Abstract
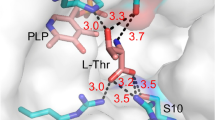
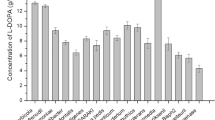
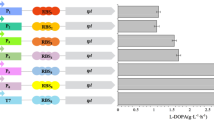
The dtaAX gene encoding a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (pyridoxal-P)-dependent low-specificity d-threonine aldolase was cloned from the chromosomal DNA of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans IFO 12669. It contains an open reading frame consisting of 1,134 nucleotides corresponding to 377 amino acid residues. The predicted amino acid sequence displayed 54% identity with that of d-threonine aldolase from gram-positive bacteria Arthrobacter sp. DK-38, but showed no significant similarity with those of other known pyridoxal-P enzymes. This gram-negative bacterial enzyme was highly overproduced in recombinant Escherichia coli cells, and the specific activity of the enzyme in the cell extract was as high as 18 U/mg (purified enzyme 38.6 U/mg), which was 6,000 times higher than that from the wild-type Alcaligenes cell extract. The recombinant enzyme was thus feasibly purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulfate fractionation and DEAE-Toyopearl chromatography steps. The recombinant low-specificity d-threonine aldolase was shown to be an efficient biocatalyst for resolution of l-β-3,4-methylenedioxyphenylserine, an intermediate for production of a therapeutic drug for Parkinson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 September 1999 / Received revision: 1 November 1999 / Accepted: 12 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Odani, M., Yasuoka, T. et al. Gene cloning and overproduction of low-specificity d-threonine aldolase from Alcaligenes xylosoxidans and its application for production of a key intermediate for parkinsonism drug. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54, 44–51 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002539900301
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002539900301