Abstract
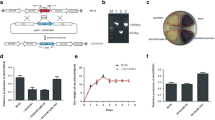
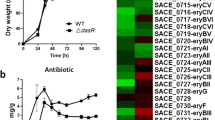
Although the genome of the Streptomyces model strain S. coelicolor was sequenced nearly two decades ago, the function of many annotated genes has not been verified, including that of gene sco1979, which was predicted to encode a transcriptional regulator of the xenobiotic response element (XRE) family. In this study, we showed that SCO1979 represses its own transcription and that deletion of sco1979 from S. coelicolor markedly enhanced production of three antibiotics, which are actinorhodin (ACT), undecylprodigiosin (RED), and calcium-dependent antibiotic (CDA), suggesting that SCO1979 represses their biosynthesis. We demonstrated that transcription of genes in the ACT, RED, and CDA pathways was generally increased in the mutant strain Δ1979 compared with levels in the wild-type strain M145. Additionally, purified recombinant SCO1979 interacted with DNA sequences upstream of sco1979 and actII-orf4, redZ, and cdaR, the pathway-specific regulators for the three pathways, implying that SCO1979 potentially regulates the ACT, RED, and CDA pathways via their specific regulators. In addition, disruption of sco1979 led to the notably delayed formation of aerial mycelium and spores, and consistent with this, transcription of genes associated with aerial hyphae and spore formation, such as chp and rdl, and ram, was reduced in Δ1979, implying the involvement of SCO1979 in cellular development control as well. In summary, our findings demonstrated that SCO1979 is a pleiotropic regulator with roles in both secondary metabolism and morphological development in S. coelicolor.
Key points
• SCO1979 is a novel Streptomyces regulator of the XRE family.
• SCO1979 regulates its own transcription.
• SCO1979 regulates antibiotic production and cellular development.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsa JA, Bird N, Ryding NJ, Findlay KC, Chater KF (2010) The complex whiJ locus mediates environmentally sensitive repression of development of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Anton Leeuw Int J G 98(2):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9443-3
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O'Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417(6885):141–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/417141a
Capstick DS, Willey JM, Buttner MJ, Elliot MA (2007) SapB and the chaplins: connections between morphogenetic proteins in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 64(3):602–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05674.x
Carniol K, Ben-Yehuda S, King N, Losick R (2005) Genetic dissection of the sporulation protein SpoIIE and its role in asymmetric division in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 187(10):3511–3520. https://doi.org/10.1128/Jb.187.10.3511-3520.2005
Chater K (2011) Differentiation in Streptomyces: the properties and programming of diverse cell-types. In: Dyson P (ed) Streptomyces: molecular biology and biotechnology. Caister Academic Press, pp 43–86
Chong L (2001) Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual, 3rd edition. Science 292(5516):446. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060677
Claessen D, Rink R, de Jong W, Siebring J, de Vreugd P, Boersma FG, Dijkhuizen L, Wosten HA (2003) A novel class of secreted hydrophobic proteins is involved in aerial hyphae formation in Streptomyces coelicolor by forming amyloid-like fibrils. Genes Dev 17(14):1714–1726. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.264303
Claessen D, Stokroos I, Deelstra HJ, Penninga NA, Bormann C, Salas JA, Dijkhuizen L, Wosten HA (2004) The formation of the rodlet layer of streptomycetes is the result of the interplay between rodlins and chaplins. Mol Microbiol 53(2):433–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04143.x
Elliot MA, Leskiw BK (1999) The BldD protein from Streptomyces coelicolor is a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol 181(21):6832–6835
Elliot M, Damji F, Passantino R, Chater K, Leskiw B (1998) The bldD gene of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): a regulatory gene involved in morphogenesis and antibiotic production. J Bacteriol 180(6):1549–1555
Elliot MA, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Leskiw BK (2001) BldD is a direct regulator of key developmental genes in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 40(1):257–269. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02387.x
Elliot MA, Karoonuthaisiri N, Huang J, Bibb MJ, Cohen SN, Kao CM, Buttner MJ (2003) The chaplins: a family of hydrophobic cell-surface proteins involved in aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces coelicolor. Genes Dev 17(14):1727–1740. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.264403
Elliot MA, Buttner MJ, Nodwell JR (2008) Multicellular development in Streptomyces. In: Whiteworth DE (ed) Myxobacteria: multicellularity and differentiation. American Society for Microbiology, pp 419–438
Errington J (2003) Regulation of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Nat Rev Microbiol 1(2):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro750
Feucht A, Abbotts L, Errington J (2002) The cell differentiation protein SpoIIE contains a regulatory site that controls its phosphatase activity in response to asymmetric septation. Mol Microbiol 45(4):1119–1130. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03082.x
Gregory MA, Till R, Smith MC (2003) Integration site for Streptomyces phage phiBT1 and development of site-specific integrating vectors. J Bacteriol 185(17):5320–5323
He Y, Wang Z, Bai L, Liang J, Zhou X, Deng Z (2010) Two pHZ1358-derivative vectors for efficient gene knockout in Streptomyces. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(4):678–682. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.0910.10031
Hopwood DA (ed) (2007) Streptomyces in nature and medicine. Oxford Univeresity Press
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (eds) (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Lakey JH, Lea EJA, Rudd BAM, Wright HM, Hopwood DA (1983) A new channel-forming antibiotic from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) which requires calcium for its activity. J Gen Microbiol 129(Dec):3565–3573
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77(1):112–143. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00054-12
Liu J, Li J, Dong H, Chen YF, Wang YS, Wu H, Li CR, Weaver DT, Zhang LX, Zhang BC (2017) Characterization of an Lrp/AsnC family regulator SCO3361, controlling actinorhodin production and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(14):5773–5783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8339-9
Liu M, Zhang PP, Zhu YP, Lu T, Wang YM, Cao GX, Shi M, Chen XL, Tao MF, Pang XH (2019) Novel two-component system MacRS is a pleiotropic regulator that controls multiple morphogenic membrane protein genes in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 85(4). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02178-18
Lu Y, Wang W, Shu D, Zhang W, Chen L, Qin Z, Yang S, Jiang W (2007) Characterization of a novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of both actinorhodin and a type I polyketide in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77(3):625–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1184-5
Lu Y, He J, Zhu H, Yu Z, Wang R, Chen Y, Dang F, Zhang W, Yang S, Jiang W (2011) An orphan histidine kinase, OhkA, regulates both secondary metabolism and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 193(12):3020–3032. https://doi.org/10.1128/Jb.00017-11
Lu T, Zhu YP, Zhang PP, Sheng DH, Cao GX, Pang XH (2018) SCO5351 is a pleiotropic factor that impacts secondary metabolism and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365(17). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny150
McCormick JR, Flardh K (2011) Signals and regulators that govern Streptomyces development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(1):206–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00317.x
Ou X, Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhao G, Ding X (2009) Characterization of rrdA, a TetR family protein gene involved in the regulation of secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(7):2158–2165. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.02209-08
Romero-Rodriguez A, Rocha D, Ruiz-Villafan B, Guzman-Trampe S, Maldonado-Carmona N, Vazquez-Hernandez M, Zelarayan A, Rodriguez-Sanoja R, Sanchez S (2017) Carbon catabolite regulation in Streptomyces: new insights and lessons learned. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11274-017-2328-0
Shu D, Chen L, Wang W, Yu Z, Ren C, Zhang W, Yang S, Lu Y, Jiang W (2009) afsQ1-Q2-sigQ is a pleiotropic but conditionally required signal transduction system for both secondary metabolism and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(6):1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1738-1
Talbot NJ (2003) Aerial morphogenesis: enter the chaplins. Curr Biol 13(18):R696–R698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2003.08.040
Tan IS, Ramamurthi KS (2014) Spore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(3):212–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12130
Tierrafria V, Licona-Cassani C, Maldonado-Carmona N, Romero-Rodriguez A, Centeno-Leija S, Marcellin E, Rodriguez-Sanoja R, Ruiz B, Nielsen L, Sanchez S (2016) Deletion of the hypothetical protein SCO2127 of Streptomyces coelicolor allowed identification of a new regulator of actinorhodin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(21):9229–9237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7811-2
Zhang P, Wu L, Zhu Y, Liu M, Wang Y, Cao G, Chen XL, Tao M, Pang X (2017) Deletion of MtrA inhibits cellular development of Streptomyces coelicolor and alters expression of developmental regulatory genes. Front Microbiol 8:2013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02013
Zhu YP, Zhang PP, Zhang J, Xu WH, Wang XY, Wu LL, Sheng DH, Ma W, Cao GX, Chen XA, Lu YH, Zhang YZ, Pang XH (2019) The developmental regulator MtrA binds GlnR boxes and represses nitrogen metabolism genes in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 112(1):29–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14252
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC0310600 to XP) and from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MC062 to XP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XP conceived the study. YZ designed the study. YZ, TL, JZ, and PZ performed the experiments. XP, MT, and YZ analyzed the data. XP wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1334 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Lu, T., Zhang, J. et al. A novel XRE family regulator that controls antibiotic production and development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 10075–10089 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10950-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10950-z