Abstract
Global burden of fungal infections and associated health risk has accelerated at an incredible pace and needs to be attended at the earliest with an unbeatable therapeutic intervention. Candida glabrata is clinically the most relevant and least drug susceptible Candida species. In the pursuit of mining alternative novel drug candidates, the antifungal activity of a monoterpene phytoactive molecule geraniol (GR) against C. glabrata biofilm was evaluated. Biofilm inhibitory and eradication ability of GR evaluated against C. glabrata along with its clinical isolates. Impact of GR on various cellular pathways was evaluated to delineate its antifungal mode of action. GR has inhibited both planktonic and sessile growth of all the studied C. glabrata strains and eradicated the mature biofilm. GR reduced the carbohydrate and eDNA content, as well as hydrolytic enzyme activity in extracellular matrix of C. glabrata. The chemical profiling, microscopic, and spectroscopic studies revealed that GR targets chitin and β-glucan in cell wall. Further, results highlighted the reduction of cell membrane ergosterol content, and blocking of ABC drug efflux pump by GR which was also confirmed by RT-PCR where expression of CDR1 and ERG4 was downregulated in GR exposed C. glabrata cells. The fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry results emphasized the alteration in mitochondrial activity, increased Ca+2 uptake, thus changing the membrane permeability ensuing increased cytochrome C release from mitochondria to cytoplasm. Indeed, GR also has arrested cell cycle in G1/S phase and interfered with DNA replication. These observations suggest GR targets multiple cellular pathways and mediated killing of C. glabrata cells via apoptosis. In conclusion, the present study strengthens the candidacy of GR as novel antifungal therapeutic.
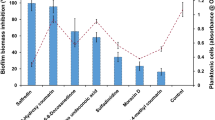
Key points • GR inhibits growth and eradicates biofilm of C. glabrata and its clinical isolates. • GR inactivates the hydrolytic enzymes in extracellular matrix. • GR mediates C. glabrata apoptosis by interfering with multiple signaling pathways. |
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Algburi A, Comito N, Kashtanov D, Dicks LMT, Chikindas ML (2017) Control of biofilm formation: antibiotics and beyond. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02508-16
Alvino GM, Collingwood D, Murphy JM, Delrow J, Brewer BJ, Raghuraman MK (2007) Replication in hydroxyurea: it’s a matter of time. Mol Cell Biol 27:6396–6406. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00719-07
Bassolé IHN, Juliani HR (2012) Essential oils in combination and their antimicrobial properties. Molecules 17:3989–4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17043989
Brookes PS, Yoon Y, Robotham JL, Anders MW, Sheu SS (2004) Calcium, ATP, and ROS: a mitochondrial love-hate triangle. Am J Phys Cell Phys 287(4):C817–C8133. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2004
Burgain A, Tebbji F, Khemiri I, Sellam A (2020) Metabolic reprogramming in the opportunistic yeast Candida albicans in response to hypoxia. mSphere 5:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1128/msphere.00913-19
Butler MS, Buss AD (2006) Natural products-the future scaffolds for novel antibiotics? Biochem Pharmacol 71:919–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2005.10.012
CLSI C (2008) Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous fungi; Approved Standard—Second Edition—Document M38-A2
Costa-de-Oliveira S, Silva AP, Miranda IM, Salvador A, Azevedo MM, Munro CA, Rodrigues AG, Pina-Vaz C (2013) Determination of chitin content in fungal cell wall: an alternative flow cytometric method. Cytom Part A 83(A):324–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.22250
de Alteriis E, Maselli V, Falanga A, Galdiero S, Di Lella FM, Gesuele R, Guida M, Galdiero E (2018) Efficiency of gold nanoparticles coated with the antimicrobial peptide indolicidin against biofilm formation and development of Candida spp. clinical isolates. Infect Drug Resist 11:915–925. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S164262
De Oliveira Pereira F, Mendes JM, De Oliveira LE (2013) Investigation on mechanism of antifungal activity of eugenol against Trichophyton rubrum. Med Mycol 51:507–513. https://doi.org/10.3109/13693786.2012.742966
De Oliveira Pereira F, Mendes JM, Lima IO, De Lira Mota KS, De Oliveira WA, De Oliveira LE (2015) Antifungal activity of geraniol and citronellol, two monoterpenes alcohols, against Trichophyton rubrum involves inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis. Pharm Biol 53:228–234. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.913299
Elshafie HS, Grul’ová D, Baranová B, Caputo L, De Martino L, Sedlák V, Camele I, De Feo V (2019) Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of essential oil extracted from Solidago canadensis L. Growing wild in Slovakia. Molecules 24:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071206
Fausto A, Rodrigues ML, Coelho C (2019) The still underestimated problem of fungal diseases worldwide. Front Microbiol 10:214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00214
Gorlenko CL, Kiselev HY, Budanova EV, Zamyatnin AA, Ikryannikova LN (2020) Plant secondary metabolites in the battle of drugs and drug-resistant bacteria: New heroes or worse clones of antibiotics? Antibiotics 9:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040170
Gupta P, Nath S, Meena RC, Kumar N (2014) Comparative effects of hypoxia and hypoxia mimetic cobalt chloride on in vitro adhesion, biofilm formation and susceptibility to amphotericin B of Candida glabrata. J Mycol Médicale/J Med Mycol 24:e169–e177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2014.08.003
Gupta P, Chanda R, Rai N, Kataria VK, Kumar N (2016) Antihypertensive, amlodipine besilate inhibits growth and biofilm of human fungal pathogen Candida. Assay Drug Dev Technol 14:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1089/adt.2016.714
Gupta P, Gupta S, Sharma M, Kumar N, Pruthi V, Poluri KM (2018) Effectiveness of phytoactive molecules on transcriptional expression, biofilm matrix, and cell wall components of Candida glabrata and its clinical isolates. ACS Omega 3:12201–12214. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01856
Gupta P, Meena RC, Kumar N (2020a) Microbial Pathogenesis Functional characterization of Candida glabrata ORF , CAGL0M02233g for its role in stress tolerance and virulence. Microb Pathog 149:104469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104469
Gupta P, Pruthi V, Poluri KM (2020b) Mechanistic insights into Candida biofilm eradication potential of eucalyptol. J Appl Microbiol:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14940
Gupta P, Goel A, Singh KR, Meher MK, Gulati K, Poluri KM (2021) Dissecting the anti-biofilm potency of kappa-carrageenan capped silver nanoparticles against Candida species. Int J Biol Macromol 172:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.035
Holmes AR, Cardno TS, Strouse JJ, Ivnitski-Steele I, Keniya MV, Lackovic K, Monk BC, Sklar LA, Cannon RD (2016) Targeting efflux pumps to overcome antifungal drug resistance. Future Med Chem 8:1485–1501. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc-2016-0050
Íñigo M, Del Pozo JL (2018) Fungal biofilms: from bench to bedside. Rev Esp Quimioter 31:35–38
Kaur R, Domergue R, Zupancic ML, Cormack BP (2005) A yeast by any other name: Candida glabrata and its interaction with the host. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2005.06.012
Kumar K, Askari F, Sahu MS, Kaur R (2019) Candida glabrata: a lot more than meets the eye. Microorganisms 7:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020039
Kwolek-mirek M, Zadrag-Tecza R (2014) Comparison of methods used for assessing the viability and vitality of yeast cells. 14:1068–1079 . https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12202
Lei Y, Fu P, Jun X, Cheng P (2019) Pharmacological properties of geraniol–a review. Planta Med 85(01):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0750-6907
Leite MCA, De Brito Bezerra AP, De Sousa JP, De Oliveira LE (2015) Investigating the antifungal activity and mechanism(s) of geraniol against Candida albicans strains. Med Mycol 53:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myu078
Mahizan NA, Yang SK, Moo CL, Song AAL, Chong CM, Chong CW, Abushelaibi A, Erin Lim SH, Lai KS (2019) Terpene derivatives as a potential agent against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) pathogens. Molecules 24:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142631
Maraki S, Mavromanolaki VE, Stafylaki D, Nioti E, Hamilos G, Kasimati A (2019) Epidemiology and antifungal susceptibility patterns of Candida isolates from Greek women with vulvovaginal candidiasis. Mycoses 62:692–697. https://doi.org/10.1111/myc.12946
Mitchell KF, Zarnowski R, Andes DR (2016) Fungal super glue: the biofilm matrix and its composition, assembly, and functions. PLoS Pathog 12:e1005828. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005828
Naglik JR, Challacombe SJ, Hube B (2003) Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinases in virulence and pathogenesis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:400–428. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.67.3.400-428.2003
Nair S, Desai S, Poonacha N, Vipra A, Sharma U (2016) Antibiofilm activity and synergistic inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms by bactericidal protein P128 in combination with antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:7280–7289. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01118-16
Orta-Zavalza E, Briones-Martin-del-Campo M, Castano I, De Las PA (2013) Catalase activity assay in Candida glabrata. Mol Microbiol 4(6). https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.1072
Pavan B, Dalpiaz A, Marani L, Beggiato S, Ferraro L, Canistro D, Paolini M, Vivarelli F, Valerii MC, Comparone A, De Fazio LD, Spisni E (2018) Geraniol pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and its multiple effects on the liver antioxidant and xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes. Front Pharmacol 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00018
Pemmaraju SC, Padmapriya K, Pruthi PA, Prasad R, Pruthi V (2016) Impact of oxidative and osmotic stresses on Candida albicans biofilm formation. Biofouling 32:897–909. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2016.1212021
Pianalto KM, Alspaugh JA (2016) New horizons in antifungal therapy. J Fungi 2:10–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof2040026
Pierce CG, Vila T, Romo JA, Montelongo-Jauregui D, Wall G, Ramasubramanian A, Lopez-Ribot JL (2017) The Candida albicans biofilm matrix: composition, structure and function. J Fungi 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-1604-7.00564-9
Reungpatthanaphong P, Dechsupa S, Meesungnoen J, Loetchutinat C, Mankhetkorn S (2003) Rhodamine B as a mitochondrial probe for measurement and monitoring of mitochondrial membrane potential in drug-sensitive and -resistant cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods 57:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-022X(03)00032-0
Ricotta EE, Lai YL, Babiker A, Strich JR, Kadri SS, Lionakis MS, Prevots DR, Adjemian J (2020) Invasive Candidiasis species distribution and trends, United States, 2009–2017. J Infect Dis:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa502
Rodrigues CF, Rodrigues ME, Silva S, Henriques M (2017) Candida glabrata biofilms: how far have we come? J Fungi 3:11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010011
Roy R, Tiwari M, Donelli G, Tiwari V (2018) Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: a focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 9:522–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2017.1313372
Saleem AF, Ahmed I, Mir F, Ali SR, Zaidi AKM (2010) Pan-resistant Acinetobacter infection in neonates in Karachi, Pakistan. J Infect Dev Ctries 4:030–037. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.533
Schwarzmüller T, Ma B, Hiller E, Istel F, Tscherner M, Brunke S, Ames L, Firon A, Green B, Cabral V, Marcet-Houben M, Jacobsen ID, Quintin J, Seider K, Frohner I, Glaser W, Jungwirth H, Bachellier-Bassi S, Chauvel M, Zeidler U, Ferrandon D, Gabaldón T, Hube B, d’Enfert C, Rupp S, Cormack B, Haynes K, Kuchler K (2014) Systematic phenotyping of a large-scale Candida glabrata deletion collection reveals novel antifungal tolerance genes. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004211
Sharma Y, Khan LA, Manzoor N (2016) Anti-Candida activity of geraniol involves disruption of cell membrane integrity and function. J Mycol Med 26:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2016.04.004
Singh S, Fatima Z, Hameed S (2016) Insights into the mode of action of anticandidal herbal monoterpenoid geraniol reveal disruption of multiple MDR mechanisms and virulence attributes in Candida albicans. Arch Microbiol 198:459–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1205-9
Singh S, Fatima Z, Ahmad K, Hameed S (2019) Fungicidal action of geraniol against Candida albicans is potentiated by abrogated CaCdr1p drug efflux and fluconazole synergism. PLoS One 13:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203079
Swamy MK, Akhtar MS, Sinniah UR (2016) Antimicrobial properties of plant essential oils against human pathogens and their mode of action: an updated review. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2016:3012462. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3012462
Taff HT, Mitchell KF, Edward JA, Andes DR (2013) Mechanisms of Candida biofilm drug resistance. Future Microbiol 8:1325–1337. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.13.101
Williams D, Silva SC, Malic S, Kuriyama T, Lewis MAO (2012) Candida biofilms and oral candidosis: treatment and prevention. Periodontol 55(1):250–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0757.2009.00338.x
Yang SK, Low LY, Yap PSX, Yusoff K, Mai CW, Lai KS, Lim SHE (2018) Plant-derived antimicrobials: insights into mitigation of antimicrobial resistance. Rec Nat Prod 12:295–316. https://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.41.17.09.058
Zarnowski R, Westler WM, Lacmbouh GA, Marita JM, Bothe JR, Bernhardt J, Sahraoui ALH, Fontainei J, Sanchez H, Hatfeld RD, Ntambi JM, Nett JE, Mitchell AP, Andes DR (2014) Novel entries in a fungal biofilm matrix encyclopedia. MBio 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01333-14
Zore GB, Thakre AD, Jadhav S, Karuppayil SM (2011) Terpenoids inhibit Candida albicans growth by affecting membrane integrity and arrest of cell cycle. Phytomedicine 18:1181–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2011.03.008
Acknowledgements
PG acknowledges the financial support of DBT-RA, from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India. HG acknowledges All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) for support through QIP scheme. KMP acknowledge the receipt of Grant CRG/2018/001329 and SB/YS/LS-380/2013 from SERB-DST, and DBT-IYBA fellowship – BT/07/IYBA/2013-19 from Government of India. Authors are thankful to the Institute Instrumentation Centre, IIT Roorkee, for microscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG and KMP conceived the research plan. PG and HG performed the experiments. PG analyzed the data. PG and KMP wrote the manuscript. All the authors have read and confirmed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
PG declares that she has no conflict of interest.
HG declares that he has no conflict of interest.
KMP declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 691 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, P., Gupta, H. & Poluri, K.M. Geraniol eradicates Candida glabrata biofilm by targeting multiple cellular pathways. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 5589–5605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11397-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11397-6