59:5758–5767.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jane Osbourn at Cambridge Antibody Technology (Melbourn, UK) for providing ScFvs. We thank George Segall and Ursala Ehmann at the VA Palo Alto Health Care System (Palo Alto, Calif.) for use of facilities and instrumentation. This work was also supported by the GlaxoSmithKline Ventures group (Philadelphia, Pa.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Northrop, J.P., Bednarski, M., Barbieri, S.O. et al. Cell surface expression of single chain antibodies with applications to imaging of gene expression in vivo. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30, 1292–1298 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1237-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-003-1237-7