Abstract
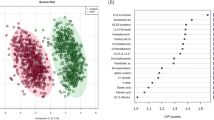
Caseous lymphadenitis (CLA), an infectious disease caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in small ruminants, is highly prevalent worldwide. Economic losses have already been associated with the disease, and little is known about the host–pathogen relationship associated with the disease. The present study aimed to perform a metabolomic study of the C. pseudotuberculosis infection in goats. Serum samples were collected from a herd of 173 goats. The animals were classified as controls (not infected), asymptomatic (seropositives but without detectable CLA clinical signs), and symptomatic (seropositive animals presenting CLA lesions), according to microbiological isolation and immunodiagnosis. The serum samples were analyzed using nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR), nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY), and Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) sequences. The NMR data were analyzed using chemometrics, and principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least square discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) were performed to discover specific biomarkers responsible for discrimination between the groups. A high dissemination of the infection by C. pseudotuberculosis was observed, being 74.57% asymptomatic and 11.56% symptomatic. In the evaluation of 62 serum samples by NMR, the techniques were satisfactory in the discrimination of the groups, being also complementary and mutually confirming, demonstrating possible biomarkers for the infection by the bacterium. Twenty metabolites of interest were identified by NOESY and 29 by CPMG, such as tryptophan, polyunsaturated fatty acids, formic acid, NAD+, and 3-hydroxybutyrate, opening promising possibilities for the use of these results in new therapeutic, immunodiagnosis, and immunoprophylactic tools, as well as for studies of the immune response against C. pseudotuberculosis.
Key points
• Sixty-two samples from healthy, CLA asymptomatic, and symptomatic goats were screened
• Twenty metabolites of interest were identified by NOESY and 29 by CPMG
• 1 H-NMR NOESY and CPMG were complementary and mutually confirming




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Almeida AK, Hegarty RS, Cowie A (2021) Meta-analysis quantifying the potential of dietary additives and rumen modifiers for methane mitigation in ruminant production systems. Anim Nutr 7:1219–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.005
Anunthawan T, de la Fuente-Núñez C, Hancock RE, Klaynongsruang S (2015) Cationic amphipathic peptides KT2 and RT2 are taken up into bacterial cells and kill planktonic and biofilm bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.02.021
Asselstine V, Lam S, Miglior F, Brito LF, Sweett H, Guan L, Waters SM, Plastow G, Cánovas A (2021) The potential for mitigation of methane emissions in ruminants through the application of metagenomics, metabolomics, and other -OMICS technologies. J Anim Sci 99:skab193. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skab193
Barding GA Jr, Béni S, Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J, Larive CK (2013) Comparison of GC-MS and NMR for metabolite profiling of rice subjected to submergence stress. J Proteome Res 12:898–909. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr300953k
Barral TD, Mariutti RB, Arni RK, Santos AJ, Loureiro D, Sokolonski AR, Azevedo V, Borsuk S, Meyer R, Portela RD (2019) A panel of recombinant proteins for the serodiagnosis of caseous lymphadenitis in goats and sheep. Microb Biotechnol 12:1313–1323. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13454
Barral TD, Kalil MA, Mariutti RB, Arni RK, Gismene C, Sousa FS, Collares T, Seixas FK, Borsuk S, Estrela-Lima A, Azevedo V, Meyer R, Portela RW (2022) Immunoprophylactic properties of the Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis-derived MBP:PLD:CP40 fusion protein. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106:8035–8051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12279-1
Bernut A, Dupont C, Ogryzko NV, Neyret A, Herrmann JL, Floto RA, Renshaw SA, Kremer L (2019) CFTR protects against Mycobacterium abscessus infection by fine-tuning host oxidative defenses. Cell Rep 26:1828-1840.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.071
Blunt MH, Cox RI, Curtain CC, Dargie JD, Ferguson KA, Holmes PH, Huisman THJ, Leat WMF, Lindsay DB, Macfarlane WV, Moodie EW, Tucker EM (1975) The blood of sheep: composition and function. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Borchers HW. Pracma: practical numerical math functions. R package version 1.7.0, 2014. Available at http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pracma . Accessed at 09th February 2023
Brunetto MA, Ruberti B, Halfen DP, Caragelasco DS, Vendramini THA, Pedrinelli V, Macedo HT, Jeremias JT, Pontieri CFF, Ocampos FMM, Colnago LA, Kogika MM (2021) Healthy and chronic kidney disease (CKD) dogs have differences in serum metabolomics and renal diet may have slowed disease progression. Metabolites 11:782. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110782
Cedeno M, Murillo-Saich J, Coras R, Cedola F, Brandy A, Prior A, Pedersen A, Mateo L, Martinez-Morillo M, Guma M (2023) Serum metabolomic profiling identifies potential biomarkers in arthritis in older adults: an exploratory study. Metabolomics 19:37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02004-y
Costa L, Huerta B, Galán-Relaño Á, Gómez-Gascón L, Almeida A, Viegas I, Maldonado A (2020) Utility assessment of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of subclinical cases of caseous lymphadenitis in small ruminant flocks. Vet Med Sci 6:796–803. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3.297
Dejean S, Gonzalez I, Cao KAL. mixOmics: omics data integration project. R package version 5.0–1, 2013. [on-line]. Available at http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=mixOmics. Accessed on February 09th 2023
de Oliveira ZT, Ribeiro D, Azevedo VAC, Lara GHB, Motta RG, da Silva RC, Siqueira AK, de Nardi JG, Listoni FJP, de Souza Araújo ML, da Silva AV, Portilho FVR, da Rocha MA, Rodrigues CA, de Almeida BO, Ribeiro MG (2021) Bacteriological, cytological, and molecular investigation of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, mycobacteria, and other bacteria in caseous lymphadenitis and healthy lymph nodes of slaughtered sheep. Braz J Microbiol 52:431–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00403-0
de Pinho RB, de Oliveira Silva MT, Bezerra FSB, Borsuk S (2021) Vaccines for caseous lymphadenitis: up-to-date and forward-looking strategies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:2287–2296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11191-4
Debik J, Sangermani M, Wang F, Madssen TS, Giskeødegård GF (2021) Multivariate analysis of NMR-based metabolomic data. NMR Biomed 35:e4638. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4638
Dona AC, Kyriakides M, Scott F, Shephard EA, Varshavi D, Veselkov K, Everett JR (2016) A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 14:135–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2016.02.005
Dorella FA, Pacheco LG, Oliveira SC, Miyoshi A, Azevedo V (2006) Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: microbiology, biochemical properties, pathogenesis and molecular studies of virulence. Vet Res 37:201–218. https://doi.org/10.1051/vetres:2005056
Familiar O, Munier-Lehmann H, Negri A, Gago F, Douguet D, Rigouts L, Hernández AI, Camarasa MJ, Pérez-Pérez MJ (2008) Exploring acyclic nucleoside analogues as inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidylate kinase. ChemMedChem 3:1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.200800060
Fonseca Pereira G, VirgínioEmerencianoNeto J, Patrícia Alves Coelho Gracindo Â, de Maria Oliveira Silva Y, Dos Santos DG, Leandro Chaves Gurgel A, de Souza Marinho FJ, da Costa Lima GF (2021) Replacement of grain maize with spineless cactus in the diet of dairy goats. J Dairy Res 88:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029921000352
Ghosh RK, Hilario E, Liu V, Wang Y, Niks D, Holmes JB, Sakhrani VV, Mueller LJ, Dunn MF (2021) Mutation of βGln114 to Ala alters the stabilities of sllosteric states in tryptophan synthase catalysis. Biochemistry 60:3173–3186. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00383
Hanna VS, Hafez EAA (2018) Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: a review. J Adv Res 11:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2018.03.005
Jennings W, Epand RM (2020) CDP-diacylglycerol, a critical intermediate in lipid metabolism. Chem Phys Lipids 230:104914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2020.104914
Kalil MA, Santos LM, Barral TD, Rodrigues DM, Pereira NP, Sá MDCA, Umsza-Guez MA, Machado BAS, Meyer R, Portela RW (2019) Brazilian green propolis as a therapeutic agent for the post-surgical treatment of caseous lymphadenitis in sheep. Front Vet Sci 6:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2019.00399
Kędzierski W, Sadok I, Kowalik S, Janczarek I, Staniszewska M (2021) Does the type of exercise affect tryptophan catabolism in horses? Animals 15:100377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2021.100377
Kelly WJ, Mackie RI, Attwood GT, Janssen PH, McAllister TA, Leahy SC (2022) Hydrogen and formate production and utilisation in the rumen and the human colon. Anim Microbiome 4:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42523-022-00174-z
Knoflach F, Bertrand D (2021) Pharmacological modulation of GABAA receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 59:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2021.04.003
Landberg J, Wright NR, Wulff T, Herrgård MJ, Nielsen AT (2020) CRISPR interference of nucleotide biosynthesis improves production of a single-domain antibody in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 117:3835–3848. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27536
Lanjekar VB, Hivarkar SS, Vasudevan G, Joshi A, Dhakephalkar PK, Dagar SS (2022) Actinomyces ruminis sp. nov., an obligately anaerobic bacterium isolated from the rumen of cattle. Arch Microbiol 205(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03339-1
Liang JB, Paengkoum P (2019) Current status, challenges and the way forward for dairy goat production in Asia - conference summary of dairy goats in Asia. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 32:1233–1243. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.19.0272
Libardo MDJ, Duncombe CJ, Green SR, Wyatt PG, Thompson S, Ray PC, Ioerger TR, Oh S, Goodwin MB, Boshoff HIM, Barry CE 3rd (2021) Resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to indole 4-carboxamides occurs through alterations in drug metabolism and tryptophan biosynthesis. Cell Chem Biol 28:1180-1191.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.02.023
Marchev AS, Vasileva LV, Amirova KM, Savova MS, Balcheva-Sivenova ZP, Georgiev MI (2021) Metabolomics and health: from nutritional crops and plant-based pharmaceuticals to profiling of human biofluids. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:6487–6503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03918-3
Moffett JR, Namboodiri MA (2003) Tryptophan and the immune response. Immunol Cell Biol 81:247–265. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1711.2003.t01-1-01177.x
Montout L, Poullet N, Bambou JC (2021) Systematic review of the interaction between nutrition and immunity in livestock: effect of dietary supplementation with synthetic amino acids. Animals 11:2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102813
Pfeuffer M, Jaudszus A (2016) Pentadecanoic and heptadecanoic acids: multifaceted odd-chain fatty acids. Adv Nutr 7:730–734. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.011387
Ranaweera RKR, Capone DL, Bastian SEP, Cozzolino D, Jeffery DW (2021) A review of wine authentication using spectroscopic approaches in combination with chemometrics. Molecules 26:4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144334
Rebouças MF, Loureiro D, Barral TD, Seyffert N, Raynal JT, Sousa TJ, Figueiredo HCP, Azevedo V, Meyer R, Portela RW (2020) Cell wall glycolipids from Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strains with different virulences differ in terms of composition and immune recognition. Braz J Microbiol 51:2101–2110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00343-9
Ruiz H, Ferrer LM, Ramos JJ, Baselga C, Alzuguren O, Tejedor MT, de Miguel R, Lacasta D (2020) The relevance of caseous lymphadenitis as a cause of culling in adult sheep. Animals 10:1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10111962
Ruiz-Cabello J, Sevilla IA, Olaizola E, Bezos J, Miguel-Coello AB, Muñoz-Mendoza M, Beraza M, Garrido JM, Izquierdo-García JL (2022) Benchtop nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic approach for the diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis. Transbound Emerg Dis 69:e859–e870. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.14365
Santos LM, Stanisic D, Menezes UJ, Mendonça MA, Barral TD, Seyffert N, Azevedo V, Durán N, Meyer R, Tasic L, Portela RW (2019) Biogenic silver nanoparticles as a post-surgical treatment for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection in small ruminants. Front Microbiol 10:824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00824
Sieniawska E, Sawicki R, Truszkiewicz W, Marchev AS, Georgiev MI (2021) Usnic acid treatment changes the composition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell envelope and alters bacterial redox status. mSystems 6:e00097-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00097-21
Silva WM, Folador EL, Soares SC, Souza GHMF, Santos AV, Sousa CS, Figueiredo H, Miyoshi A, Le Loir Y, Silva A, Azevedo V (2017) Label-free quantitative proteomics of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolates reveals differences between Biovars ovis and equi strains. BMC Genomics 18:451. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3835-y
Stanisic D, Fregonesi NL, Barros CHN, Pontes JGM, Fulaz S, Menezes UJ, Nicoleti JL, Castro TLP, Seyffert N, Azevedo V, Durán N, Portela RW, Tasic L (2018) NMR insights on nano silver post-surgical treatment of superficial caseous lymphadenitis in small ruminants. RSC Adv 8:40778–40786. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08218a
Tatituri RVV, Hsu FF (2021) Characterization of the uncommon lipid families in Corynebacterium glutamicum by mass spectrometry. Methods Mol Biol 2306:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1410-5_15
Vale VL, Silva Mda C, de Souza AP, Trindade SC, de Moura-Costa LF, Dos Santos-Lima EK, Nascimento IL, Cardoso HS, Marques Ede J, Paule BJ, Nascimento RJ (2016) Humoral and cellular immune responses in mice against secreted and somatic antigens from a Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis attenuated strain: Immune response against a C. pseudotuberculosis strain. BMC Vet Res 2:195. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-
Watanabe M, Roth TL, Bauer SJ, Lane A, Romick-Rosendale LE (2016) Feasibility study of NMR based serum metabolomic profiling to animal health monitoring: a case study on iron storage disease in captive Sumatran rhinoceros (Dicerorhinussumatrensis). Plos One 11:e0156318. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156318
Wei Y, Jia C, Lan Y, Hou X, Zuo J, Li J, Wang T, Mao G (2019) The association of tryptophan and phenylalanine are associated with arsenic-induced skin lesions in a Chinese population chronically exposed to arsenic via drinking water: a case-control study. BMJ Open 9:e025336. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025336
Xu B, Chen M, Yao M, Ji X, Mao Z, Tang W, Qiao S, Schick SF, Mao JH, Hang B, Xia Y (2015) Metabolomics reveals metabolic changes in male reproductive cells exposed to thirdhand smoke. Sci Rep 5:15512. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15512
Zhu C, Zhang Q, Zhao X, Yang Z, Yang F, Yang Y, Tang J, Laghi L (2023) Metabolomic analysis of multiple biological specimens (feces, serum, and urine) by 1H-NMR spectroscopy from dairy cows with clinical mastitis. Animals 13:741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040741
Acknowledgements
The authors are profoundly grateful to Francisca Soares (LABIMUNO ICS/UFBA) for the technical assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa e Extensão (FAPEX). TDB was a PhD Fellow from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). DAEF, LT, and VA are research fellows from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). RWP is a technical development fellow from CNPq (Proc. 310058/2022–8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JLN and ESB conceived the research, conducted experiments, and wrote the manuscript. DS, MJ, TDB, SAH, and DAEF conducted experiments. VA, LT, and RM obtained resources, supervised the experiments, and critically reviewed the manuscript. RWP conceived research, obtained results, supervised the experiments, analyzed data, edited the manuscript, and critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (CEUA) of the Federal Rural University of the Semiarid (UFERSA) under the protocol number 23091003895/2014–71.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nicoleti, J.L., Braga, E.S., Stanisic, D. et al. A serum NMR metabolomic analysis of the Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection in goats. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 4593–4603 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12595-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12595-0